Intelligent Network
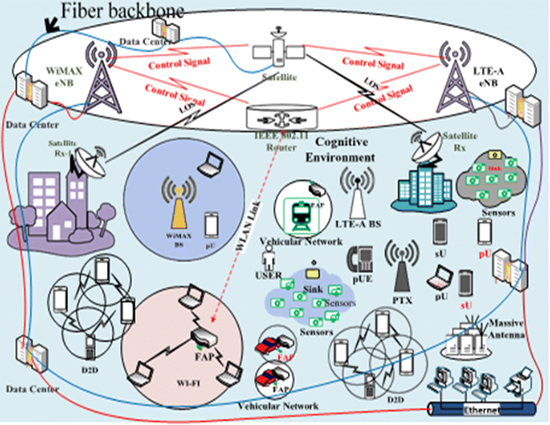
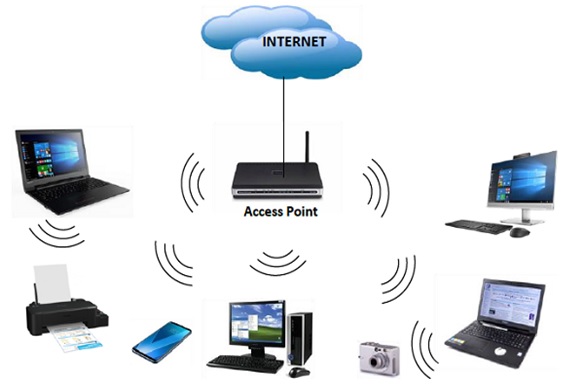
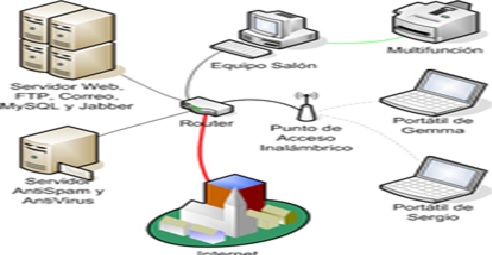
An Intelligent Network (IN) is a telephone network architecture devised to deliver increased service management control. The service logic and switching facilities are located separately, allowing for the changing or increasing of services without the need to redesign switching equipment as shown in figure 1.
An IN can enable a variety of additional features to be added to a particular network, from call queuing and call transfer, to Universal Personal Telecommunications services.
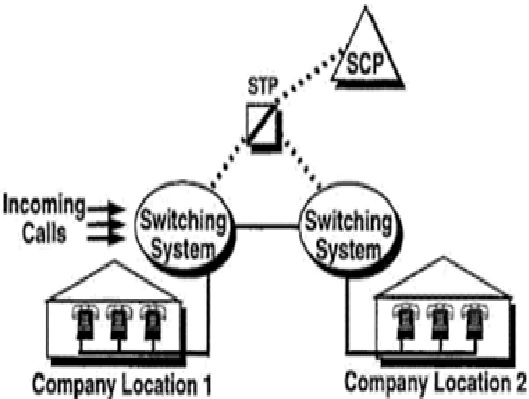
Figure 1. An Overview: Intelligent Network
Benefits of intelligent network in business
Intelligent networks offer a whole range of potential benefits to businesses. [1] They can help maximise profit. And minimise disruption. Here are some of the key ways that an intelligent network could help you.
Simple service onboarding
One of the greatest deterrents to upgrading systems or implementing new services is the disruption to legacy systems, and expense it can engender. Because intelligent networks can be added to or revised without any form of physical intervention, future modification is completely painless. And extremely quick to implement.
Customisable service
Finding the right network plan for your business can be difficult. A basic package may not be enough for your needs. But all the bells and whistles can be both expensive and unnecessary. With an intelligent network, you can simply select the services that are appropriate to your requirements. Not every business needs an overseas MMS service, call screening, or a home area discount. With an intelligent network, you get to choose what’s important.
Better connectivity
An intelligent network architecture delivers greater stability of connectivity. This means that your business is less likely to experience lost revenue though the failure of payment terminals. Or through poor customer experience.
Greater security
Autonomous networking allows for procedures to be set in place to enhance the security of an intelligent network and all the data that passes through it. Through the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI), processes can be easily implemented to automatically detect and remove anomalous activity.
Intelligent networks are being adopted by an ever-growing number of businesses globally. Because they simplify a previously complicated system. Offering almost infinite scalability, and the potential for ongoing evolution.
A telephone network architecture that separates service logic from switching equipment, which allows new services to be added without having to redesign switches to support new services. It encourages competition among service providers, [2] because it makes it easier for a provider to add services and offers customers more service choices.
The Advanced Intelligent Network (AIN)
The Advanced Intelligent Network (AIN) is a type of telecommunications system that layers computer intelligence on top of traditional telephone switching equipment, thereby enabling advanced services without major network upgrades. It can be used on both wired and wireless networks, and relies on massive computer databases to manage and route calls to the appropriate service. Telecommunications providers may use the technology to provide a value-added service such as conference calling or call screening as shown in figure 2.
Advanced Intelligent Network technology is implemented on the “service layer,” meaning all of the advanced functions and intelligence operate in a realm above the electrical switches and other equipment in a telecommunications network. [3] This is important because it means an AIN can be established or upgraded without investing in large amounts of new networking equipment. It also means the technology will work on many different types of networks, i.e., from traditional wired telephone networks to wireless mobile phone networks.
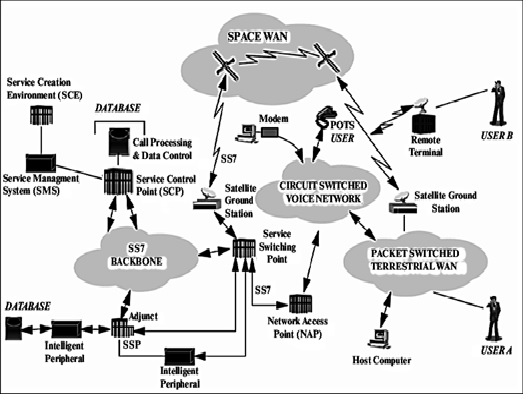
Figure 2. Advanced Intelligence Network
Most of the so-called intelligence in an Advanced Intelligence Network comes from large computer databases known as Service Control Points (SCPs). When a customer makes a call requiring advanced services, a special type of switch called a Service Switching Point (SSP) transmits information to an SCP using a family of telecommunications protocols called Signalling System 7 (SS7). The SCP consults its database and then replies to the SSP with instructions on how and where the call should be sent. Special tools allow the SCP’s databases to be updated with new services, thus allowing telecom providers to introduce new features without costly hardware upgrades.
Since adding a new service is as simple as updating a computer database, telecom providers have a great deal of freedom in determining what features their Advanced Intelligent Network provides. Common services include advanced billing or toll-free calling, conference calling, caller ID, or advanced routing functions. More advanced possibilities include televoting, abbreviated number dialling, and Local Number Portability (LNP), which allows consumers to move their phone numbers to different houses or service providers.
One potential drawback to Advanced Intelligent Network technology is that it was designed in a time when traditional voice-only analog telephone networks were dominant. As communications networks have grown to include cellular, digital, and Voice Over Internet Protocol (VoIP) technology, telecommunications companies have expressed growing interest in network architectures designed for voice, data, and multimedia. New technologies like the Internet Protocol Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) are expected to make up the Next Generation Intelligent Network (NGIN), a paradigm that will blur the distinction between telecommunications and computer networks.
References:
- https://www.iot-now.com/2021/08/06/111935-what-is-an-intelligent-network-and-how-could-it-help-your-business/
- https://www.easytechjunkie.com/what-is-the-advanced-intelligent-network.htm
- https://docs.genesys.com/Glossary:Advanced_Intelligent_Network
Cite this article:
D. Vinotha (2021), Intelligent Network, AnaTechMaz, pp. 3