Oculus Rift
An Oculus Rift is a head-mounted display manufactured by Oculus VR. It is a specially designed virtual reality display that makes use of state-of-the-art display systems, optics and refresh rates to provide a high level of visual fidelity and an immersive, wide field of view. It has an advanced display [1] technology combined with a low latency tracking system to give a lifelike experience to the wearer.
Techopedia Explains Oculus Rift
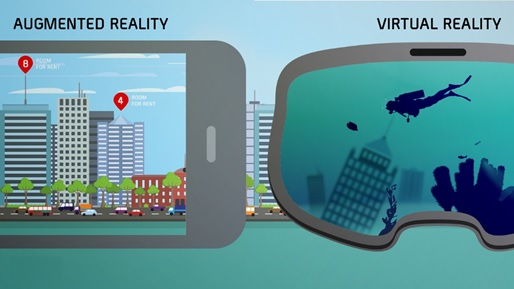
Virtual reality systems simulate lifelike experiences with the help of advanced display technologies and motion tracking. The Oculus Rift is one such VR system that works as a wearable headset capable of letting the users experience a virtual environment.
The specifications of the Oculus Rift are:
- Head-mounted display
- OLED display technology
- 2160 × 1200 resolution (1800 × 1200 per eye)
- 90 Hz refresh rate
- 110 degrees or greater field of view (nominal)
Compatible with Microsoft Windows (plans for OS X and Linux compatibility)
The Oculus Rift is designed to give a feeling of presence and provide a lifelike experience with its specialized design and software. It is customizable and adaptable to various uses. One common application is to enhance the gaming experience.
The Oculus Rift comprises an integrated audio VR, thus providing a 3-D audio effect. It also includes rotational and positional tracking accomplished with the help of infrared sensors. Therefore, it can be used while users are sitting, standing or walking around the room.
Through Meant to be Seen (MTBS)'s virtual reality and 3D discussion forums,Palmer Luckey, the founder of Oculus and long time MTBS discussion forum moderator developed the idea of creating a new head-mounted display that was both more effective than what was then on the market, and inexpensive for gamers.
The first rough prototype was hacked together in 2011 by Palmer Luckey (then 18 years old) in his parents’ garage in Long Beach, California. Coincidentally, John Carmack had been doing his own research and happened [2] upon Luckey's developments as a fellow member of MTBS After sampling an early prototype, Carmack favored Luckey's approach and just before the 2012 Electronic Entertainment Expo, Id Software announced that their future updated version of Doom 3, BFG Edition, would be compatible with head-mounted display units.
In June 2012, during the E3 convention, Carmack introduced a duct taped head-mounted display based on Luckey's Oculus Rift prototype, which ran Carmack's own software. The unit featured a high speed IMU and a 5.6-inch (14 cm) LCD, visible via dual lenses, that were positioned over the eyes to provide a 90 degrees horizontal and 110 degrees vertical stereoscopic 3D perspective.
Two months after being formed as a company, Palmer's Oculus VR launched a Kickstarter crowdfunding campaign on August 1 of 2012 for their virtual reality headset, named the Rift. The main purpose of the Kickstarter was to get an Oculus Rift prototype—now referred to as DK1 (Development Kit 1)—into the hands of developers to begin integration of the device into their games. The DK1 was given as a reward to backers who pledged $300 or more on Kickstarter, and was later sold publicly for $300 on their website. These kits sold at a rate of 4–5 per minute for the first day, before slowing down throughout the week.
The Rift DK1 was released on March 29, 2013, and uses a 7-inch (18 cm) screen with a significantly lower pixel switching time than the original prototype, reducing latency and motion blur when turning one's head quickly. The pixel fill is also better, reducing the screen door effect and making individual pixels less noticeable. The LCD is brighter and the color depth is 24 bits per pixel.
The 7-inch screen also makes the stereoscopic 3D no longer 100% overlapping, the left eye seeing extra area to the left and the right eye seeing extra area to the right, in which there is no 3D depth perception. The field of view (FOV) is more than 90 degrees horizontal (110 degrees diagonal), which is more than double the FOV of previous VR devices from other companies, and is the primary [3] strength of the device. The resolution is 1280×800 (16:10 aspect ratio), which leads to an effective of 640×800 per eye (4:5 aspect ratio). However, since the device does not feature a 100% overlap between the eyes, the combined horizontal resolution is effectively greater than 640. The image for each eye is shown in the panel as a barrel distorted image that is then corrected by pincushion effect created by lenses in the headset, generating a spherical-mapped image for each eye.
Initial prototypes used a Hillcrest Labs 3DoF head tracker that is normally 125 Hz, with a special firmware requested by John Carmack that makes it run at 250 Hz, tracker latency being vital due to the dependency of virtual reality's realism on response time. The latest version includes Oculus's new 1000 Hz Adjacent Reality Tracker, which aims to provide much lower latency tracking than almost any other tracker. It uses a combination of three-axis gyros, accelerometers, and magnetometers, which make it capable of absolute (relative to Earth) head orientation tracking without drift.
The Development Kit 1 also included interchangeable lenses that aim to allow for simple dioptric correction.
The entire source for the Rift DK1 was released to the public in September 2014, including the firmware, schematics, and mechanicals for the device. The firmware is released under a simplified BSD license, while the schematics and mechanicals are released under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Techopedia Explains Oculus Rift
In June 2013, a prototype of the Rift that used a 1080p LCD panel was shown at Electronic Entertainment Expo. This step forwards to twice the number of pixels as DK1 significantly reduced the screen door effect and made objects in the virtual world clearer, especially at a distance. The poor resolution had been the main criticism of the DK1. This HD prototype is the only prototype of the Rift shown to the public which did not turn into a publicly available developer kit.
In January 2014, an updated prototype codenamed "Crystal Cove" was unveiled at Consumer Electronics Show, which used a special low-persistence of vision OLED display as well as a new motion tracking system that utilized an external camera to track infrared dots located on the headset. The new motion tracking system would allow the system to detect actions such as leaning or crouching, which was claimed to help alleviate sickness experienced by users when the software did not respond to these actions.
First consumer version
Oculus VR announced on May 6, 2015, that the consumer version of the Rift would ship in the first quarter of 2016, and on March 25, 2016 the first batch of headsets began shipping to consumers.
The consumer version is an improved version of the Crescent Bay Prototype, featuring per-eye displays with a 1080×1200 resolution [4], running at 90 Hz, 360-degree positional tracking, integrated audio, a vastly increased positional tracking volume, and a heavy focus on consumer ergonomics and aesthetics.
In March 2019, during the announcement of the Rift S, it was said that the Rift S would replace the original Rift. However, Oculus VR stated that they planned to support the CV1 with software updates for "the foreseeable future figure1.

Figure 1. Oculus Rift
Industrial and professional
- As well as the consumer uses, the Rift has attracted significant interest from industry and professional spheres for productivity enhancement, visualization, and advertising.
- A number of architecture firms have been experimenting with using the Rift for visualization and design. With the right software, the Rift allows architects to see exactly what their building will look like and get an understanding of the scale that is impossible on a traditional monitor.
- In early 2015, Audi started [5] using Rift Developer Kit 2's at dealerships to help customers configure the car they are interested in, as well as to see what driving a race in the car would be like.
- The Norwegian Army has been experimenting with the Rift Development Kit 2 to allow for a greater situational awareness of armoured vehicle drivers and commanders.
- The use of Oculus Rift on an innovative virtual operator station assists the control of a teleoperated military mobile robot Tactical Robotic System (TAROS). Human operators can have intuitive control and mediate 3D view from stereovision cameras.
- Oculus Medium is a Painting Experience for Oculus Rift.
References:
- whatis.techtarget.com/definition/Oculus-Rift
- https://www.techopedia.com/definition/31556
- https://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/Oculus-Rift
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oculus_Rift
- https://www.thefreedictionary.com/Oculus+Rift
Cite this article:
S. Nandhinidwaraka (2021) Oculus Rift, AnaTechMaz, pp 7