This Breakthrough Material Could Transform the Future of Renewable Energy
Understanding Catalytic Functionality
“Our goal is to deepen our understanding of how materials function as catalysts under electrocatalytic conditions,” said Djire. “Ultimately, this knowledge could help us pinpoint the essential components needed to produce chemicals and fuels from earth-abundant resources.”
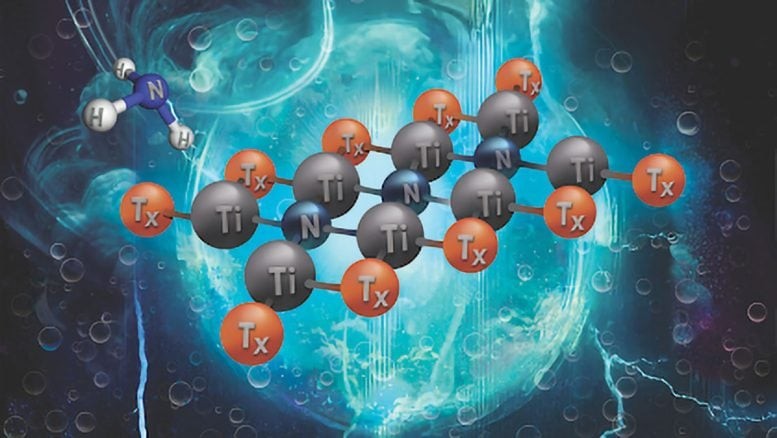
Figure 1. Breakthrough Material Poised to Transform Renewable Energy.
The structure of MXenes plays a crucial role in determining their catalytic behavior. By adjusting the lattice nitrogen reactivity—specifically by substituting a carbon atom with a nitrogen atom—researchers can alter the material’s vibrational properties, which describe how molecules move and interact with energy. Figure 1 shows Breakthrough Material Poised to Transform Renewable Energy.
According to Yoo, this tunability makes MXenes highly adaptable for specialized renewable energy applications. Their customizable nature positions them as strong candidates to replace current electrocatalyst materials, which are often costly and less efficient.
“MXenes are ideal candidates among transition metal-based materials,” Yoo said. “Nitride MXenes, in particular, show enhanced electrocatalytic performance compared to their more commonly studied carbide counterparts.”
Computational and Experimental Insights
The study was supported by first-principles computational analyses conducted by Ph.D. student Hao-En Lai from Dr. Balbuena’s group. The researchers evaluated changes in surface vibrational modes when MXenes interacted with energy-relevant solvents. These insights allowed the team to quantify molecular interactions—particularly in processes such as ammonia synthesis—further advancing the understanding of MXene-based catalysis.
Probing Vibrational Behavior with Raman Spectroscopy
Throughout this research, Djire, Yoo, and their team have explored the vibrational properties of titanium nitride using Raman spectroscopy—a non-destructive analytical technique that provides detailed insight into a material’s chemical structure and bonding.
“One of the most significant aspects of this work is Raman spectroscopy’s ability to reveal lattice nitrogen reactivity,” said Yoo. “This fundamentally reshapes our understanding of the electrocatalytic systems involving MXenes.”
Yoo added that continued Raman spectroscopic studies of nitride MXenes, especially in combination with polar solvents, could pave the way for major scientific breakthroughs.
“We demonstrate that electrochemical ammonia synthesis can occur through the protonation and replenishment of lattice nitrogen,” Djire explained. “Ultimately, our goal is to achieve an atomistic-level understanding of how individual atoms within a material’s structure contribute to its overall function.”
Source:SciTECHDaily
Cite this article:
Priyadharshini S (2025), This Breakthrough Material Could Transform the Future of Renewable Energy, AnaTechMaz, pp. 297