Methods of Natural Language Processing
Natural language processing strives to build machines that understand and respond to text or voice data—and respond with text or speech of their own—in much the same way humans do.
Natural language processing (NLP) refers to the branch of computer science—and more specifically, the branch of artificial intelligence or AI—concerned with giving computers the ability to understand text and spoken words in much the same way human beings can.
NLP combines computational linguistics—rule-based modeling of human language—with statistical, machine learning, and deep learning models. Together, these technologies enable computers to process human language [1] in the form of text or voice data and to ‘understand’ its full meaning, complete with the speaker or writer’s intent and sentiment.
NLP drives computer programs that translate text from one language to another, respond to spoken commands, and summarize large volumes of text rapidly—even in real time. There’s a good chance you’ve interacted with NLP in the form of voice-operated GPS systems, digital assistants, speech-to-text dictation software, customer service chatbots, and other consumer conveniences. But NLP also plays a growing role in enterprise solutions that help streamline business operations, increase employee productivity, and simplify mission-critical business processes.
NLP tasks
- Part of speech tagging, also called grammatical tagging, is the process of determining the part of speech of a particular word or piece of text based on its use and context. Part of speech identifies ‘make’ as a verb in ‘I can make a paper plane,’ and as a noun in ‘What make of car do you own?’
- Word sense disambiguation is the selection of the meaning of a word with multiple meanings through a process of semantic analysis that determine the word that makes the most sense in the given context. For example, word sense disambiguation helps distinguish the meaning of the verb 'make' in ‘make the grade’ (achieve) vs. ‘make a bet’ (place).
- Named entity recognition, or NEM, identifies words or phrases as useful entities. NEM identifies ‘Kentucky’ as a location or ‘Fred’ as a man's name.
- Co-reference resolution is the task of identifying if and when two words refer to the same entity. The most common example is determining the person or object to which a certain pronoun refers (e.g., ‘she’ = ‘Mary’), but it can also involve identifying a metaphor or an idiom in the text (e.g., an instance in which 'bear' isn't an animal but a large hairy person).
- Sentiment analysis attempts [2] to extract subjective qualities—attitudes, emotions, sarcasm, confusion, suspicion—from text.
- Natural language generation is sometimes described as the opposite of speech recognition or speech-to-text; it's the task of putting structured information into human language.
- Speech Recognition-The translation of spoken language into text.
- Natural Language Understanding (NLU)-The computer’s ability to understand what we say.
- Natural Language Generation(NLG)-The generation of natural language by a computer below the figure1 shown.
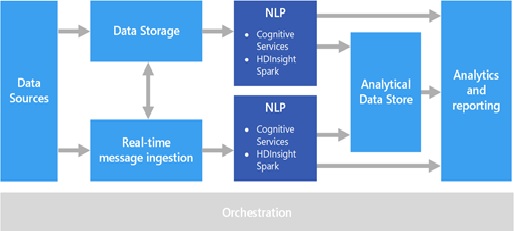
Figure1: Natural Language Processing.
Technologies related to Natural Language Processing
- Machine Translation: NLP is used for language translation from one language to another through a computer.
- Chatterbots: : NLP is used for chatter [3] bots that communicate with other chat bots or humans through auditory or textual methods.
- AI Software: NLP is used in question-answering software for knowledge representation, analytical reasoning as well as information retrieval.
References:
- https://www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/natural-language-processing
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/natural-language-processing-overview
- https://www.tutorialspoint.com/artificial_intelligence/artificial
Cite this article:
S Nandhinidwaraka (2021), Methods Natural Language Processing, pp. 9