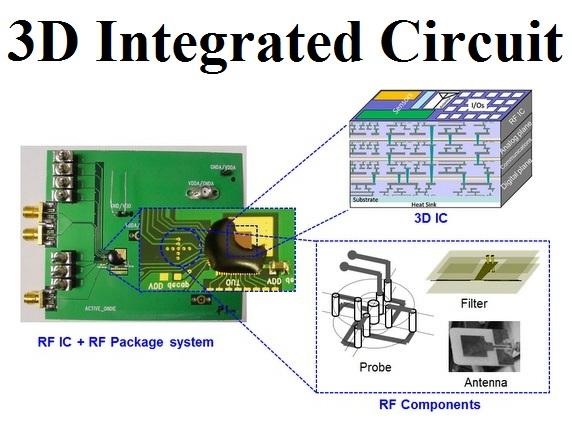
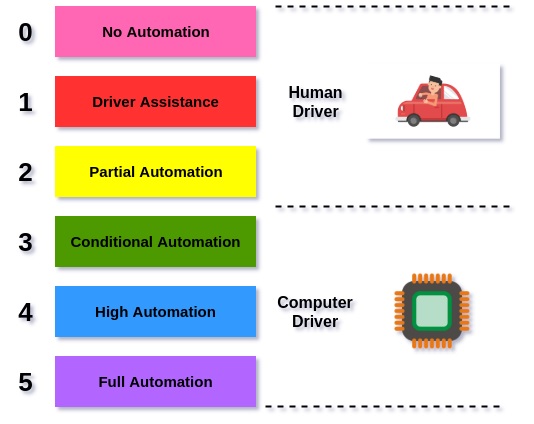
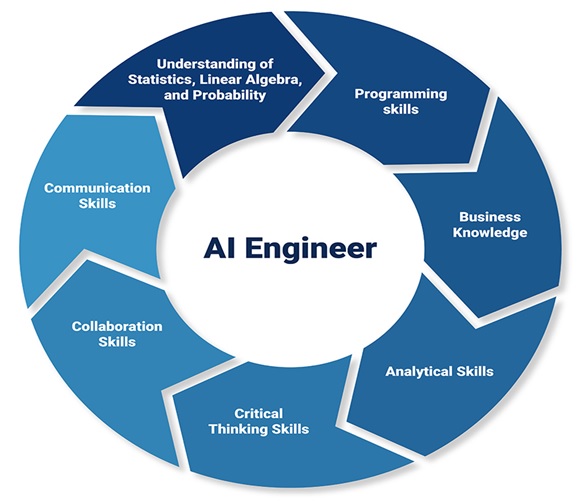
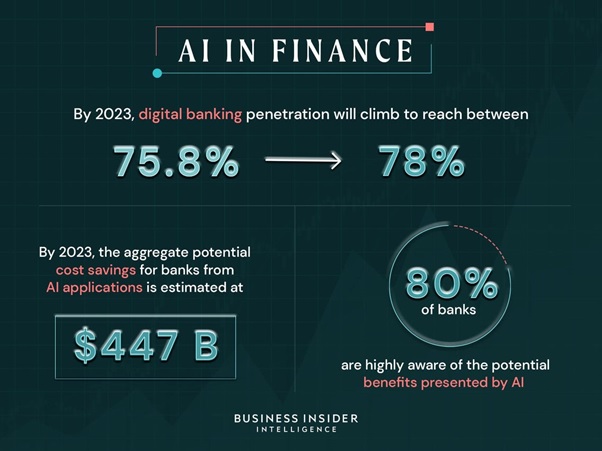
The Future Technologies of Extended reality (XR) in HealthCare
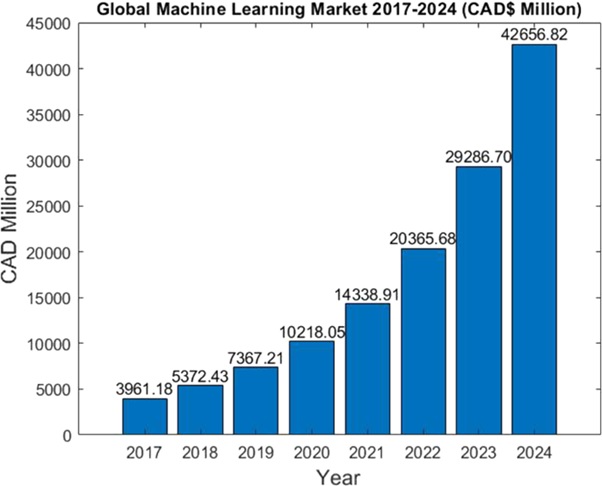
Extended reality (XR) is one of the key technologies shaping up the future of healthcare. The utilization of XR in the industry is already showing signs that it can diminish costs, increase access, and improve outcomes for individuals around the globe.
The intermingling of academic research patterns, moves by major corporations as well as several startups, and mainstream acknowledgment of the innovations exhibit that a future where healthcare is formed by XR is inescapable. [1] However, regardless of whether your company will profit by these progressions is far from being unavoidable.
Most notably, XR will drive a realignment of the current convictions about where healthcare happens, who gives the care, and who profits from it. As healthcare reaches out of the hospital and the doctor's office and into individuals' homes, the outskirts of businesses will be broken down as entertainment, wellness, med-tech, social media, and hardware organizations all vying for a piece of the healthcare pie.
On the other hand, XR will also serve as an important learning tool, [2] replacing plastic bodies and other equipment students use to learn human anatomy and even how to perform certain surgeries. Figure 1 shows the Extended reality (XR) in HealthCare.
Patients too will get to benefit from the technology, with for instance doctors, pharma and other companies providing them with immersive content about their conditions.
Returning the Response
Once the user’s intent has been identified, the chatbot must provide the most appropriate response for the user’s request. The answer may be:
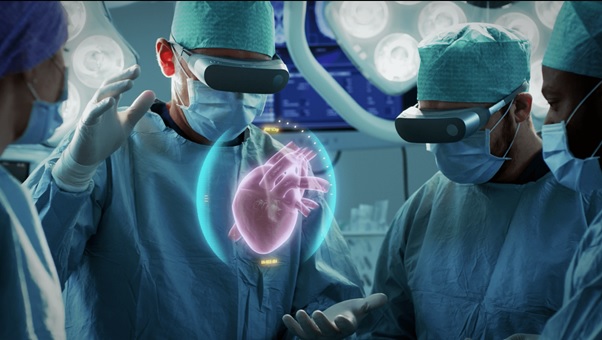
Figure 1: Extended reality (XR) in HealthCare
This report will focus mainly on the applications of VR in healthcare, [3] with reference to the use of AR and MR in training and education.
Extended Reality (XR) is an umbrella term encapsulating AR, VR, MR and everything in between.
Virtual Reality (VR) immerses users in a fully digital environment through a headset or surrounding display. This environment can be computer-generated or filmed in 360-degree video.
Augmented Reality (AR) presents digital information, objects, or media in the real world through a mobile device or headset. These elements can appear as a flat graphical overlay or can behave as a seemingly real ‘3D’ object.
Mixed Reality (MR) is the latter form of AR described above where physical and digital objects co-exist – in other words, the digital objects appear anchored to the real-world environment.
Immersive (or XR) technology solutions are being delivered in a variety of ways. Augmented reality experiences are usually accessed through a mobile phone or headset, displaying an overlay of digital objects in the user’s environment. Virtual reality is used to immerse users in a completely digital environment, usually through a headset.
Immersive technologies cover a wide spectrum and can also include adjacent technologies such as haptics which assist in immersing the user in a virtual world through an enhanced sense of touch. Often taking the form of a pair of gloves or an articulated arm, haptic technology enables users to not only see and hear their environment but feel it through vibration and changes in temperature.
A range of Head Mounted Display (HMDs) and devices are available on the market to deliver immersive experiences. Below are examples of some of the most commonly used headsets as well as other interfaces used to experience VR and AR.
References:
- https://www.xrhealthuk.org/the-growing-value-of-xr-in-healthcare
- https://dhbriefs.com/xr-healthcare/
- https://www.htmedia.in/archives/blog/extended-reality-in-healthcare-why-medical-marketers-should-be-excited
Cite this article:
Vinotha D (2021) The Future Technologies of Extended reality (XR) in HealthCare, Anatechmaz, pp. 17