Major Players in Nuclear Fusion and Quantum Tech in 2024
Each passing year brings us closer to groundbreaking advancements in quantum mechanics and nuclear fusion. 2024 continued this trend, with notable breakthroughs in projects worldwide that have the potential to revolutionize computing, energy, telecommunications, and electronics. Here's a look at some of the key highlights.
Next-Generation Electronics Powered by Quantum Simulators
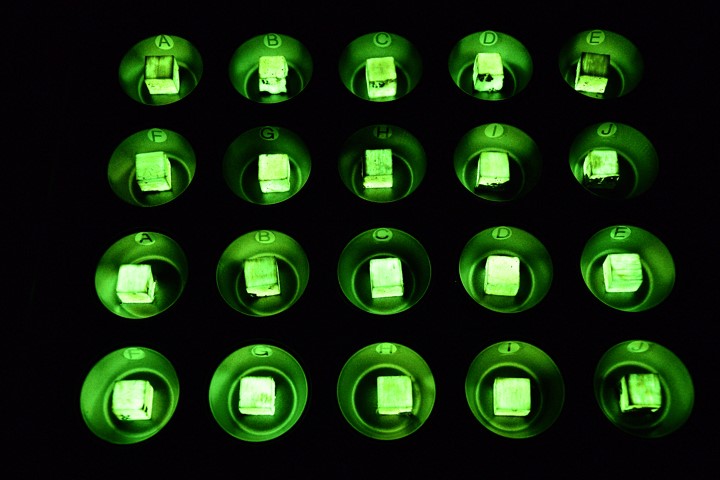
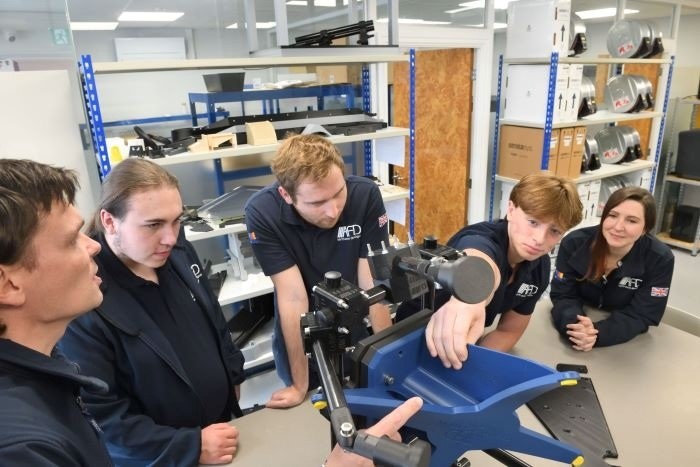
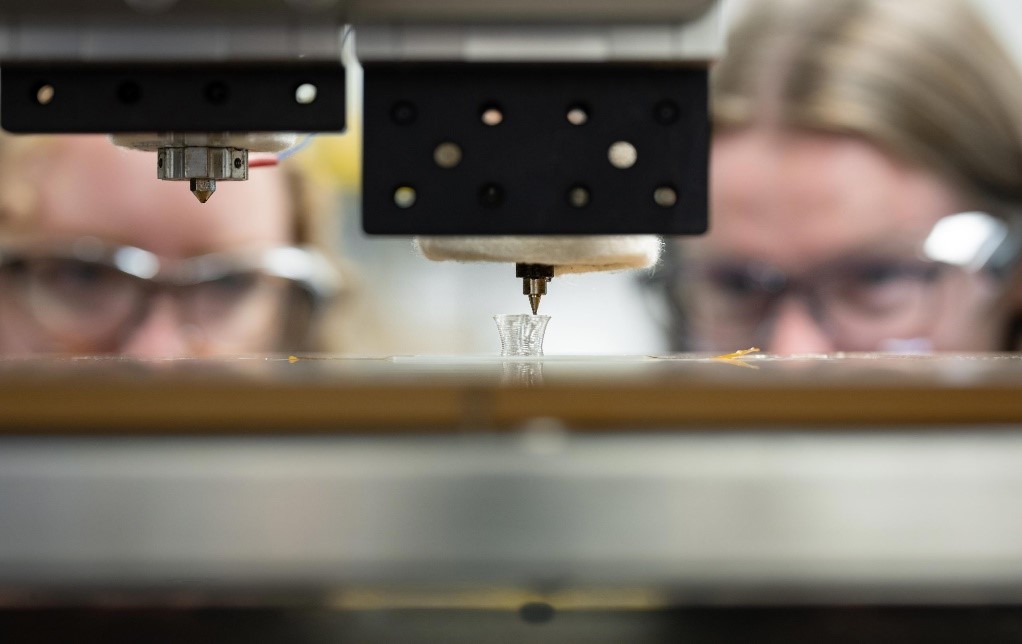
An important focus in quantum technology is the development of quantum computers, though these machines remain a few years away from practical use. In the meantime, physicists are turning to quantum simulators to better understand the complex quantum chemistry of materials, a task too challenging for even the most powerful supercomputers.
Figure 1. 2024's Key Advances in Nuclear Fusion and Quantum Tech
Researchers at MIT have developed a 16-qubit device capable of simulating the chemistry of various materials and observing how electrons in these materials behave when exposed to an electromagnetic field. They believe this research could aid engineers in developing new materials for next-generation electronics, without needing to synthesize the materials first. Figure 1 shows 2024's Key Advances in Nuclear Fusion and Quantum Tech.
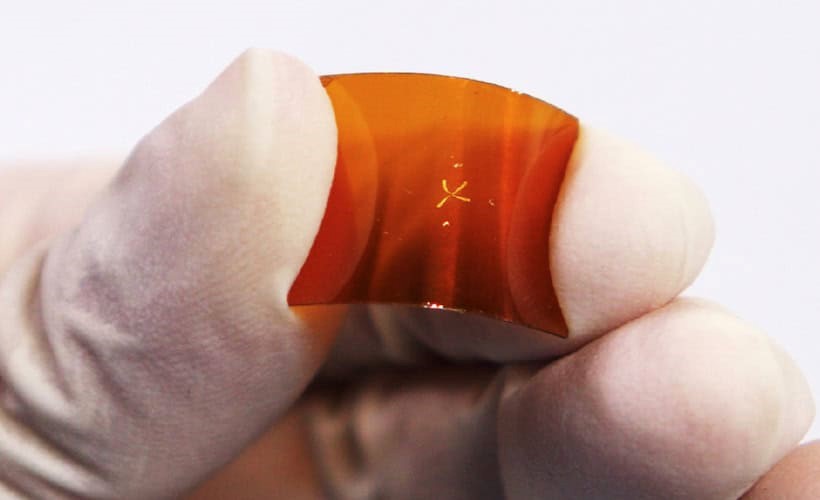
Diamond Bonded to Sapphire
It may sound like luxurious jewelry, but diamond fused to sapphire could be the next breakthrough in quantum technology. Diamond, a crystal of carbon atoms, is known for being inert, hard, and an excellent electrical insulator and heat conductor, making it highly useful in quantum technologies. However, bonding diamond to other materials has been a challenge, as it typically only grows on other diamond surfaces.
A new technique that slightly "loosens" the carbon atoms in diamond has successfully enabled it to bond with sapphire, silicon, lithium, and other materials, potentially expanding its applications in various technologies.
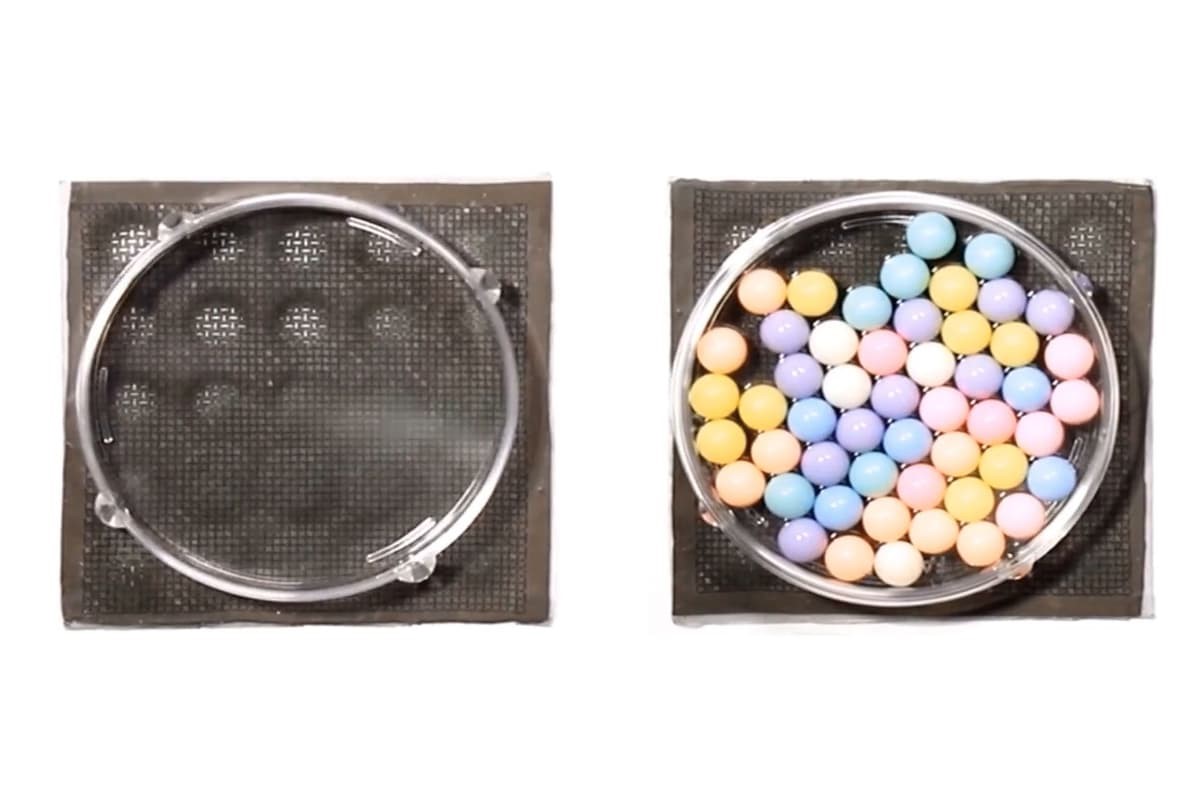
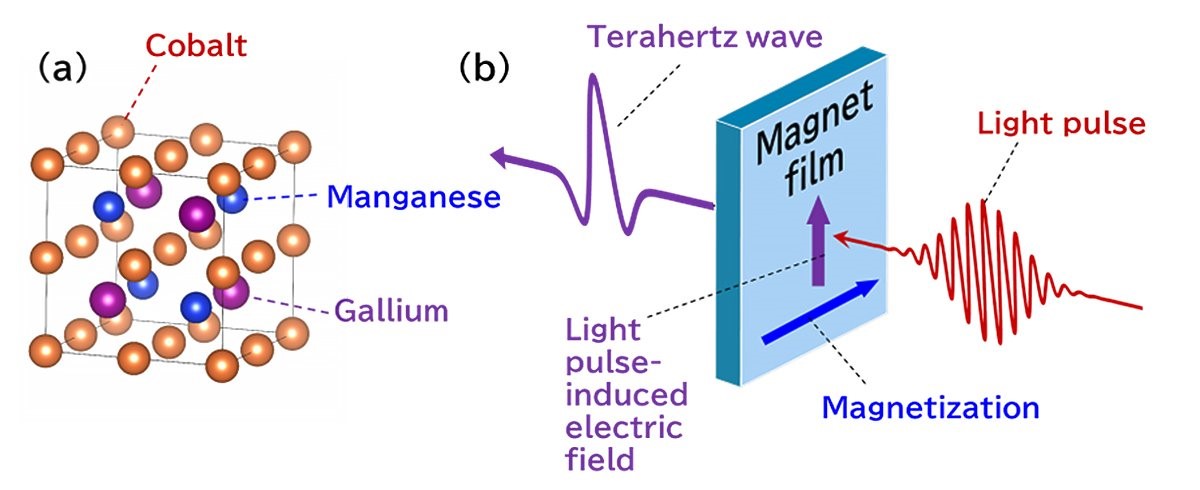
Quantum Sensing – At the Atomic Level
Physicists have created the first quantum sensor capable of making measurements at the atomic scale—just tenths of a nanometer. By harnessing the peculiarities of quantum mechanics, such as particle spin and quantum entanglement, these sensors offer highly precise measurements. This breakthrough sensor can simultaneously measure electric and magnetic fields at the atomic level, a crucial advancement for understanding the fundamental properties of materials.
New Zealand Joins Nuclear Fusion Initiative
OpenStar Technologies, a New Zealand-based company, has made history as the first in the country to activate a fusion machine. This device employs a unique method to replicate the energy-generating process of stars' cores. Nuclear fusion remains a coveted breakthrough in modern physics as researchers seek alternative, sustainable energy sources. OpenStar is working on developing a levitated dipole, a novel approach distinct from the typical doughnut-shaped tokamak used in most nuclear reactors. This year, the company successfully achieved its first plasma.
Spanish Fusion Reactor Makes Strides in Energy Development
On the opposite side of the globe, in Spain, another nuclear fusion experiment is taking a unique approach. The SMART (SMall Aspect Ratio Tokamak) is being developed at the University of Seville. It is the only tokamak in the world designed with negative triangularity, referring to the plasma's shape within the device. Construction of SMART is now underway.
Source:COSMOS
Cite this article:
Janani R (2024), Major Players in Nuclear Fusion and Quantum Tech in 2024, AnaTechMaz, pp. 83