Advanced Driver Assistance System (ADAS)
Advanced driver assistance systems, or ADAS, is the term used to describe the growing number of safety functions designed to improve driver, passenger and pedestrian safety by reducing both the severity and overall number of motor vehicle accidents. ADAS can warn drivers of potential dangers, intervene to help the driver remain in control in order to prevent an accident and, if necessary, reduce the severity of an accident if it can’t be avoided. In short, ADAS compensates for our mistakes, be they inattentiveness, erroneous control inputs or, up to a point, downright stupidity. [1]
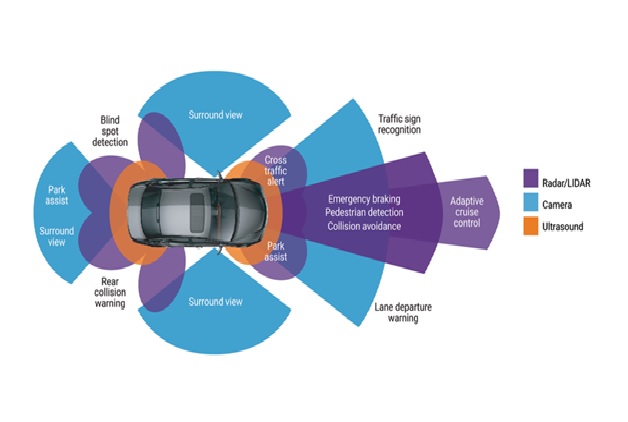
Figure 1. The Advanced Driver Assistance System (ADAS)
Figure 1 shows ADAS works by alerting the driver to danger or even taking action to avoid an accident. ADAS-equipped vehicles can sense the environment around themselves, process this information quickly and accurately in a computer system, and provide the correct output to the driver.
ADAS-equipped vehicles have an array of advanced sensors that augment the eyes, ears, and decision-making of the human driver. [2]
ADAS Applications
Some of the most common ADAS applications are:
1. Adaptive Cruise Control
Adaptive cruise control (ACC) is particularly helpful on the highway, where drivers can find it difficult to monitor their speed and other cars over a long period of time. Advanced cruise control can automatically accelerate, slow down, and at times stop the vehicle, depending on the actions other objects in the immediate area.
2. Glare-Free High Beam and Pixel Light
Glare-free high beam and pixel light uses sensors to adjust to darkness and the vehicle’s surroundings without disturbing oncoming traffic. This new headlight application detects the lights of other vehicles and redirects the vehicle’s lights away to prevent other road users from being temporarily blinded.
3. Adaptive Light Control
Adaptive light control adapts the vehicle’s headlights to external lighting conditions. It changes the strength, direction, and rotation of the headlights depending on the vehicle’s environment and darkness.
4. Automatic Parking
Automatic parking helps inform drivers of blind spots so they know when to turn the steering wheel and stop. Vehicles equipped with rearview cameras have a better view of their surroundings than traditional side mirrors. Some systems can even complete parking automatically without the driver’s help by combining the input of multiple sensors. [3]
References:
- https://www.oxts.com/what-is-adas/
- https://dewesoft.com/daq/what-is-adas
- https://www.synopsys.com/automotive/what-is-adas.html
Cite this article:
Thanusri swetha J (2021), Advanced Driver Assistance System (ADAS), Anatechmaz, pp. 33