Hosting Apps and Services at The Edge
This year, I expect to see more cross-border businesses with distributed user bases begin to host latency-intensive apps and services at the edge of the network
As many people know, edge compute servers come in two options: bare metal servers and virtual machines (VMs). Bare metal is a physical server that you rent from a local service provider, while a VM is a virtualized, logical part of a server. Bare metal gives you full control of your instance, while VM requires sharing a tenancy with other VMs on the same machine.

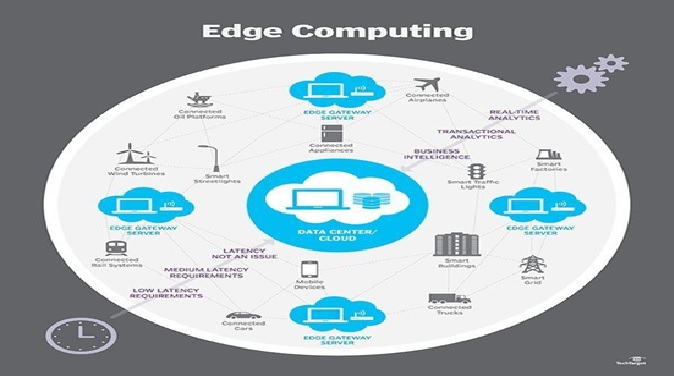
Figure 1. Hosting Apps and Services at The Edge
Hosting Apps and Services at The Edge is shown in figure 1. Migrating to a new hosting model is no small feat, but edge hosting provides several advantages over the traditional central server model.
Hosting apps and services at the edge offers several advantages
- Improved Performance
- Increased Reliability
- Cost-Effective Scalability
- Enhanced Security
- Better Bandwidth Management
Hosting apps and services at the edge can provide significant benefits for businesses looking to improve the performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness of their applications and services. By leveraging edge computing, businesses can deliver more responsive and engaging experiences for their customers while managing their costs and enhancing their security.
Hosting apps and services at the edge offers several disadvantages
- Limited Scalability
- Higher Complexity
- Higher Costs
- Security Risks
- Lack of Standardization
While hosting apps and services at the edge can provide significant benefits, businesses need to carefully consider the potential disadvantages and ensure that their use cases and requirements align with the capabilities and limitations of edge computing.
Edge computing refers to the practice of processing and storing data closer to where it is generated or consumed, as opposed to relying solely on a centralized cloud infrastructure. This can improve performance, reduce latency, and increase reliability, especially for applications and services that require real-time responsiveness or operate in remote or bandwidth-constrained environments.
One approach to hosting apps and services at the edge is to use cloud providers that offer edge computing capabilities. These providers typically have a global network of edge locations that are strategically positioned in different geographic regions to minimize latency and optimize data delivery.
References:
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestechcouncil/2023/03/17/top-six-edge-computing-trends-to-know-about-in-2023/?sh=6303db126754
- https://www.telerik.com/blogs/future-hosting-edge-computing
Cite this article:
Gokula Nandhini K (2023), Hosting Apps and Services at The Edge, AnaTechMaz, pp.72