Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality
Virtual Reality
Virtual Reality (VR) is the use of computer technology to create a simulated environment. Unlike traditional user interfaces, VR places the user inside an experience. Instead of viewing a screen in front of them, users are immersed and able to interact with 3D worlds. By simulating as many senses as possible, such as vision, hearing, touch, even smell, the computer is transformed into a gatekeeper to this artificial world. The only limits to near-real VR experiences are the availability of content and cheap computing power.
- Virtual Reality (VR) is the use of computer technology to create a simulated environment.
- Virtual Reality’s most immediately-recognizable component is the head-mounted display (HMD). Human beings are visual creatures, and display technology is often the single biggest difference between [1] immersive Virtual Reality systems and traditional user interfaces.
- Major players in Virtual Reality include HTC Vive, Oculus Rift and PlayStation VR (PSVR)
Virtual Reality Technology
Virtual Reality’s most immediately-recognizable component is the head-mounted display (HMD). Human beings are visual creatures, and display technology is often the single biggest difference between immersive Virtual Reality systems and traditional user interfaces. For instance, CAVE automatic virtual environments actively display virtual content onto room-sized screens. While they are fun for people in universities and big labs, consumer and industrial wearables are the wild west.
With a multiplicity of emerging hardware and software options, the future of wearables is unfolding but yet unknown. Concepts such as the HTC Vive Pro Eye, Oculus Quest and Playstation VR are leading the way, but there are also players like Google, Apple, Samsung, Lenovo and others [2] who may surprise the industry with new levels of immersion and usability. Whomever comes out ahead, the simplicity of buying a helmet-sized device that can work in a living-room, office, or factory floor has made HMDs center stage when it comes to Virtual Reality technologies.
Virtual Reality and the importance of audio
Convincing Virtual Reality applications require more than just graphics. Both hearing and vision are central to a person’s sense of space. In fact, human beings react more quickly to audio cues than to visual cues. In order to create truly immersive Virtual Reality experiences, accurate environmental sounds and spatial characteristics are a must. These lend a powerful sense of presence to a virtual world. To experience the binaural audio details that go into a Virtual Reality experience, put on some headphones and tinker with this audio infographic published by The Verge.
Augmented Reality
Augmented reality (AR) is an enhanced version of the real physical world that is achieved through the use of digital visual elements, sound, or other sensory stimuli delivered via technology. It is a growing trend among companies involved in mobile computing and business applications in particular.
Amid the rise of data collection and analysis, one of augmented reality’s primary goals is to highlight specific [3] features of the physical world, increase understanding of those features, and derive smart and accessible insight that can be applied to real-world applications. Such big data can help inform companies' decision-making and gain insight into consumer spending habits, among others.
Augmented Reality vs. Virtual Reality
Augmented reality uses the existing real-world environment and puts virtual information on top of it to enhance the experience figure1 shows below.
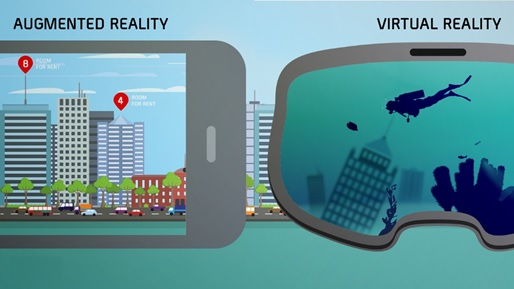
Figure 1. Augmented reality and Virtual reality
In contrast, virtual reality immerses users, allowing them to "inhabit" an entirely different environment altogether, notably a virtual one created and rendered by computers. Users may be immersed [4] in an animated scene or an actual location that has been photographed and embedded in a virtual reality app. Through a virtual reality viewer, users can look up, down, or any which way, as if they were actually there.
| Virtual Reality | Augmented Reality |
|---|---|
| A virtual environment that is entirely immersive | The system adds to the existing scene. |
| The visual senses are controlled by the system in virtual reality. | In augmented reality, the user is always aware of their presence in the real environment. |
| Virtual reality is 75% virtual and 25% real. | AR is made up of 25% virtual content and 75% real content. |
| This technique requires at least a 50 Mbps connection to completely immerse the user in the action VR. | This technology, which partially immerses the user in the action, necessitates a bandwidth of up to 100 Mbps. |
| A virtual reality headset is required. | There’s no need for an augmented reality headset. |
| The VR user is secluded from the actual world and immersed in a wholly fictional universe when utilizing VR technology. | End-users can interact with virtual items that are closer to them while still being in touch with the actual world. |
| It is utilized in the game sector to enhance fictional reality. | Both the actual and virtual worlds benefit from it. |
Level of immersion Users in Virtual Reality are completely cut off from the outside world. Virtual reality [5] is a comprehensive simulation that is not based on reality. It’s not about seclusion with augmented reality; it’s about enriching the physical environment.
References:
- https://www.marxentlabs.com/what-is-v
- https://www.explainthatstuff.com/virtualreality.html
- https://www.vrs.org.uk/virtual-reality/what-is-vi
- https://www.uplarn.com/virtual-reality-and-augmented-reality
- https://www.javatpoint.com/augmented-reality-vs-virtual-reality
Cite this article:
S. Nandhinidwaraka (2021) Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality, AnaTechMaz, pp 2