Gesture Recognition Breakthrough: Skyrmions Power Energy-Efficient Computing
Researchers at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) have advanced Brownian reservoir computing by using skyrmions to detect hand gestures, demonstrating superior energy efficiency compared to neural networks. "We were impressed to see that our hardware approach and concept worked so well – and even better than energy-intensive software solutions that employ neural networks," remarked Grischa Beneke, a member of Professor Mathias Kläui's team. Using Range-Doppler radar data, the system precisely recognized gestures by harnessing the random motions of skyrmions, offering a significant leap in energy-efficient computing without requiring extensive training like traditional methods.
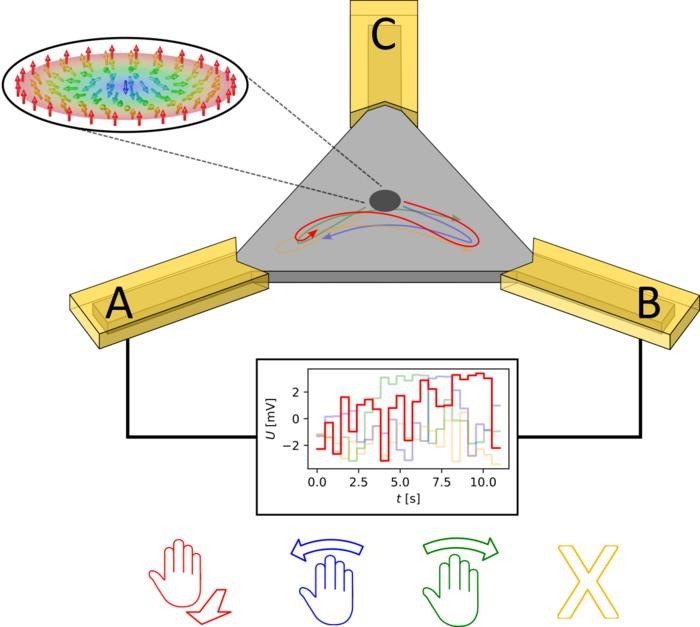
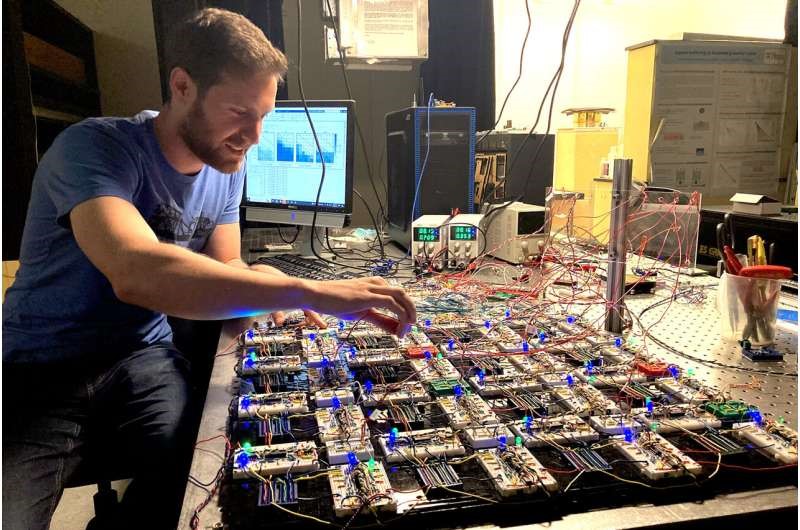
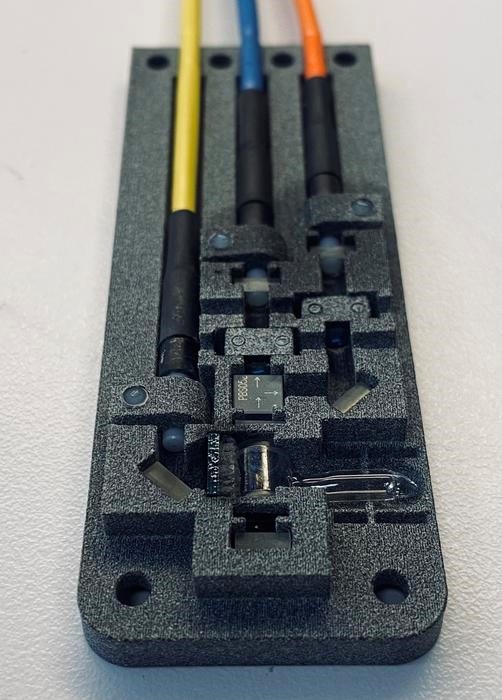
Figure 1. Brownian Reservoir Computer. (Credit: Grischa Beneke / JGU)
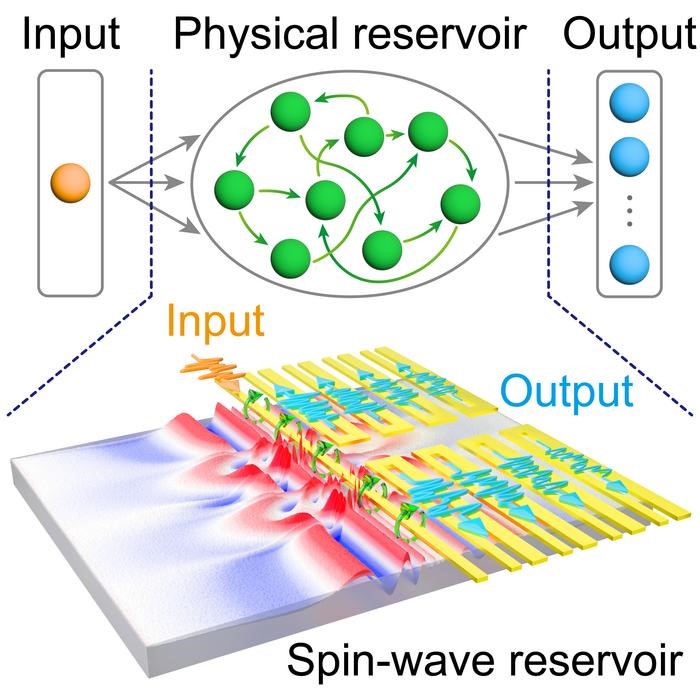
Figure 1 shows Brownian reservoir computer. Reservoir computing systems function similarly to neural networks but require less energy since they don’t need extensive training. Instead, only the output mechanism needs to be trained, as explained by Beneke. In their study published in Nature Communications [1, 2], the team recorded gestures like swiping left or right using radar sensors, which then fed data into a unique triangular reservoir composed of a thin-film stack. Here, skyrmions – magnetic whirls with huge potential for non-traditional computing – moved in reaction to the signals, enabling gesture recognition.
In comparison to software-based approaches, this system achieved similar, if not better, accuracy with significantly lower energy demands. Skyrmions’ random motions require minimal currents, making this hardware approach more efficient. The research team believes that further advancements, such as integrating a magnetic tunnel junction, could miniaturize the system and enhance its performance. Supported by international collaboration and industry partners, the team expects rapid future development of this technology.
Source: Johannes Gutenberg Universitaet Mainz
References:
- https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2024/09/240916115430.htm
- https://www.eurekalert.org/news-releases/1058122
Cite this article:
Hana M (2024), Gesture Recognition Breakthrough: Skyrmions Power Energy-Efficient Computing, AnaTechMaz, pp. 313