Edge Analytics
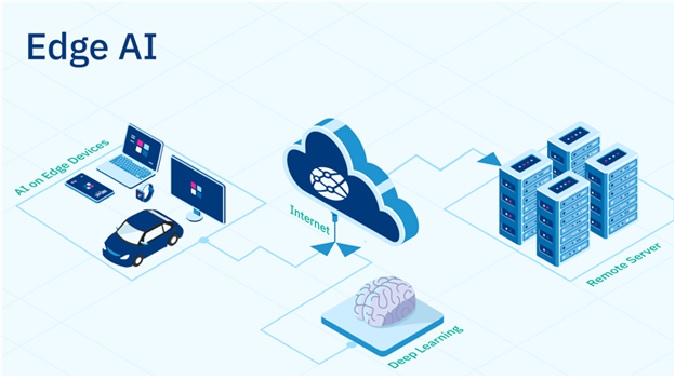
Edge analytics is a type of analytics that involves processing data locally on edge devices, rather than sending the data to a central server for processing. Edge analytics enables organizations to gain insights from data in real-time, improving decision-making and reducing the need for data transmission and storage.
Edge analytics is particularly useful for applications that require immediate responses, such as industrial automation, healthcare, and autonomous vehicles. By processing data locally on edge devices, organizations can reduce latency and ensure that critical decisions are made in real-time.

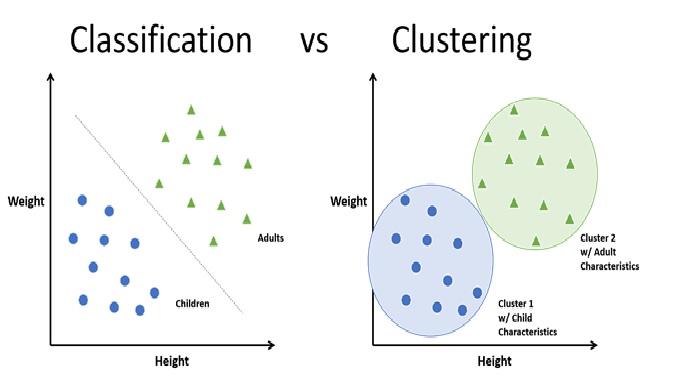
Figure 1. Edge Analytics
Figure 1 is an illustration of Edge Analytics. Here are the basic steps of how edge analytics works:
- Data Acquisition: The first step is to acquire data from the edge devices. This can be done using sensors, cameras, or other data collection methods.
- Data Pre-processing: Once the data is acquired, it is pre-processed on the edge device to filter out noise and irrelevant data. Pre-processing can involve tasks like data cleaning, normalization, and feature extraction.
- Data Analysis: The pre-processed data is analyzed locally on the edge device using machine learning algorithms, statistical models, or other data analytics techniques to gain insights and detect anomalies.
- Decision-making: Based on the insights gained from data analysis, the edge device can make real-time decisions and take actions, such as adjusting equipment settings, sending alerts, or triggering an emergency shutdown.
- Data Transmission: Depending on the application, the analyzed data may need to be transmitted to a central server for further processing or storage. However, by analyzing the data locally on the edge device, the amount of data that needs to be transmitted can be reduced, which lowers the bandwidth requirements and reduces the cost of data transmission.
Some benefits of Edge analytics include:
- Improved Real-time Decision-making: Edge analytics enables organizations to make decisions in real-time, improving operational efficiency and enabling rapid responses to changing conditions.
- Reduced Latency: Edge analytics reduces the time it takes to send data to a central server for processing and back, reducing latency and improving response times.
- Improved Data Privacy: Edge analytics processes data locally on edge devices, reducing the need to send data to a central server for processing, which can help to maintain data privacy and security.
- Reduced Bandwidth Requirements: Edge analytics reduces the amount of data that needs to be transmitted to a central server for processing, reducing bandwidth requirements and lowering the cost of data transmission.
- Improved Reliability: Edge analytics can continue to function even if the connection to a central server is lost, ensuring that critical applications continue to operate.
- Improved Scalability: Edge analytics can be deployed on a large number of devices, making it ideal for applications that require scalability, such as smart cities or industrial automation.
Overall, Edge analytics is an emerging field with significant potential for innovation and disruption in various industries. By processing data locally on edge devices, organizations can gain real-time insights, reduce latency, improve data privacy and security, and lower the cost of data transmission.
Cite this article:
Hana M (2023), Edge Analytics, AnaTechMaz, pp.219