Overview of Session Initiation Protocol
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is used to signal and control interactive communication sessions. The uses for such sessions include voice, video, chat and instant messaging, as well as interactive games and virtual reality. The SIP protocol is increasingly being used to provide Voice over IP, Presence and Instant Messaging in Next Generation Networks, and being mandated for many new applications, including 3G telephony.
SIP is a protocol developed primarily by the SIPCORE working group of the IETF (see the SIPCORE Charter) and is an alternative to the ITU Recommendation H.323, but is a more lightweight and general-purpose, text-based protocol based on HTTP.
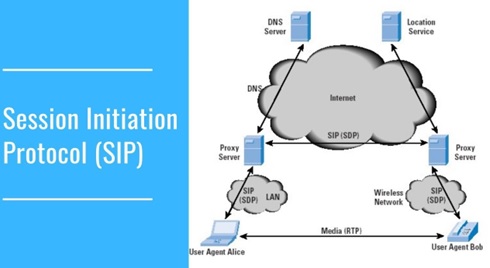
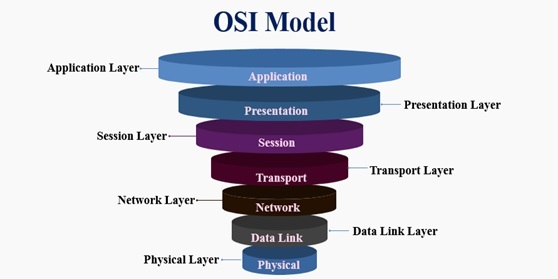
Figure 1. Overview of Session Initiation Protocol
Figure 1 shows Basically SIP is an application layer protocol. It is a simple network signalling protocol for creating and terminating sessions with one or more participants. The SIP protocol is designed to be independent of the underlying transport protocol, so SIP applications can run on TCP, UDP, or other lower-layer networking protocols.
SIP features
The SIP communications protocol determines five attributes when establishing and terminating multimedia sessions:
- user location
- user availability
- user capabilities
- session setup
- session management
SIP sessions can include internet telephony, video conferencing and other forms of unified communications. The protocol can be used to invite participants to unicast or multicast sessions that do not necessarily involve the initiator.
SIP versus VoIP
VoIP is a family of technologies that all support sending or receiving voice messages over the internet. SIP is an application protocol used to carry all forms of digital media, including voice messages—so SIP is a specific technology that supports VoIP calls.
SIP trunk
An SIP trunk is the interconnection between two domains of the Unified Communications network. By creating these interconnections, SIP trunking allows us to partition the network into public and private domains.
Public domains are generally managed by an internet telephone service provider (ITSPs), while private domains are connected to someone's personal server. ITSPs use SIP trunking to securely deliver telephone and streaming media services to users equipped with private branch exchange.
References:
- https://www.metaswitch.com/knowledge-center/reference/what-is-session-initiation-protocol-sip
- https://www.tutorialspoint.com/session_initiation_protocol/session_initiation_protocol_introduction.htm#
- https://www.techtarget.com/searchunifiedcommunications/definition/Session-Initiation-Protocol
- https://www.extrahop.com/resources/protocols/sip/
Cite this article:
Janani R (2023), Overview of Session Initiation Protocol, AnaTechMaz, pp.96