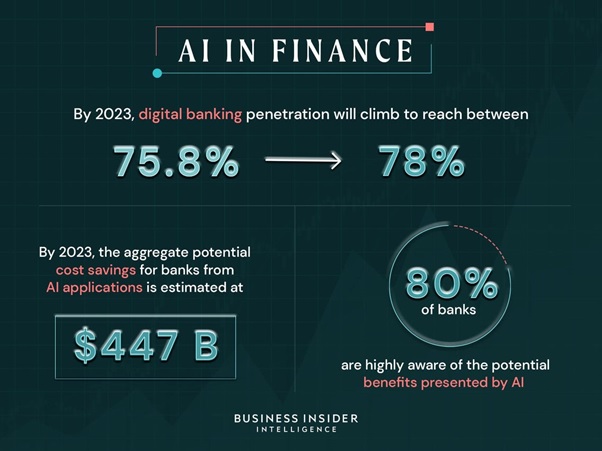
An Overview: The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) is the network of Internet-connected medical devices, hardware infrastructure, and software applications used to connect healthcare information technology. Sometimes referred to as IoT in healthcare, IoMT allows wireless and remote devices to securely communicate over the Internet to allow rapid and flexible analysis of medical data. [1] It can reduce unnecessary hospital visits and the burden on health care systems by connecting patients to their physicians and allowing the transfer of medical data over a secure network.
IoMT’s impact on the healthcare market is undeniable and irreversible. The broader Internet of Things (IoT) includes the network of all Internet-connected devices, including: internet connected factory equipment, biometric cybersecurity scanners, and autonomous farming equipment. IoMT is focused specifically on healthcare and medical applications. Given the sensitivity and strict regulations around healthcare data, IoMT requires a more comprehensive security infrastructure than other IoT systems.
The IoMT is made up of medical devices, healthcare software, and information technology (“IT”) systems that are connected and networked together. [2] A heartrate monitor that transmits data to a hospital’s cloud where it can be reviewed by a physician provides an example of a device and IT system within the IoMT. The figure 1 shows the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT).

Figure 1: The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
IoMT holds numerous benefits for both patients and healthcare providers [3].
- Personalized, precision diagnoses and therapeutics — Many IoMT devices are designed to track a patient’s vital signs in detail and depth, to a degree that wouldn’t be possible during a brief office visit. For example, with a month’s worth of blood pressure or pulse rate readings, a doctor can more accurately diagnose a condition and create a more personalized and effective treatment plan.
- Remote medical treatment and advice — The very nature of IoMT devices means they can capture data from anywhere — such as a patient’s home then transmit that information securely to the physician, all without requiring a visit to the office.
- Patient empowerment — IoMT devices such as wearables and smart scales let patients take control of their vitals, giving them information they would otherwise have to visit a doctor to get. Rather than waiting for an annual checkup, patients can now keep tabs on their health in real-time.
IoMT Provider Benefits
- Cost control – With the cost of medical care ballooning in recent years, providers are embracing cost-effective healthcare technologies. In 2015, Goldman Sachs predicted the savings from IoMT technologies, namely remote patient monitoring, would total about $305 billion.
- Improved patient monitoring – Chronically and seriously ill patients need more intensive monitoring, sometimes requiring around-the-clock care. IoMT devices allow physicians to monitor patients from afar without having to rely on human caregivers, alerting them instantly if something goes awry.
- Upgraded operations – IoMT improves hospitals’ operations by giving providers and administrators easier, centralized control over their facilities. IoMT devices can provide them with more visibility into their environment, and provide physicians with new technologies like robotic surgical aids and high-resolution digital imaging systems.
Implementing IoMT is not without its share of challenges, [4] the biggest being security and privacy. Medical data is highly regulated most notably by the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and providers have a heavy burden to prevent its compromise. Introducing IoMT devices into the environment invites some level of risk, largely due to the copious amount of additional data that flows between patients and providers.
Interoperability and standards are other hurdles that IoMT vendors face. In an ideal world, healthcare IoT equipment from one vendor would work seamlessly with another vendor’s infrastructure, but that hasn’t been the case, and uniform standards have been elusive. While some certification processes have emerged, the industry is still a long way from having universal interoperability. The Internet of Things (IoT), a network of wirelessly connected physical devices that exchange data, has transformed the healthcare industry and it shows no signs of stopping.
References:
- https://ordr.net/article/what-is-iomt/
- https://aabme.asme.org/posts/internet-of-medical-things-revolutionizing-healthcare
- https://atltechnology.com/blog/internet-of-medical-things/
- https://www.splunk.com/en_us/data-insider/what-is-the-internet-of-medical-things-iomt.html
Cite this article:
Vinotha D (2021) An Overview: The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT), Anatechmaz, pp. 22