Difference Between Microprocessor and Microcontrollers
Nandhinidwaraka S
October 22, 2021 | 03:45 PM Technology
What is a Microprocessor (MPU)?
A microprocessor is essentially the brain of a computer system—it is a central processing unit (CPU) on a single integrated chip. However, it lacks memory, input/output ports, and other peripherals, which need to be added externally.
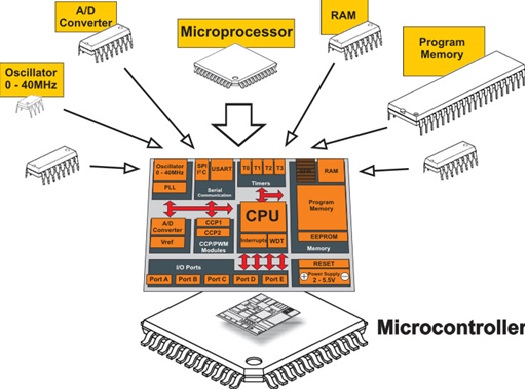
Figure 1. Microprocessor vs Microcontroller: Key Differences Explained.
What is a Microcontroller (MCU)?
A microcontroller is a complete embedded system on a single chip. It contains a CPU along with memory (RAM, ROM), I/O ports, timers, and sometimes even communication modules and ADCs—all integrated. Figure 1 shows Microprocessor vs Microcontroller: Key Differences Explained.
Internal Architecture and Components
Microprocessor:
- Contains only the CPU
- Needs external components:
- RAM (temporary memory)
- ROM (program storage)
- Timers and other peripherals
Microcontroller:
- All components are built-in:
- CPU + RAM + ROM
- Input/Output ports
- Timers, ADC (Analog to Digital Converter), DAC
- Serial and parallel communication interfaces
Design and Development Complexity
microprocessor:
- Requires complex hardware design
- Usually needs an Operating System (OS) like Windows or Linux
- Greater flexibility and scalability
microcontroller:
- Requires simpler design
- Can run without an OS (bare-metal)
- Easier to develop and deploy for embedded systems
Usage and Applications
Microprocessor Applications:
General-purpose computing
Used in:
- Personal computers (PCs)
- Laptops
- Servers
- High-performance systems
Reference:
- https://www.electromaker.io/blog/article/microcontroller-or-microprocessor-which-is-right-for-your-new-product?srsltid=AfmBOoofyuRI_SfDTjazFfv4itajYhVUoodQ38HPeq7WOQURhRCZi2ym&utm_source=chatgpt.com
Cite this article:
Nandhinidwaraka S (2021), Difference Between Microprocessor and Microcontrollers, AnaTechMaz, pp. 38
Previous Post Data Leakage Detection System
Next Post Features of Electronic Eye Circuit