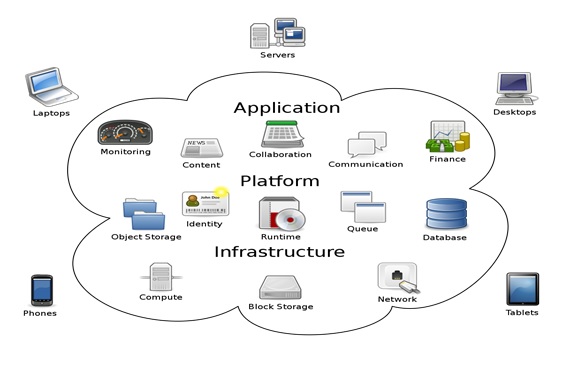
SD – WAN (Software-Defined Wide Area Network)
SD-WAN is a software-based approach to manage Wide Area networks (WANs). This technology lowers operational costs and improvement in resource usage in multisite deployments. Network administrator using this SD-WAN technology can use bandwidth more efficiently and help to ensure enhanced performance for business-critical applications without compromising data security and privacy.SD concept in SD-WAN technologies separate the control plane from the data plane and centralize the control plane from which multiple devices are controlled. Control plane acts like a shared service which is accessible to all administrators within an organization or in a multi tenancy environment.SD-WAN supports on premises data centres, Software-as-a-service (SaaS) and public cloud infrastructure-as-a-service (laaS) applications to optimize their performance. SD-WAN allows proper security for each user and devices irrespective of their physical location.[1]
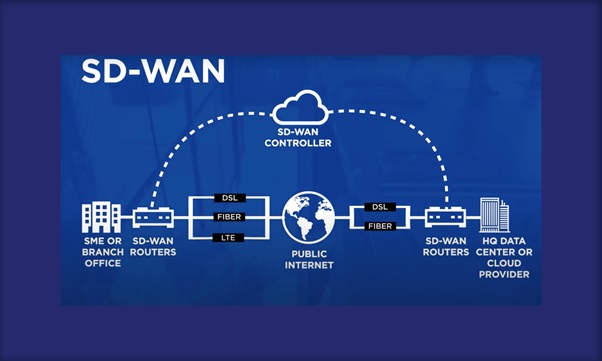
Figure 1. SD – WAN (Software defined Wide Area Network) Infrastructure
Because of its virtualized architecture, SD-WAN doesn’t require specific hardware for specialized network functions. Instead, the infrastructure is made of commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) equipment, also known as white-boxes.
Certain types of COTS hardware, such as universal customer premises equipment (uCPE) can host a variety of network functions. This simplifies network management at a network edge or organization’s headquarters. Enterprise can deploy SD-WAN in a DIY manner, where the business owns the network and equipment and takes full responsibility for the network operation and upkeep. In turn, enterprises can use a managed service provider, who owns all. network equipment and maintains some control over the network, and takes the brunt of the network management responsibility.[2]
Benefits
The key benefits include:
- Increased bandwidth at a lower cost since the network traffic can be provisioned for optimal speeds and throttle low-priority applications.
- Centralized management across branch networks through a simple management console, which reduces the need for manual configuration and on-site IT staff.
- Full visibility into the network, as the controller gives operators a holistic view of the network.
- More options for connection type and vendor selection, since the network can reside on COTS hardware and use both private and public connections to route its traffic.[2]
- Application-aware policies with end-to-end segmentation and real-time access control
- Integrated threat protection enforced at the right place
- Secure traffic across broadband Internet and into the cloud
- Distribute security to the branch and remote endpoints with NGFW, DNS security, and NGAV [3]
New business models drive the need for a new network model.
SD-WAN addresses the current IT challenges. This new approach to network connectivity can lower operational costs and improve resource usage for multisite deployments. Network administrators can use bandwidth more efficiently and can help ensure high levels of performance for critical applications without sacrificing security or data privacy.
References:
- https://networkinterview.com/top-10-networking-technology-trends/
- https://www.sdxcentral.com/networking/sd-wan/definitions/software-defined-sdn-wan/
- https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/enterprise-networks/sd-wan/what-is-sd-wan.html#~benefits
Cite this article:
Thanusri swetha J (2021), SD-WAN (Software defined Wide Area Network), AnaTechMaz, pp. 13