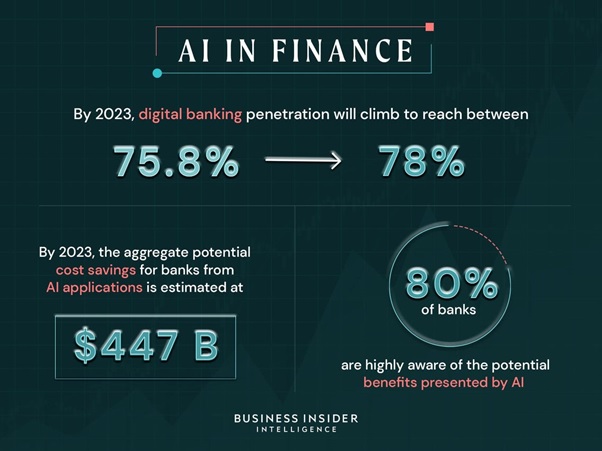
The Evolution of Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) in Healthcare
The IoMT market consists of smart devices, such as wearables and medical/vital monitors, strictly for health care use on the body, in the home, or in community, [1] clinic or hospital settings; and associated real-time location, telehealth and other services.
On-Body Segment
The on-body segment can be broadly divided into consumer health wearables and medical and clinical-grade wearables.
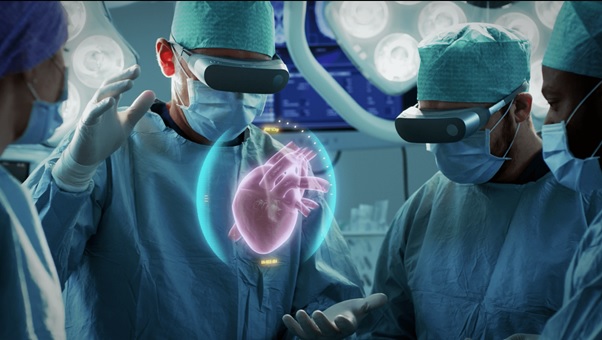
Consumer on-body IoMT devices are wearable devices that anyone can buy to track health metrics for both personal use and for sharing with healthcare providers. In addition to tracking a standard metric, such as heart rate, these devices can be early warning signs for more serious health conditions. The figure 1 shows the IMoT Healthcare.
Clinical on-body IoMT devices are like the consumer devices but afford a wider array of sensor options. For instance, glucose sensors can be worn by diabetic patients to alert them to fluctuations in glucose levels. [2] Many of these devices can share data directly with a patient’s doctors to ensure they get fast and accurate treatment.

Figure 1: IMoT in Healthcare
In-Home Segment
The in-home segment includes personal emergency response systems (PERS), remote patient monitoring (RPM) and telehealth virtual visits.
A PERS integrates wearable device/relay units and a live medical call center service to increase self-reliance for homebound or limited-mobility seniors. The package allows users to quickly communicate and receive emergency medical care.
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) is the use of medical devices to transmit metrics such as blood pressure or oxygen saturation from recently discharged patients to their hospital for review by their doctors. This can reduce hospital readmissions by catching issues before they become serious.
Telehealth virtual visits include virtual consultations that help patients manage their conditions and obtain prescriptions or recommended care plans. [3] Examples include video consultations and evaluation of symptoms or lesions through video observation and digital tests.
Community Segment
Community IoMT is the use of IoMT devices throughout a broader town or geographic area. For example, mobility services are devices used to track patients while in transit in a vehicle. Similarly, emergency response intelligence systems are used by paramedics and first responders to track patient metrics outside of the hospital setting.
In addition to mobile and emergency care, community IoMT also involves technologies that enable remote services. For example, point of care devices can be used by healthcare providers in non-traditional medical settings such as a field hospital, and kiosks can be used to dispense medicines to people in areas with limited or no access to traditional infrastructure.
Mixed Reality (MR) is the latter form of AR described above where physical and digital objects co-exist – in other words, the digital objects appear anchored to the real-world environment.
Suppliers may also use IoMT devices in logistics to help in the transport of healthcare goods or medical equipment. For instance, sensors can monitor temperature- or pressure-sensitive shipping containers to ensure that quality is maintained throughout the shipping process.
In-Clinic Segment
This segment includes IoMT devices that are used for administrative or clinical functions (either in the clinic, in the telehealth model, or at the point of care). Point-of-care devices here differ from those in the community segment in one key aspect: instead of the care provider physically using a device, the provider can be located remotely while a device is used by qualified staff.
In-Hospital Segment
Hospitals must manage the quality and supply of their medical assets over time, and they also need to understand how personnel and patients are moving throughout the premises. Healthcare professionals use IoMT sensors and other tracking systems to track all of these interactions so that administrators can get a comprehensive understanding of what is going on.
References:
- https://aabme.asme.org/posts/internet-of-medical-things-revolutionizing-healthcare
- https://ordr.net/article/what-is-iomt/
- https://ordr.net/article/iot-healthcare-examples/
Cite this article:
Vinotha D (2021) The Evolution of Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) in Healthcare, Anatechmaz, pp. 18