IIT Bombay Study Proposes Innovations for Enhanced Robot Cooperation
Novel algorithms have been developed to enhance cooperation among autonomous robots by enabling real-time monitoring and dynamic task allocation. These algorithms, proposed by Keshab Patra and his team at the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay (IIT Bombay), under the guidance of Prof. Anirban Guha and Prof. Arpita Sinha [1], aim to improve efficiency by facilitating better communication and coordination among robots.
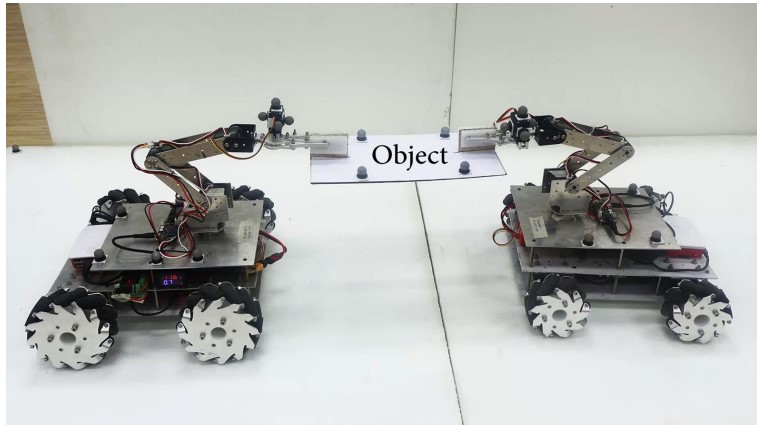
Figure 1. Enhanced Robot Cooperation. (Credit: IIT Bombay)
Figure 1 shows enhanced robot cooperation. In their recent study, the IIT Bombay team introduces three innovative algorithms that empower robots to assess their task capabilities in real-time and adjust task allocation accordingly based on their individual strengths and limitations [1]. These algorithms enable robots to identify changes in the environment or task requirements and make adjustments on-the-fly to optimize performance.
The first algorithm, TaskCapability, evaluates various parameters of each robot, such as grip strength and stability, assigning them values to assess their capabilities. The second algorithm, Online Task Capability, compares these parameters with those of other robots to identify underperforming ones [2]. Finally, the third algorithm, Online Task Allocator, utilizes data from the previous algorithms to determine the number of robots needed for a task and assign specific tasks to each robot accordingly.
By implementing these algorithms, robots can contribute according to their abilities, leading to increased productivity and efficiency in cooperative tasks [2]. Additionally, real-time communication between robots helps minimize errors and collisions, further enhancing their collaborative work.
Compared to conventional algorithms, which often rely on pre-programmed paths and limited real-time adjustments, the new algorithms offer significant improvements in speed and efficiency. Tests conducted on industrial robots like UR5 and Franka-Emika Panda demonstrated that the new algorithms outperformed conventional ones by a significant margin.
Furthermore, the new algorithms reduce computation time by 85%, enabling robots to make real-time adjustments during cooperative operations. This innovation has the potential to revolutionize task assignment and execution in complex automated systems, such as car assembly lines, by optimizing the use of each robot's unique capabilities.
Overall, the introduction of these real-time algorithms promises to enhance the performance of cooperative robots and pave the way for more efficient and adaptable automated systems in various industries.
Source: IIT Bombay
References:
- https://timelinedaily.com/technology/iit-bombay-conducts-study-to-enhance-cooperation-among-robots
- https://theprint.in/economy/iit-bombay-develops-technique-to-improve-efficiency-of-robots/2066379/
Cite this article:
Hana M (2024), IIT Bombay Study Proposes Innovations for Enhanced Robot Cooperation, AnaTechMaz, pp. 18