Artificial intelligence in self-driving cars
A self-driving car (sometimes called an autonomous car or driverless car) is a vehicle that uses a combination of sensors, cameras, radar and artificial intelligence (AI) to travel between destinations without a human operator. [1]
Self-driving cars, also referred to as autonomous cars, are cars which are capable of driving with little to no human input. A fully self-driving car would be able to drive you from Los Angeles to New York City all on its own while you sit back, relax, and enjoy the smooth ride. Self-driving cars have been receiving tremendous attention as of late, in large part due to the technological boom of Artificial Intelligence (AI). In just the past few years, AI has gone from being nearly forgotten to becoming the largest Research and Development (R & D) investment of many organizations across the world.
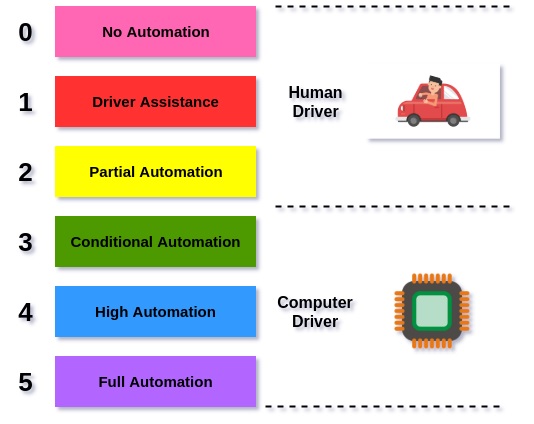
Figure 1. Level of automation
Figure 1 shows about self-driving cars, most technical experts will refer to levels of autonomy. The level of autonomy of a self-driving car refers to how much of the driving is done by a computer versus a human. The higher the level, the more of the driving that is done by a computer.[1]
Self-driving car see
The three major sensors used by self-driving cars work together as the human eyes and brain. These sensors are cameras, radar, and lidar. Together, they give the car a clear view of its environment. They help the car to identify the location, speed, and 3D shapes of objects that are close to it. Additionally, self-driving cars are now being built with inertial measurement units that monitor and control both acceleration and location.
Reliable cameras
Self-driving cars have a number of cameras at every angle for a perfect view of their surroundings. While some cameras have a broader field of view of about 120 degrees, others have a narrower view for long-distance vision. Fish-eye cameras provide extensive visuals for parking purposes.
Radar detectors
Radar detectors augment the efforts of camera sensors at night or whenever visibility is poor. They send pulses of radio waves to locate an object and send back signals about the speed and location of that object.
Laser focus
Lidar sensors calculate distance through pulsed lasers, by empowering driverless cars with 3D visuals of their surroundings, adding richer information about shape and depth.
LiDAR
LiDAR is one of the most important technologies used in the development of self-driving vehicles. Basically, it is a device that sends out pulses of light that bounce off an object and returns back to the LiDAR sensor which determines its distance. The LiDAR produces a 3D Point Cloud which is a digital representation of the way the car sees the physical world. [3]
References:
- https://searchenterpriseai.techtarget.com/definition/driverless-car
- https://towardsdatascience.com/your-guide-to-ai-for-self-driving-cars-in-2020-218289719619
- https://mindy-support.com/news-post/how-machine-learning-in-automotive-makes-self-driving-cars-a-reality/
Cite this article:
Thanusri swetha J (2021), Artifical intelligence in self-driving cars, Anatechmaz, pp. 25