Wireless Network
Digital wireless communication is not a new idea. Earlier, Morse code implemented the wireless network. Now-a-days, the modern digital systems use wireless systems of the same idea as Morse code as implemented but with better performance.
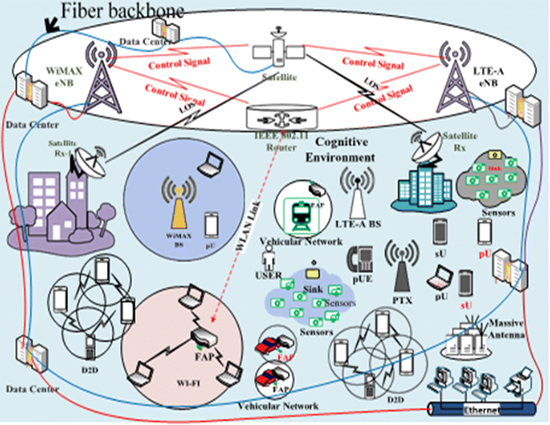
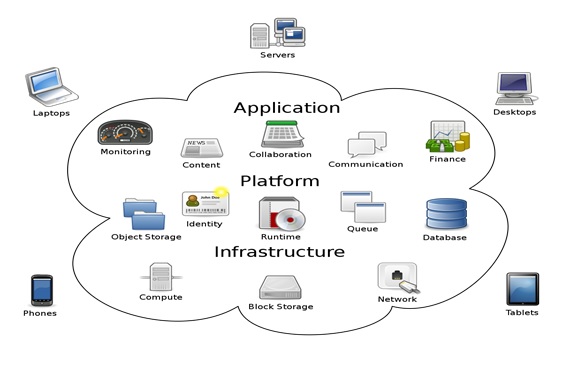
Computer networks that are not connected by cables are called wireless networks. They generally use radio waves [1] for communication between the network nodes. They allow devices to be connected to the network while roaming around within the network coverage figure1.
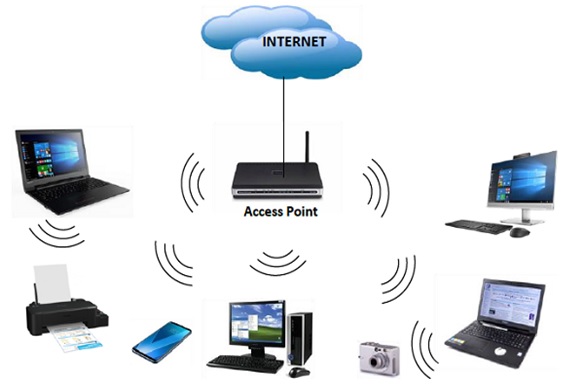
Figure 1. Access Point
A wireless network is a computer network that uses wireless data connections between network nodes.
Wireless networking is a method by which homes, telecommunications networks and business installations avoid the costly process of introducing cables into a building, or as a connection between various equipment locations. Admin telecommunications [2] networks are generally implemented and administered using radio communication. This implementation takes place at the physical level (layer) of the OSI model network structure.
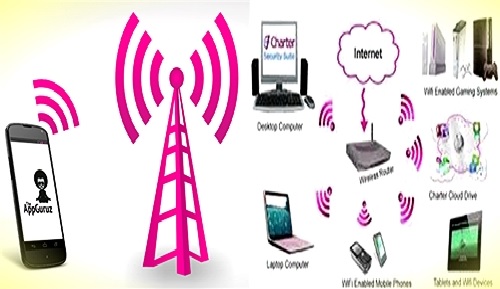
Examples of wireless networks include cell phone networks, wireless local area networks (WLANs), wireless sensor networks, satellite communication networks, and terrestrial microwave networks.
Wireless Networks
The first professional wireless network was developed under the brand ALOHAnet in 1969 at the University of Hawaii and became operational in June 1971. The first commercial wireless network was the WaveLAN product family, developed by NCR in 1986.
1973 – Ethernet 802.3
1991 – 2G cell phone network
June 1997 – 802.11 "Wi-Fi" protocol first release
1999 – 803.11 VoIP integration
Underlying technology
Wireless revolution
Advances in MOSFET (MOS transistor) wireless technology enabled the development of digital wireless networks. The wide adoption of RF CMOS (radio frequency CMOS), power MOSFET and LDMOS (lateral diffused MOS) devices led to the development and proliferation of digital wireless networks by the 1990s, with further advances in MOSFET technology [3] leading to increasing bandwidth in the 2000s (Edholm's law). Most of the essential elements of wireless networks are built from MOSFETs, including the mobile transceivers, basestation modules, routers, RFpoweramplifiers,telecommunication circuits, RF circuits, and radio transceivers, in networks such as 2G, 3G, and 4G.
Wireless network elements
The telecommunications network at the physical layer also consists of many interconnected wireline network elements (NEs). These NEs can be stand-alone systems or products that are either supplied by a single manufacturer or are assembled by the service provider (user) or system integrator with parts from several different manufacturers.
Wireless NEs are the products and devices used by a wireless carrier to provide support for the backhaul network as well as a mobile switching center (MSC).
Reliable wireless service depends on the network elements at the physical layer to be protected against all operational environments and applications (see GR-3171, Generic Requirements for Network Elements Used in Wireless Networks – Physical Layer Criteria).
What are especially important are the NEs that are located on the cell tower to the base station (BS) cabinet. The attachment hardware and the positioning of the antenna and associated closures and cables are required to have adequate strength, robustness, corrosion resistance, and resistance against wind, storms, icing, and other weather conditions. Requirements for individual components, such as hardware, cables, connectors, and closures, shall take into consideration the structure to which they are attached.
Each standard varies in geographical range, thus making one standard more ideal than the next depending on what it is one is trying to accomplish with a wireless network. The performance of wireless networks satisfies a variety of applications such as voice and video. The use of this technology also gives room for expansions, such as from 2G to 3G and, 4G and 5G technologies, which stand for the fourth and fifth generation of cell phone mobile communications standards. As wireless networking has become commonplace, sophistication increases through configuration of network hardware and software, and greater capacity to send and receive larger amounts of data, faster, is achieved. Now the wireless network has been running on LTE, which is a 4G mobile communication standard. Users of an LTE network should have data speeds that are 10x faster than a 3G network.
Space
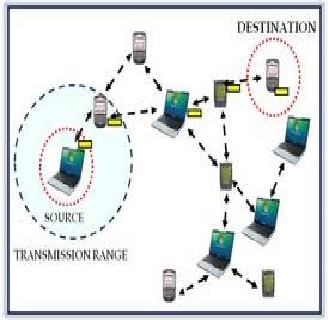
Space is another characteristic of wireless networking. Wireless networks offer many advantages when it comes to difficult-to-wire areas trying to communicate such as across a street or river, a warehouse on the other side of the premises or buildings that are physically separated but [4] operate as one. Wireless networks allow for users to designate a certain space which the network will be able to communicate with other devices through that network.
Space is also created in homes as a result of eliminating clutters of wiring. This technology allows for an alternative to installing physical network mediums such as TPs, coaxes, or fiber-optics, which can also be expensive.
Home
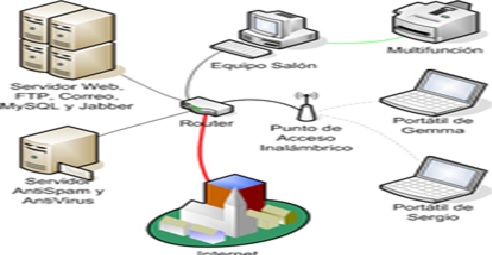
For homeowners, wireless technology is an effective option compared to Ethernet for sharing printers, scanners, and high-speed Internet connections. WLANs help save the cost of installation of cable mediums, save time from physical installation, and also creates mobility for devices connected to the network. Wireless networks are simple and require as few as one single wireless access point connected directly to the Internet via a router.
References:
- Whats is mean by wireless network? Reterived march 2020 from its en.wikipedia.org
- https://www.conceptdraw.com/How-To-Guide/wireless-network
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wireless-sensor-network-wsn
- https://www.oreilly.com/library/view/80211-wireless-networks/
Cite this article:
D. Vinotha (2021), Wireless Network, AnaTechMaz, pp. 6