How Advanced Sensors Enhance Precision and Efficiency in Automated Welding
Maximum productivity and consistent quality are essential in automated welding. Achieving this demands high-precision sensors that can handle tasks such as path planning, distance control, and quality inspections, according to Glenn Wedgbrow, Business Development Manager at Micro-Epsilon UK.

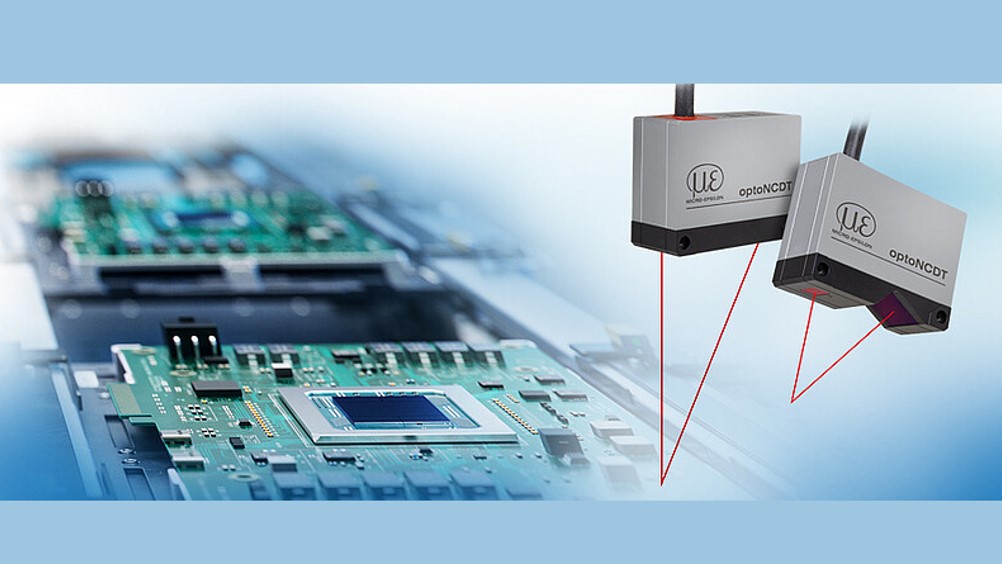
Figure 1. How Cutting-Edge Sensors Enhance Accuracy and Efficiency in Automated Welding
Route Optimization
3D Scanning of Parts Prior to Laser Cladding
In laser cladding, a laser beam melts the component surface, and a powdered filler material is added to create a new, pore-free layer. Before the laser processing begins, the components are scanned from multiple angles using a scan CONTROL laser scanner. The scanners' primary function is to detect the shape and identify any deviations from the desired form. They deliver stable measurements regardless of the material’s reflectivity. The collected data is then transferred to the user’s software, where it is compiled into a 3D model, which guides the laser welding head's path planning. The welding nozzle is positioned at the correct distance from the surface and follows the calculated trajectory. Figure 1 shows How Cutting-Edge Sensors Enhance Accuracy and Efficiency in Automated Welding.
Completely Automated 3D Repair Welding
Scan CONTROL laser scanners play a crucial role in the repair welding of large parts by determining both the welding track and the robot path. The process begins with a laser scanner, mounted on a robot, scanning the surface of the worn area. The 3D data of the damaged region, along with the robot's position data, is collected. These measurements are then integrated into the CAD model of the component. By comparing the high-resolution measurement data with the target contour, the volume difference is calculated, and the required welding path is determined. This information is then sent to the robot's control system for precise execution.
Weld Path Calculation for Gas Valves
The alignment of the welding head with the seam is crucial for ensuring the quality of automated welding. Even slight deviations can impact the weld quality, potentially leading to manual rework or rejection. scanCONTROL laser profile sensors are utilized to measure the profile, delivering accurate seam information, even on challenging surfaces. The calculated paths correct any deviations from component tolerances, ensuring the welding head remains correctly positioned over the seam throughout the process.
Control of the Welding Head
Automated Distance Control in Laser Welding
In fully automated welding systems, precise positioning of the welding head is vital for ensuring high-quality welds. The optoNCDT 1900 laser sensors are used for accurate and dynamic distance measurements from the steel plates. With excellent resistance to ambient light, these sensors are perfectly suited for controlling the distance of welding heads in such applications.
Controlling the Focal Point in Additive Manufacturing
In additive manufacturing techniques like selective metal melting, controlling the laser's focal point is essential for both process speed and quality. To accurately measure the distance between the print head and the powder surface and to regulate the laser's focal point, optoNCDT 1900 laser sensors are employed. Their high measurement rate and repeatability ensure fast and reliable distance measurements, regardless of the alloy used.
Measuring the Displacement of Electrodes in Resistance Welding
Eddy current sensors from Micro-Epsilon are used in resistance welding to measure electrode displacement, ensuring high-quality welded joints. These non-contact sensors are resistant to welding currents, vibrations, and temperature fluctuations, providing reliable performance in harsh conditions. Their high resolution and frequency response enable precise electrode position control, ensuring consistent welding joint quality.
Ensuring Quality
3D Inspection of Weld Seams with Laser Scanners
Micro-Epsilon’s laser scanners provide high-resolution, 3D inspections for weld seams, capturing intricate shapes and details. With the 3D View software, users can easily visualize the data, and multiple interfaces allow seamless integration with existing image processing systems.
Sheet Edge Measurement in Laser Welding
In automated robotic welding, laser scanners monitor the quality of longitudinal welds by measuring edge position along the sheet. The scanCONTROL SMART sensors streamline the process by eliminating the need for an external controller, simplifying installation.
Measurement of Cooling Time in Welding Units
Micro-Epsilon’s high-performance pyrometers accurately document welding parameters, such as cooling time. These sensors, with double laser sighting, measure metallic surfaces and allow precise tracking of cooling times, with adjustable limit values and customizable measurement distances.
Weld Seam Tracking for Pipeline Inspection
Pipeline maintenance relies on precise weld seam inspection, particularly under extreme conditions. The scanCONTROL laser scanner tracks weld seam positioning and adjusts the test unit based on surface variations, such as dirt or corrosion, ensuring accurate seam inspection.
Colour Sensors for Weld Seam Presence Check
For quality assurance in gear part welding, Micro-Epsilon’s CFO100 colour sensors monitor the weld seam’s presence, even as the component rotates. The multi-teach function ensures accurate detection, providing a switching signal when no seam is found.
Diameter Measurement of Welding Wires
Micro-Epsilon’s X-Frame optical micrometers measure welding wire diameter continuously, using two high-resolution laser micrometers. The system’s digital interface transmits the measurements to the control system for real-time monitoring.
Optical Weld Seam Inspection with Industrial Endoscopes
Rigid and video endoscopes are essential for inspecting weld seams in hard-to-reach areas before, during, and after welding. These tools examine parameters such as wear, cleanliness, and surface quality, and can be integrated into image processing solutions for automatic evaluation.
Colour Sensors for Automatic Weld Spot Detection
Micro-Epsilon’s CFO colour sensors are used to automatically identify weld spots on brass strips during spot welding [1]. The multi-teach function ensures reliable detection, sending output signals to the control system for subsequent processing.
References:
- https://www.eurekamagazine.co.uk/content/technology/how-advanced-sensors-improve-precision-and-efficiency-in-automated-welding/
Cite this article:
Janani R (2025), How Advanced Sensors Enhance Precision and Efficiency in Automated Welding, AnaTechMaz, pp.293