Methods of Media Access Control
In this manner, the point in these networks is to have the option to use the transmission capacity effectively, and ensure decency to all nodes. As we probably are aware, wireless networks contrast gigantically from wired networks moreover, ad hoc wireless networks have significantly progressively explicit attributes, for example, node versatility, power requirements.
Thus, new protocols are required for controlling access to the physical medium. The special properties of the ad hoc network make the structure of a medium access control (MAC) protocol all the more testing.
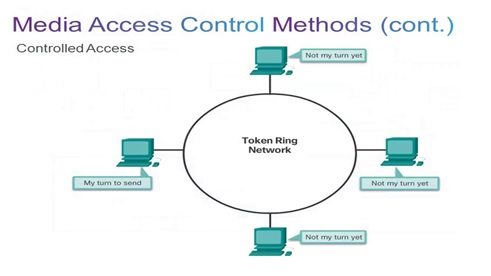
Figure 1. The Methods of Media Access Control
Figure 1 shows This network channel through which data is transmitted between terminal nodes to avoid collision has three various ways of accomplishing this purpose. They include:
- Carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance (CSMA/CA)
- Carrier sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD)
- Token passing
Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD):
In this method, a station monitors the medium after it sends a frame to see if the transmission was successful. If successful, the transmission is finished, if not, the frame is sent again.
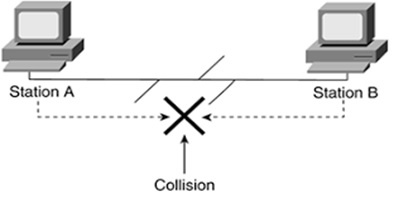
Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD)
Carrier sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD) is the opposite of CSMA/CA. Instead of detecting data to transmit signal intention to prevent a collision, it observes the cable to detect the signal before transmitting.
Collision detection means that when a collision is detected by the media access control policy, transmitting by the network stations stops at a random length of time before transmitting starts again.
Token-Passing
The Token-Passing Protocol relies on a control signal called the token. A token is a 24-bit packet that circulates throughout the network from NIC to NIC in an orderly fashion. If a workstation wants to transmit a message, first it must seize the token. At that point, the workstation has complete control over the communications channel. The existence of only one token eliminates the possibility of signal collisions. This means that only one station can speak at a time.
References:
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/responsibilities-and-design-issues-of-mac-protocol/
- https://www.getkisi.com/blog/media-access-control
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/carrier-sense-multiple-access-csma/
- https://ecomputernotes.com/computernetworkingnotes/network-technologies/how-does-a-token-passing-protocol-works
Cite this article:
Janani R (2023), Methods of Media Access Control, AnaTechMaz, pp.93