Network Computing
Network computing refers to the use of computers and other devices in a linked network, rather than as unconnected, stand-alone devices. As computing technology has progressed during the last few decades, network computing has become more frequent, especially with the creation of cheap and relatively simple consumer products such as wireless routers, which turn the typical home computer setup into a local area network.
In network computing, computers often share broadband and other resources. Many larger business networks also share hard drive [1] space, where any networked computer has access to the same data through a server or other hardware setup. Networking can be a more efficient way to deliver more functionality to a large number of computers or devices. In some cases, for example, a network may allow for lower software licensing fees than buying the software for a specific number of stand-alone devices.
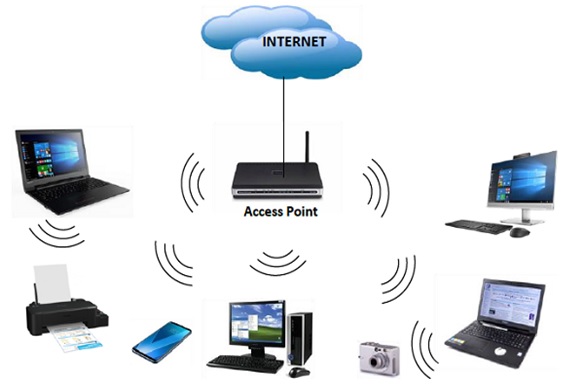
More recent developments have made network computing more sophisticated. One is the process of network virtualization, where hardware networks may be logically partitioned. Another is cloud computing, where the shared network resources can be located remotely for greater data security figure1.
Figure 1. Network computing.
There are five main types of Computer Networks:
- LAN (Local Area Network) – Systems connected in a small network like in a building or a small office It is inexpensive It uses Ethernet or Token-ring technology.
- PAN (Personal Area Network) – The smallest computer network Devices may be connected through Bluetooth or other infra-red enables devices It has a connectivity range of upto 10 metres
- MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) – A network that can be connected within a city, for example, cable TV Connection It can be in the form of Ethernet, ATM, Token-ring
- WAN (Wide Area Network) – A network which covers over a country or a larger range of people Telephonic lines are also [2] connected through WAN Internet is the biggest WAN
- VPN (Virtual Private Network): – A network which is constructed by using public wires to connect to a private network There are a number of systems which enable.
What Are the Advantages of Computer Networking?
- People can share information freely. Computer networking allows individuals and businesses to share information freely with one another. This information can be in several different formats.
- It allows for frequent collaboration. Computer networks allow multiple people to be logged into the same platform at once.
- The cost of joining a computer network is going down. In 1984, the cost of a Tandy 1000 was $1,200.
- Computer networking data can be stored off-line. With the numerous threats to computer systems, the internet, and technology structures, there is a need to store information off-line to protect.
- Anyone can connect to a [3] computer network. There is a minimal skill set required to connect to a modern computer network.
- Computer connections can be personalized. The modern computer network isn’t an all-or-nothing system.
Disadvantages of Network: These are main disadvantages of Computer Networks:
- It lacks robustness – If a PC system’s principle server separates, the whole framework would end up futile.
- It lacks independence – PC organizing includes a procedure that is worked utilizing PCs, so individuals will depend a greater amount of PC work.
- Virus and Malware – On the off chance that even one PC on a system gets contaminated with an infection, there is a possibility [4] for alternate frameworks.
- Cost of network – The expense of executing the system including cabling and equipment can be expensive.
Network Devices
Discussed below are a few important network devices from the exam point of view:
Network Repeater -Used to generate incoming electrical, wireless or optical signals
Network Hub – It is a small network device. It joins multiple computers together to form a single network segment.
Network Switch -It is a small hardware device which joins multiple computers together with a single LAN
Network Router -This device interfaces in multiple networks whose task is to copy packages from one network to another. It provides connectivity inside enterprises, between Enterprises and the Internet and within an ISP.
Network Bridge -It reads the outermost section of the data packet to tell where the message is going. It reduces the traffic on other network segments.
Modem -This device converts digital signals into analog signals. It is always placed between a telephone and a computer system.
All the information given above will help candidates prepare themselves for the Computer Knowledge section in the upcoming Government exams and ace it.
Before moving forward with the article and learning more about the types of computer networks, it is important [5] for candidates to understand what is a network and how it affects the functioning of one or more computers connected with each other.
A group of computers which are connected to each other and follow similar usage protocols for the purpose of sharing information and having communications provided by the networking nodes is called a Computer Network.
A network may be small where it may include just one system or maybe as large as what one may want. The nodes may further be classified into various types. These include:
- Personal Computers
- Servers
- Networking Hardware
- General Hosts
- Topology
- Interpreters
Given below are the eight types of Network Topologies:
Point to Point Topology –Point to Point topology is the simplest topology that connects two nodes directly together with a common link.
Bus Topology – A bus topology is such that there is a single line to which all nodes are connected and the nodes connect only to the bus
Mesh Topology – This type of topology contains at least two nodes with two or more paths between them
Ring Topology – In this topology every node has exactly two branches connected to it. The ring is broken and cannot work if one of the nodes on the ring fails.
Star Topology – In this network topology, the peripheral nodes are connected to a central node, which rebroadcasts all the transmissions received from any peripheral node to all peripheral nodes on the network, including the originating node.
Tree Topology – In this type of topology nodes are connected in the form of a tree. The function of the central node in this topology may be distributed.
Line Topology – In this topology all the nodes are connected in a straight line.
Hybrid Topology –When two more types of topologies combine together, they form a Hybrid topology.
References:
- https://www.networkcomputing.com
- https://www.techopedia.com/definition/23619
- www.networkstraining.com/different-types-of-networks
- https://vittana.org/11-advantages-and-disadvantages-of-computer-networking
- www.geeksforgeeks.org/network-virtualization-in-cloud-computing
Cite this article:
D. Vinotha (2021), Network Computing, AnaTechMaz, pp. 5