The development Cloud Load Balancing
Cloud load-balancing is the process of distributing workloads & computing resources within a cloud technology's environment. It also helps organizations & enterprises to manage workload demands by allocating resources among multiple systems or servers. Cloud load balancing also involves hosting the distribution of workload traffic that resides over the internet.
Application of cloud load balancing
Load balancing can be implemented in hardware as is the case with F5's Big IP server or in software also such as Apache mod_proxy_balancer, the pound load-balancers & reverse-proxy software. Load balancing is an optimization [1] technique which can be used to enhance utilization & throughput, lower latency, reduce response time & avoid overloading of systems.
- Cloud load balancing can transfer loads to servers globally whereas DNS load balancers cannot.
- Cloud load balancers have the ability to deliver users to the closest regional server without interrupting the user's tasks.
- Cloud load balancers addresses issue relating to TTL reliancy used in DNS load balancing.
- Cloud load balancing has the capability to increase response time by routing remote sessions to the best performing data-centers.
Goals of load balancing
- Application Response time
- Availability of application - efficiently
- Time of day
- User location
- The current & total capacity of data centers in which application is deployed
The purpose of cloud load balancing is to distribute the traffic across the instances of your organizational applications. When you can successfully spread or distribute the load, then the risks associated with performance [2] hassles will gradually reduce. With the use of Cloud Load Balancer, it is evident that you will have the potential to serve content to users over the system at a faster pace.
External Load Balancing/Balancers
- If you intend to use external load balancers with global load balancing type, then you must take up the premium tier services of the Network Service Tiers. But, if you are opting for regional load balancing, then you can prefer using the Standard tier. There are four options for you within the type of external load balancers that includes:
- HTTP(S) load balancing for the respective traffic.
- TCP proxy for the TCP traffic type. It is for the ports except 8080 and 80, without any SSL offload.
- SSL proxy for the SSL offloads over the ports, except 8080 and 80.
- Network load balancer for the UDP/TCP traffic.
Internal Load Balancing/Balancers
Just like the network load balancer and HTTP(S) load balancer, internal load balancer is not any hardware device [3], appliance, or instance. It has the potential to support several connections every second, as per the need.
The use of load balancing techniques based upon the type of traffic is what helps you choose the proficient options amongst all:
- For HTTP(S) traffic, you can prefer to use Internal or External HTTP(S) load balancing.
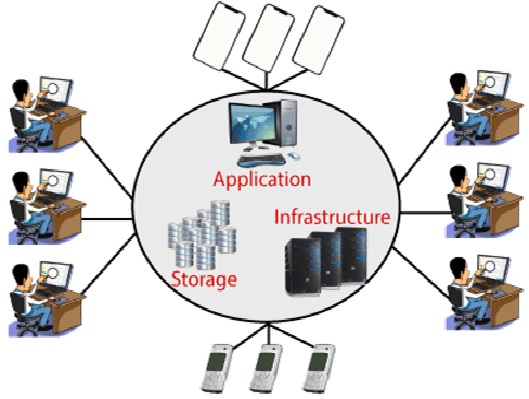
- For TCP traffic, you can prefer to use TCP proxy load balancing, Internal UDP/TCP load balancing, and network load balancing figure1 shown below.
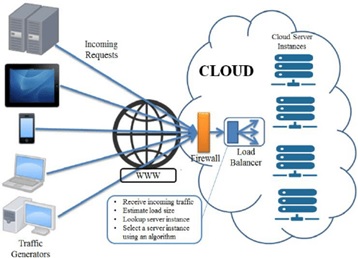
Figure1. cloud load balancing
References:
- www.w3schools.in/cloud-computing/load-balancing
- https://www.w3schools.in/cloud-computing/load-balancing
- https://www.whizlabs.com/blog/what-is-cloud-load-balancing-a-complete-guide
Cite this article:
S. Nandhinidwaraka (2021), The Development of Cloud Load Balancing, AnaTechMaz, pp. 5