Cloud Database
Cloud Computing is the delivery of computing services such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, intelligence, and more, over the Cloud (Internet).
Cloud Computing provides an alternative to the on-premises datacentre. With an on-premises datacentre, we have to manage everything, such as purchasing and installing hardware, virtualization, installing the operating system [1], and any other required applications, setting up the network, configuring the firewall, and setting up storage for data. After doing all the set-up, we become responsible for maintaining it through its entire lifecycle.
But if we choose Cloud Computing, a cloud vendor is responsible for the hardware purchase and maintenance. They also provide a wide variety of software and platform as a service. We can take any required services on rent. The cloud computing services will be charged based on usage. The cloud environment provides an easily accessible online portal that makes handy for the user to manage the compute, storage, network, and application resources. Some cloud service providers are in the following figure1.
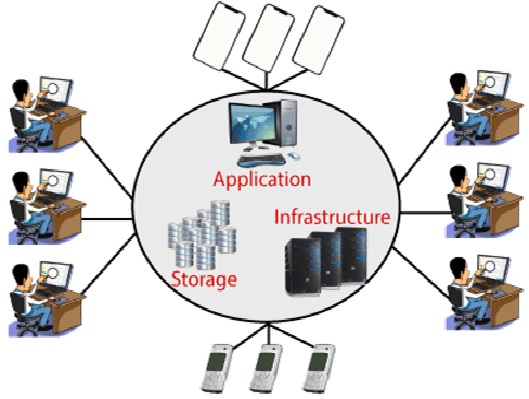
Figure 1: Cloud computing application, infrastructer, storage
Advantages of cloud computing
- Cost: It reduces the huge capital costs of buying hardware and software.
- Speed: Resources can be accessed in minutes, typically within a few clicks.
- Scalability: We can increase or decrease the requirement of resources according to the business requirements.
- Productivity: While using cloud computing, we put less operational effort. We do not need to apply patching, as well as no need to maintain hardware and software. So, in this way, the IT team can be more productive and focus on achieving business goals.Reliability: Backup and recovery of data are less expensive and very fast for business continuity.
- Security: Many cloud vendors offer a broad set of policies, technologies, and controls that strengthen our data security.
Types of Cloud Computing
- Public Cloud:The cloud resources that are owned and operated by a third-party cloud service provider are termed as public clouds. It delivers computing resources such as servers, software, and storage over the internet
- Private Cloud:The cloud computing resources that are exclusively used inside a single business or organization are termed [2] as a private cloud. A private cloud may physically be located on the company’s on-site datacentre or hosted by a third-party service provider.
- Hybrid Cloud:It is the combination of public and private clouds, which is bounded together by technology that allows data applications to be shared between them. Hybrid cloud provides flexibility and more deployment options to the business.
Types of Cloud Services
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): In IaaS, we can rent IT infrastructures like servers and virtual machines (VMs), storage, networks, operating systems from a cloud service vendor. We can create VM running Windows or Linux and install anything we want on it [3]. Using IaaS, we don’t need to care about the hardware or virtualization software, but other than that, we do have to manage everything else. Using IaaS, we get maximum flexibility, but still, we need to put more effort into maintenance.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): This service provides an on-demand environment for developing, testing, delivering, and managing software applications. The developer is responsible for the application, and the PaaS vendor provides the ability to deploy and run it. Using PaaS, the flexibility gets reduce, but the management of the environment is taken care of by the cloud vendors.
Software as a Service (SaaS): It provides a centrally hosted and managed software services to the end-users. It delivers software over the internet, on-demand, and typically on a subscription basis. E.g., Microsoft One Drive, Dropbox, WordPress, Office 365, and Amazon Kindle. SaaS is used to minimize the operational cost to the maximum extent it shown below the figure 2.
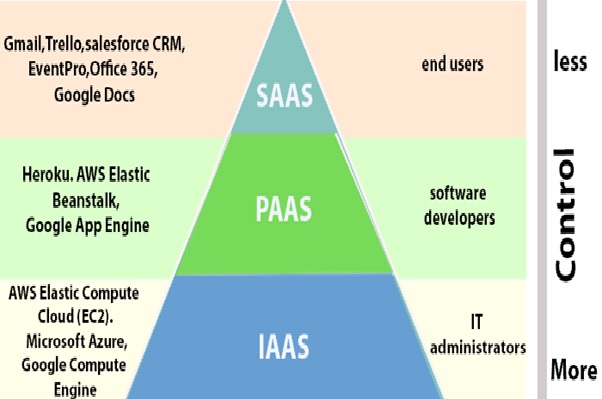
Figure 2: cloud computing have beencreating three sectors SAAS,PAAS,IAAS.
NIST lists the following as the five essential characteristics of cloud computing:
- On-demand self-service:Cloud resources can be accessed or provisioned without human interaction. With this model, consumers can gain immediate access to cloud services upon signup. Organizations can also create mechanisms for allowing employees, customers, or partners to access internal cloud services on demand according to predetermined logics without needing to go through IT services.
- Broad network access:: Users can access cloud services and resources through any device and in any networked location provided that they have permission.
- Resource pooling:Cloud provider resources are shared by multiple tenants while keeping the data of individual clients hidden from other clients.
- Rapid elasticity:Unlike on-premise hardware and software, cloud computing resources can be rapidly increased, decreased, or otherwise [4] modified based on the cloud user’s changing needs.
- Measured service:Usage of cloud resources is metered so that businesses and other cloud users need only pay for the resources they use in any given billing cycle. These characteristics offer a wide variety of transformative opportunities for businesses and individuals alike, which we’ll discuss later in the section Benefits of Cloud Computing. To gain some additional context, let’s briefly review the emergence of cloud computing.
History of Cloud Computing
Many aspects of cloud computing can be traced as far back as the 1950s, when universities and companies rented out computation time on mainframe computers. At the time, renting was one of the only ways to access computing resources as computing technology was too large and expensive to be owned or managed by individuals. By the 1960s, computer scientists like John McCarthy of Stanford University and J.C.R Licklider of The U.S. Department of Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) began proposing ideas that anticipated some of the major features of cloud computing today, such as the conceptualization of computing as a public utility and the possibility of a network of computers that would allow people to access data and programs from anywhere in the world.
Cloud computing, however, didn’t become a mainstream reality and a popular term until the first decade of the 21st century. This decade saw the launch of cloud services like Amazon’s Elastic Compute (EC2) and Simple Storage Service (S3) in 2006, Heroku in 2007, Google Cloud Platform in 2008, Alibaba Cloud in 2009, Windows Azure (now Microsoft Azure) in 2010, IBM’s SmartCloud in 2011, and DigitalOcean in 2011. These services allowed existing businesses to optimize costs by migrating their in-house IT infrastructure to cloud-based resources and provided independent developers and small developer teams resources for creating and deploying apps. Cloud-based applications, known as Software as a Service (SasS) — which we’ll discuss in greater detail in the Cloud Delivery Models section — also became popular during this time period. Unlike on-premise software, or software that users need to physically install and maintain on their machines [5], SaaS increased the availability of applications by allowing users to access them from a variety of devices on demand.
Some of these cloud-based applications — such as Google’s productivity apps (Gmail, Drive, and Docs) and Microsoft 365 (a cloud-based version of the Microsoft Office Suite) — were offered by the same companies that launched cloud infrastructure services, while other pre-existing software products, such as Adobe Creative Cloud, were launched as cloud-based applications using the services of cloud providers. New SaaS products and businesses also emerged based on the novel opportunities of these cloud providers, such as Netflix’s streaming services in 2007, the music platform Spotify in 2008, the file-hosting service Dropbox in 2009, the video conferencing service Zoom in 2012, and the communication tool Slack in 2013. Today, cloud-based IT infrastructure and cloud-based applications have become a popular choice for both businesses and individual users and their market share is expected to grow.
References:
- Whats is cloud computing and its meaning? Reterived at may from 2020 www.slideshare.net/Rkmishra00/cloud-computing-32035613.
- https://www.javatpoint.com/introduction-to-cloud-computing
- https://www.digitalocean.com/.../a-general-introduction-to-cloud-computing
- https://www.slideshare.net/Rkmishra00/cloud-computing-32035613
- https://azure.microsoft.com/en-in/overview/what-is-cloud-computing
Cite this article:
D. Vinotha (2021), Cloud Database, AnaTechMaz, pp. 3