Big Data Analytics
Big data analytics is the use of advanced analytic techniques against very large, diverse data sets that include structured, semi-structured and unstructured data, from different sources, and in different sizes from terabytes to zettabytes.
Big data is a term applied to data sets whose size or type is beyond the ability of traditional relational databases to capture, manage and process the data with low latency. Big data has one or more of the following characteristics: high volume, high velocity or high variety. Artificial intelligence (AI), mobile, social and the Internet of Things (IoT) are driving data complexity through new forms and sources of data. [1] For example, big data comes from sensors, devices, video/audio, networks, log files, transactional applications, web, and social media — much of it generated in real time and at a very large scale.
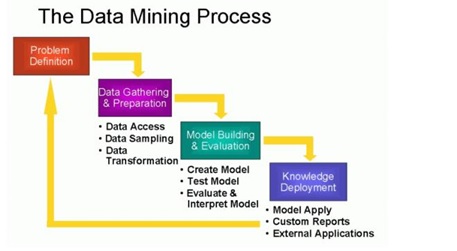
Analysis of big data allows analysts, researchers and business users to make better and faster decisions using data that was previously inaccessible or unusable. Businesses can use advanced analytics techniques such as text analytics, machine learning, predictive analytics, data mining, statistics and natural language processing to gain new insights from previously untapped data sources independently or together with existing enterprise data as shown in figure 1.
Figure 1: Big data analytics
Big data analytics helps organizations harness their data and use it to identify new opportunities. That, in turn, leads to smarter business moves, more efficient operations, higher profits and happier customers. [2] In his report Big Data in Big Companies, IIA Director of Research Tom Davenport interviewed more than 50 businesses to understand how they used big data. He found they got value in the following ways:
- Cost reduction. Big data technologies such as Hadoop and cloud-based analytics bring significant cost advantages when it comes to storing large amounts of data – plus they can identify more efficient ways of doing business.
- Faster, better decision making. With the speed of Hadoop and in-memory analytics, combined with the ability to analyze new sources of data, businesses are able to analyze information immediately – and make decisions based on what they’ve learned.
- New products and services. With the ability to gauge customer needs and satisfaction through analytics comes the power to give customers what they want. Davenport points out that with big data analytics, more companies are creating new products to meet customers’ needs.
Benefits & Advantages of Big Data Analytics
Risk ManagementBanco de Oro, a Phillippine banking company, uses Big Data analytics to identify fraudulent activities and discrepancies. [3] The organization leverages it to narrow down a list of suspects or root causes of problems.
Product Development and InnovationsRolls-Royce, one of the largest manufacturers of jet engines for airlines and armed forces across the globe, uses Big Data analytics to analyze how efficient the engine designs are and if there is any need for improvements.
Quicker and Better Decision Making Within OrganizationsStarbucks uses Big Data analytics to make strategic decisions. For example, the company leverages it to decide if a particular location would be suitable for a new outlet or not. They will analyze several different factors, such as population, demographics, accessibility of the location, and more.
Improve Customer ExperienceDelta Air Lines uses Big Data analysis to improve customer experiences. They monitor tweets to find out their customers’ experience regarding their journeys, delays, and so on. The airline identifies negative tweets and does what’s necessary to remedy the situation. By publicly addressing these issues and offering solutions, it helps the airline build good customer relations.
Here are some of the key big data analytics tools:
- Hadoop - helps in storing and analyzing data
- MongoDB - used on datasets that change frequently
- Talend - used for data integration and management
- Cassandra - a distributed database used to handle chunks of data
- Spark - used for real-time processing and analyzing large amounts of data
- STORM - an open-source real-time computational system
- Kafka - a distributed streaming platform that is used for fault-tolerant storage
Big Data Industry Applications
Here are some of the sectors where [4] Big Data is actively used:
- Ecommerce - Predicting customer trends and optimizing prices are a few of the ways e-commerce uses Big Data analytics
- Marketing - Big Data analytics helps to drive high ROI marketing campaigns, which result in improved sales
- Education - Used to develop new and improve existing courses based on market requirements
- Healthcare - With the help of a patient’s medical history, Big Data analytics is used to predict how likely they are to have health issues
- Media and entertainment - Used to understand the demand of shows, movies, songs, and more to deliver a personalized recommendation list to its users
- Banking - Customer income and spending patterns help to predict the likelihood of choosing various banking offers, like loans and credit cards
- Telecommunications - Used to forecast network capacity and improve customer experience
- Government - Big Data analytics helps governments in law enforcement, among other things
References:
- https://www.ibm.com/in-en/analytics/hadoop/big-data-analytics
- https://www.sas.com/en_us/insights/analytics/big-data-analytics.html
- https://www.qubole.com/big-data-analytics/
- https://www.simplilearn.com/what-is-big-data-analytics-article#the_lifecycle_phases_of_big_data_analytics
Cite this article:
D. Vinotha (2021), Big Data Analytics pp. 4