Essential Factors of Cloud Cryptography
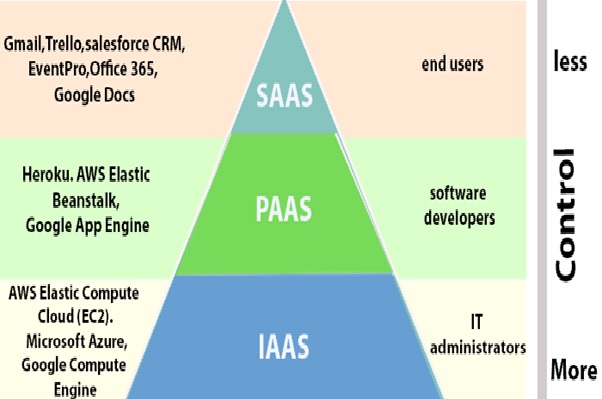
Cloud computing is a framework for offering on-demand network access to a pooled pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, software, and services) that can be quickly provisioned and released with limited maintenance activity or service provider involvement. In cloud computing, resources are abstracted and virtualized from the cloud provider's IT infrastructure and made accessible to the customer. Cloud infrastructure provides various advantages to cloud consumers and other core stakeholders. Some of these benefits are access to data stored on the cloud regardless of the location, pay-on-demand basis, flexibility and elasticity, and economic benefits by saving the company from buying hardware and other IT infrastructure. Despite all these benefits, cloud computing has its fair share of concerns. The main concern in the cloud computing industry is security. The first and most obvious concern is privacy considerations. That is if another party is housing all your data, how do you know that it’s safe and secure Since the internet [1] powers cloud computing, data migrated to the cloud could be assessed by anyone from anywhere when security is breached. Hackers can go to any extent in order to compromise data .From selling your confidential information to rivals and those on the dark web to encrypting your storage and data unless you pay them off, or they can simply delete anything to harm your company and defend their actions based on ideological views .This will have a massive effect on the company's reputation, as well as depleting the interest consumers have in the company, resulting in customer loss .Whatever the case, hackers are a serious concern for your data managed on a cloud. Because your data is held on someone else's computers, you may be at the mercy of whatever security measures they support. Organizations do not have much control over what happens to their data as everything on the cloud including security is managed by the cloud provider.
- Data Encryption Standard (DES)
DES is a standard for data encryption that uses a secret key for both encryption and decryption. It adopts a 64-bit secret key, of which 56 bits are randomly generated and the other8 bits are used for error detection. It employs a data encryption algorithm (DEA), a secret block cipher employing a 56-bit key operating on 64-bit blocks. It is the archetypal block cipher- an algorithm that takes a fixed-length string of plaintext bits and transforms it into a ciphertext bit string of the same length. DES design allows users to implement it in hardware and use it for single-user encryption, such as files stored on a hard disk in encrypted form. - Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)
It is a National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) specification for encrypting electronic data. It also helps to encrypt digital information such as telecommunications, financial, and government data. It is being used by US government agencies to sensitive unclassified materials. AES consists of symmetric key algorithm: both encryption and decryption are performed using the same key. It is an iterated block cipher that works by repeating the defined steps multiple times [2]. It has 128-bit block size, with key sizes of 128, 192, and 256 bits for AES-128, AES-192, and AES-256, respectively. The design of AES makes its use efficient in both software and hardware and also works at multiple network layers. - Blowfish
Blowfish is a type of symmetric algorithm designed to replace DES or IDEA algorithms. It uses the same secret key to encrypt and decrypt data. The algorithm splits the data into a block length of 64 bits and produces a key ranging from 32 bits to 448 bits. Due to its high speed and overall efficiency, blowfish is used in password protection tools to e-commerce websites for securing payments. It is a 16-round Feistel cipher working on 64-bit blocks. However, unlike DES, its key size ranges from 32 bits to 448 bits figure1shown below

Figure1.Cloud Cryptography
Cloud Cryptography is encryption that safeguards data stored within the cloud. Several measures are being placed within cloud cryptography which adds a strong layer of protection to secure data to avoid being breached, hacked or affected by malware. Any data hosted by cloud providers are secured with encryption, permitting users to access shared cloud services securely and conveniently. Cloud Cryptography secures sensitive data without delaying the delivery of information.
Advantages of Cloud Cryptography
- The data remains private for the users. This reduces cybercrime from hackers.
- Organization receives notifications immediately if an unauthorized person tries to make modifications. The users who have cryptographic keys are granted access.
- The encryption [3] prevents the data from being vulnerable when the data is being brought over from one computer to another.
- Cloud encryption permits organizations to be proactive in their defence against data breaches and cyberattacks and have become a necessity in today’s data-driven world.
References:
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/an-overview-of-cloud-cryptography
- www.ijert.org/cloud-cryptography-a-security-aspect
- https://www.ijcns.latticescipub.com/wp-content/uploads/papers/v1i1/
Cite this article:
S. Nandhinidwaraka (2021), Essential Factors of Cloud Cryptography, AnaTechMaz, pp. 9