The Technology Of 5nm Processor
Vinotha D
October 19, 2021 | 1:00 PM Technology
The 5nm (nanometer) processor technology represents a major advancement in semiconductor manufacturing, enabling faster, more power-efficient, and densely packed chips. It’s part of a long trend in miniaturizing transistors—the building blocks of processors—allowing more to be placed on a single chip. Here's a breakdown of what makes 5nm processors technologically significant: Figure 1 shows Inside the Breakthrough Technology of 5nm Processors
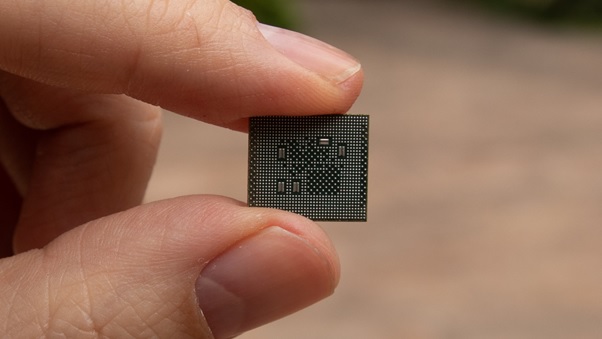
Figure 1. Inside the Breakthrough Technology of 5nm Processors.
What Does "5nm" Mean?
- "5nm" refers to the process node, which is a marketing term used by semiconductor companies. It used to relate to the actual gate length of a transistor, but today it's more symbolic of each new generation of technology.
- At 5nm, billions of transistors can fit into a chip the size of a fingernail—up to 171 million transistors per mm², compared to 96 million per mm² in 7nm chips.
Key Technologies Behind 5nm Chips:
- 5nm chips use EUV lithography for precise patterning of transistors on silicon wafers.
- EUV has a wavelength of 13.5nm, enabling finer details and more accurate etching than traditional DUV (Deep Ultraviolet).
- Most 5nm chips still use FinFET (Fin Field-Effect Transistors), which are 3D transistors that reduce power leakage./li>
- Some advanced variants explore GAAFETs (Gate-All-Around FETs), which further improve control over current flow.
- Smaller transistors reduce resistance and capacitance, allowing higher frequencies (speed) and lower power consumption.
- Enables better performance for mobile devices, data centers, AI, and edge computing.
1.Extreme Ultraviolet Lithography (EUV)
2.FinFET or Nanosheet Transistors
3.Increased Density and Performance
Real-World Examples:
- Apple A14 Bionic (in iPhone 12): First commercial 5nm chip.
- Apple M1 / M1 Pro / M1 Max: Desktop-class performance in a mobile chip.
- AMD Zen 4 & NVIDIA chips: Incorporate TSMC’s 5nm process for better gaming and server performance.
- Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 and Samsung Exynos 2100 also use 5nm nodes.
Challenges in 5nm Technology:
- Cost: Manufacturing 5nm chips is expensive; fabs cost billions.
- Design Complexity: Needs advanced software tools and longer design cycles.
- Thermal Management: More transistors = more heat in smaller areas.
What’s Next After 5nm?
- The industry is moving to 3nm and 2nm nodes.
- New architectures like GAAFET, chiplets, and 3D stacking are being explored to sustain Moore’s Law.
Reference:
- https://semiconductor.samsung.com/news-events/news/samsung-introduces-the-industrys-first-5nm-processor-powering-the-next-generation-of-wearables/
Cite this article:
Vinotha D (2021), The Technology Of 5nm Processor, AnaTechMaz, pp. 31
Previous Post The Platform of Bitcoin Mining
Next Post AI in Cloud Computing