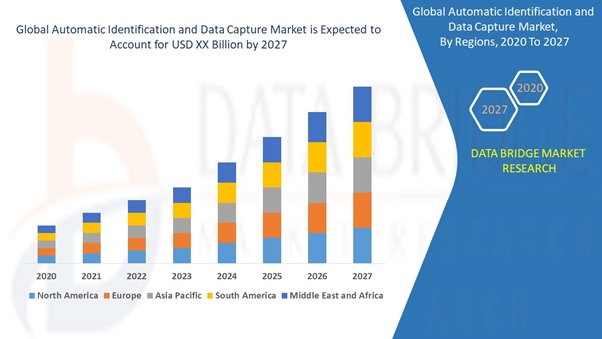
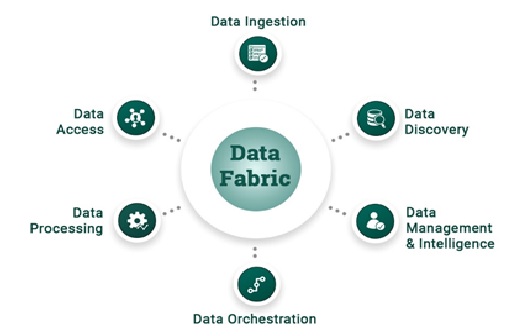
Automatic Identification of Data Collection
Automatic identification and data collection (also called AIDC, Auto ID, automatic data capture and automatic data collection) is a family of technologies that identify, verify, record, communicate and store information on discrete, packaged or containerized items.The most common technologies used to identify and capture data are barcodes, handheld and fixed-position [1] scanners and imagers, radio frequency identification (RFID) tags and readers, and voice recognition, weighing and cubing devices. Typical applications include figure 1 shown below receiving and putaway, inventory picking, order fulfillment, determination of weight and volume, and tracking and tracing throughout the supply chain.
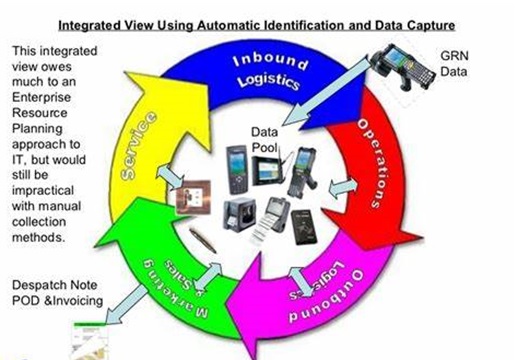
Figure 1: Automatic Identification of Data Collection
The information associated with the object is called identification data. This data may be in different forms like images, voice or finger prints. This data will be converted into a digital file before typing the data into computer system. Hence, a transducer is used in order accomplish this task means for converting the original data into digital file.
AIDC Components
- Data encoding – In this, the alphanumeric characters will be translated into the form that can be read by a machine.
- Machine scanning – The machine scanner reads the encoded data and converts the data into electric signals.
- Data decoding – The electrical signals will be transformed into digital data which later converted into alphanumeric characters.
Barcodes:
Barcodes consist of small images of lines (bars) and spaces affixed to retail store items, ID cards and postal mail to identify a particular product number, person or location. A barcode reader uses a laser [2] beam that is sensitive to the reflections from the line and space thickness and variation
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID):
This technology acts as the base in automated data collection, identification and analysis systems worldwide. RFID obtains information on an item without making direct contact with the item. Depending on the technology variation used, reading and writing distances can vary from few millimeters to several meters.
Biometrics:
Biometrics system consists of a scanning device or a reader, software that converts the scanned biological data, like finger prints, voice characteristics etc, into digital format and compares captured biological data with the stored data of that individual.
Magnetic Stripes:
Almost every individual carry card like credit cards, IDs, ATM cards etc. All these cards are cropped with magnetic stripe. The technology has been with us for many years. These stripes contain information about the [3] owner of the respective card. The information in magnetic stripes is read by magnetic stripe reader.
Optical Character Recognition (OCR):
Optical character recognition is the electronic or mechanical translation of scanned images of text that may be handwritten, typewritten or printed, into machine encoded text.
Smart Cards:
A smart card, a chip card or integrated circuit card (ICC), is any pocket-sized plastic card with embedded integrated circuits. It is an electronic recording device. Most smart cards looks like a credit or debit card, but smart cards can function on at least three levels.
References:
- https://www.mhi.org/fundamentals/automatic-identification
- https://searcherp.techtarget.com/definition/Automatic-Identification-and-Data-Capture-AIDC
- https://www.engineersgarage.com/automatic-identification-and-data-capture-aidc-technology/
Cite this article:
S Nandhinidwaraka (2021) Automatic Identification of Data Collection, Anatechmaz, pp. 18