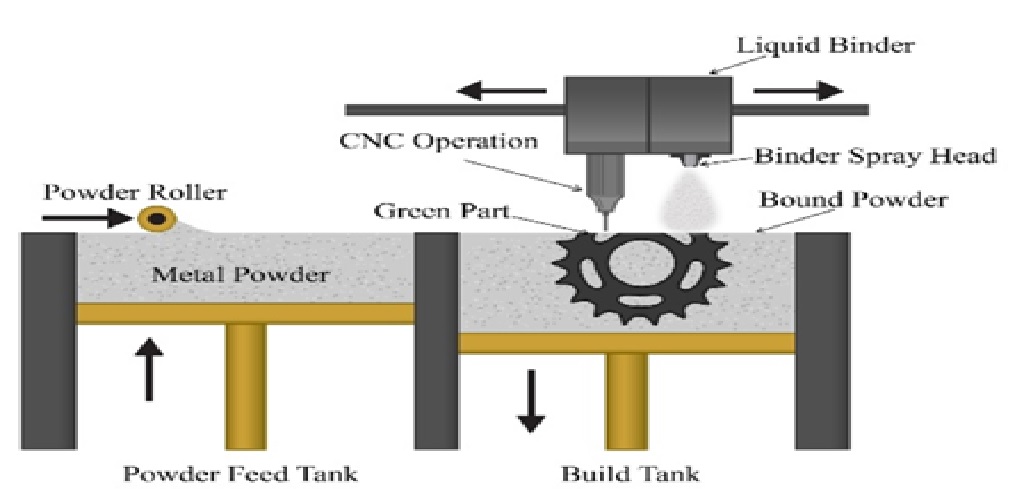
The Future of 3D Metal Printing Technology
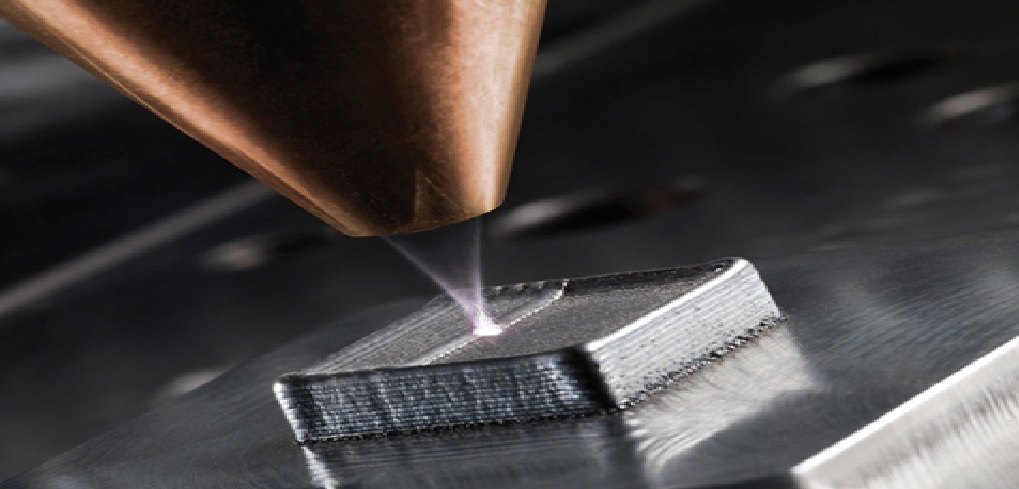
Developments in laser technology, such as the introduction of the femtosecond laser, could expand the use of additive manufacturing techniques so that they can be used with a much greater range of metals and metal alloys. [1] Femtosecond lasers are useful for 3D metal printing because they can deliver a very short pulse of high-energy laser light, allowing them to fuse metal powders with a greater-than-ever level of precision. The future of 3D Metal Printing is shown in figure 1.
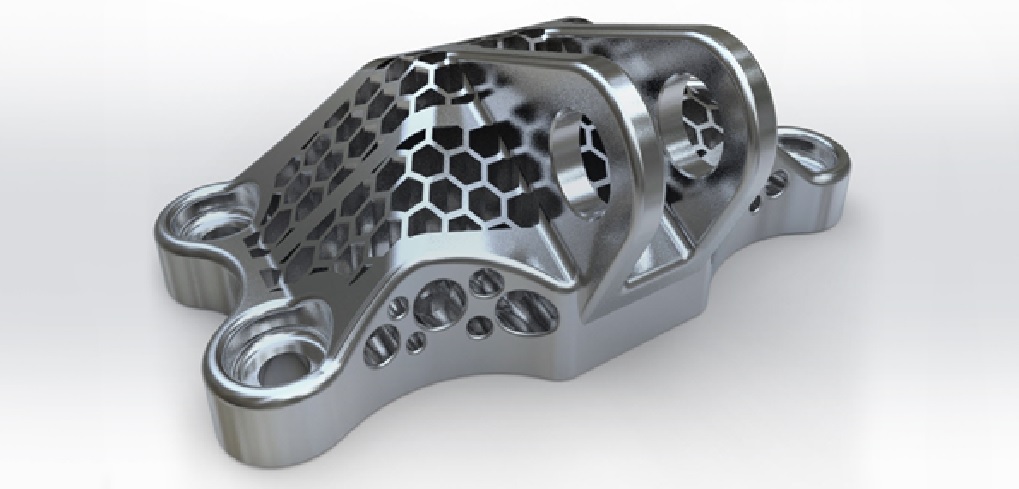

Figure 1: The Future of 3D Metal Printing
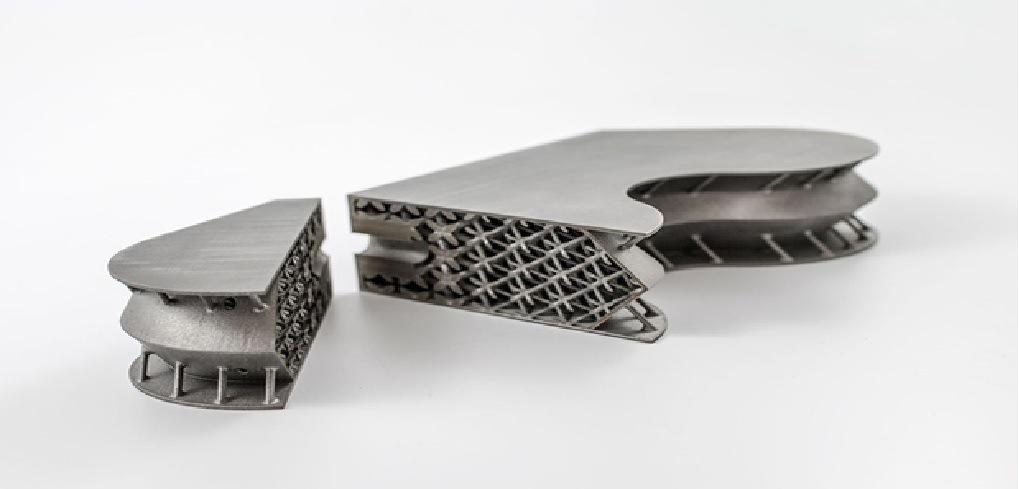
As 3D metal printing techniques continue to develop and the costs of the technology fall further, 3D printing could play an ever-greater role in metal manufacturing. 3D printing techniques avoid many of the typical pitfalls of metal manufacturing, such as the need for post-production heat treatments and specialized machines for milling and finishing the metal object. 3D metal printing could also significantly speed up production in many areas of metal manufacturing.
While 3D printing may not be taking over the entire manufacturing industry just yet, [2] analysts predict there will be a great deal of growth and the market will be worth 32.78 billion USD by 2023.
The economics of metal printing could be changed by 3D printing too, with a new technique called bound-metal deposition. The technique can build objects at a rate of 500 cubic inches an hour compared to one to two cubic inches an hour when using a typical laser-based metal printer.
The full consequences of 3D printing in the manufacturing industry are hard to predict. But based on what’s happened already in the industry and what analysts expect to see in the coming years, it seems safe to say that we haven’t seen 3D printing used to its full potential just yet.
Widespread 3D printing enabled distributed manufacturing, or decentralized production, has not emerged in a manner anticipated by some and the usefulness of frothy jargon, such as Industry 4.0 or the Fourth Industrial Revolution is queried. [3] Yet, unbridled techno-optimism, whereby “the future” is a multifarious panacea, and unchecked skepticism are both extreme states, will a rational, cooler, middle path be plotted through the decade by analysts and commentators.
And finally, but of critical importance, are the people behind the technology. As the additive manufacturing leaders surveyed for this article illustrate, 3D printing is a global industry. For the visions articulated below to be realized in the coming decade, our sector needs to continue to attract the best and brightest. The trifecta of additive manufacturing – machines, materials, software – can be advanced by those with a diverse skill-set, therefore striving for an inclusive industry will benefit all.
Here are five predictions [4].
- Scalability from Rapid Prototyping to Production
- Making the Supply Chain More Resilient Through Digitization
- Offering Greater Flexibility and More Customized Designs
- The Future of Digital is all about Materials
- Creating a More Sustainable Future with 3D Printing
References:
- https://www.element.com/nucleus/2016/dmls-vs-slm-3d-printing-for-metal-manufacturing
- https://www.northbridgeinsurance.ca/blog/3d-printing-manufacturing/
- https://3dprintingindustry.com/news/100-3d-printing-experts-predict-the-future-of-3d-printing-in-2030-167623/
- https://www.jabil.com/blog/future-of-3d-printing-additive-manufacturing-looks-bright.html
Cite this article:
Vinotha D (2021) The Development of Metal 3D Printing Technology, AnaTechmaz, pp 6