Blue Brain Technology
The Blue Brain Project was a Swiss neuroscience initiative launched in May 2005 at EPFL (École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne) under Professor Henry Markram’s leadership . It aimed to build the world’s first biologically detailed digital reconstruction and simulation of a mammalian brain—starting with the mouse brain, in order to uncover fundamental principles of brain structure and function.
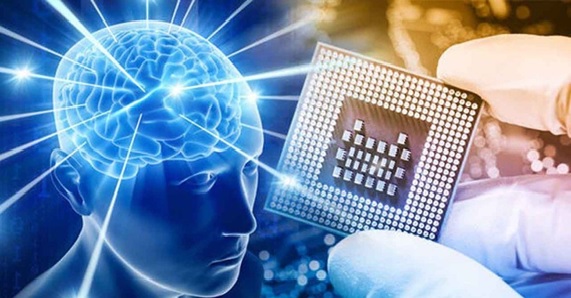
Figure 1. Inside the Digital Mind: Exploring Blue Brain Technology.
Through massive supercomputing power (IBM’s Blue Gene system), the project simulated neocortical microcircuits down to individual neurons and synapses using data-driven, bottom up reconstruction methods. Figure 1 shows Inside the Digital Mind: Exploring Blue Brain Technology
Introduction to Blue Brain Technology
The Blue Brain Project is a Swiss research initiative launched in 2005 by École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL). Led by neuroscientist Henry Markram, the project's goal is to create a virtual brain by reverse-engineering the mammalian brain down to the molecular level using supercomputers.
- It uses IBM’s Blue Gene supercomputers (hence the name).
- The ultimate aim is to simulate the human brain and understand its structure and function.
- It started with rat neocortical columns, the smallest functional units in the brain.
Goals and Vision
The project seeks to:
- Understand consciousness by mapping how brain activity leads to perception and awareness.
- Simulate diseases like Alzheimer's, autism, and epilepsy for research and drug development.
- Build a centralized brain data repository for global neuroscience collaboration.
- Enable machine learning systems inspired by real neural processes.
The long-term vision includes creating a “Human Brain Cloud” that merges neuroscience and artificial intelligence.
What a Blue Brain Works
Blue Brain uses a combination of:
- Supercomputing (e.g., Blue Gene/L)
- Mathematical modeling to simulate neurons and synapses.
- 3D brain reconstruction based on digitized experimental data.
- Simulation software like NEURON and BluePyOpt.
Challenges and Future Prospects
challenges:
- The human brain has 86 billion neurons, making full simulation extremely complex.
- Gathering detailed biological data is time-consuming and expensive.
- Ethical concerns around AI and consciousness.
Future Prospects:
- May help cure brain disorders by offering testable digital models.
- Could power brain-inspired AI systems with cognitive capabilities.
- Pave the way for neuromorphic computing—chips modeled after the brain.
Reference:
- https://indiaai.gov.in/article/exploring-blue-brain-project-the-world-s-first-artificial-brain?utm_source=chatgpt.com
Cite this article:
Thanusri swetha J (2021), Blue Brain Technology, AnaTechMaz, pp. 35