Data governance
Before we define data governance, let us establish what we mean by “data.” In terms of IT, data is information that is stored and processed on a digital device like a server, database, computer, tablet, or smartphone. Now that we have dealt with the basics, we move on to explaining data governance. Data governance is an umbrella term for collecting practices, policies, processes, roles, standards, and metrics dedicated to helping an organization realize its goals using efficient and practical information. Data governance manages the availability, integrity, security, and usability of all data residing in enterprise systems.
Among trends in business intelligence, assigning dedicated data roles like that of data stewards is a significant move that can reap rich dividends. BI software with built-in role-based permission controls and authentication protocols is in demand. A readymade governance framework helps secure data per industry standards. Strict oversight and penalties ensure organizations are serious about compliance, so it’s unlikely theyll accept anything less when shopping for BI tools.

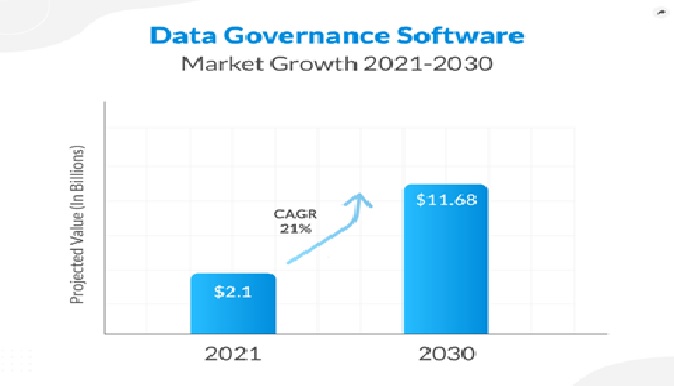
Figure .1Data governance
Figure 1 shows data governance refers to the process of managing the availability, usability, integrity, and security of the data used in an organization. It involves establishing policies and procedures to ensure that data is used in a consistent, controlled, and compliant manner. The goal of data governance is to optimize the value of an organization's data assets, while minimizing risks associated with data misuse, unauthorized access, or data breaches.
Data governance includes the following key components:
- Data architecture:Several programming languages have been developed for quantum computing, including Q#, Qi skit, and Cira. The development of standards for these languages can help ensure compatibility across different quantum computing platforms.
- Data quality:Standards for quantum hardware interfaces can help ensure that quantum computers from different vendors can communicate with each other and with classical computers.
- Data security:The unique properties of quantum mechanics can be leveraged to develop secure communication protocols that are resistant to hacking by classical computers. The development of standards for these protocols can help ensure their interoperability and reliability.
- Data privacy: As quantum computers become more complex, error correction becomes increasingly important. Standards for quantum error correction can help ensure that error correction algorithms are interoperable across different quantum computing platforms.
- Data management:Quantum metrology is the science of making precise measurements using quantum systems. Standards for quantum metrology can help ensure the accuracy and reproducibility of quantum measurements across different platforms.
Overall, data governance is essential for organizations to effectively manage and leverage their data assets in a responsible and secure manner.
References:
- https://www.simplilearn.com/what-is-data-governance-article
- https://www.selecthub.com/business-intelligence/business-intelligence-trends/
Cite this article:
Janani R (2023),Data governance, AnaTechmaz, pp.45