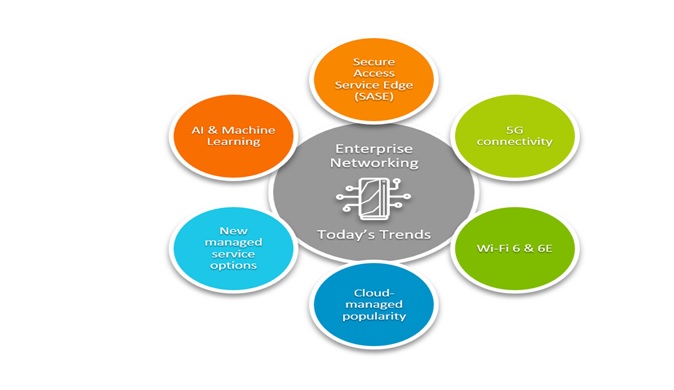
5G and Wi-Fi 6G Technology
5G or fifth generation cellular technology. It is characterized by increased speed, reduced latency and improve flexibility in wireless services. It helps organizations to mobilize workforces, extend automation, supporting new applications with increased network capacity and high data rates.
5G gives seamless open roaming capabilities between cellular and Wi FI access. 5G would solve the issue of many wireless devices connected at once – and IoT makes it worse by slowing wireless network performance. Wi Fi 6 infrastructure is ready to go however Wi Fi 6 capable devices such as computers and mobile phones manufacturers need to adopt new standards.
The requirements of future 6G wireless communications demand to support massive data-driven applications and the increasing number of users. Unlike existing works, this paper highlights the recent activities and trends toward 6G technology, network requirement, essential enabling technologies for 6G networks, and a detailed use case analysis between 5G and 6G networks. Moreover, this paper surveys emerging 6G connectivity solutions, such as holographic beamforming, artificial intelligence-enabled IoT networks, edge computing, and backscatter communications to serve smart communities. Furthermore, several future research directions to accomplish 6G-based IoT networks are also highlighted.

Figure 1.5G and Wi-Fi 6G Technology
Figure 1. shows 5G and Wi-Fi 6 are both next-generation wireless technologies that offer significant improvements in terms of speed, capacity, and reliability compared to their predecessors.
5G is a cellular network technology that promises faster download and upload speeds, lower latency, and increased network capacity compared to 4G. 5G operates on high-frequency radio waves, known as millimetre waves, which allows for higher data transfer rates but also requires more infrastructure to be deployed.
Wi-Fi 6, on the other hand, is the latest version of the Wi-Fi standard, also known as 802.11ax. Wi-Fi 6 promises faster speeds, increased capacity, and better performance in high-density environments such as stadiums, airports, and office buildings. Wi-Fi 6 operates on both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequencies and introduces new technologies such as MU-MIMO and OFDMA to improve network efficiency.
While 5G and Wi-Fi 6 are both designed to offer high-speed wireless connectivity, they serve different purposes and operate in different frequency bands. 5G is primarily aimed at providing cellular connectivity for mobile devices, while Wi-Fi 6 is designed for local area networking within a building or campus.
In summary, 5G and Wi-Fi 6 are both exciting technologies that promise to deliver faster and more reliable wireless connectivity. However, they serve different purposes and operate in different frequency bands, so their adoption and deployment will depend on specific use cases and requirements.
References:
- https://networkinterview.com/top-10-networking-technology-trends/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2405959522000959
Cite this article:
Janani R (2023),5G and Wi-Fi 6g Technology, AnatechMaz, pp.81