Deploying to the Edge
Edge computing is the deployment of computing and storage resources at the location where data is produced. This ideally puts compute and storage at the same point as the data source at the network edge.
Edge computing is a distributed information technology (IT) architecture in which client data is processed at the periphery of the network, as close to the originating source as possible.
Edge computing is all a matter of location. In traditional enterprise computing, data is produced at a client endpoint, such as a user's computer. That data is moved across a WAN such as the internet, through the corporate LA N, where the data is stored and worked upon by an enterprise application. Results of that work are then conveyed back to the client endpoint. This remains a proven and time-tested approach to client-server computing for most typical business applications.
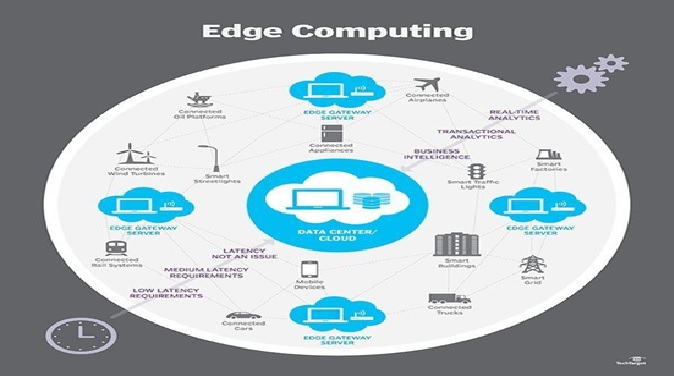
Figure 1. Edge computing brings data processing closer to the data source
Edge computing brings data processing closer to the data source is shown in figure 1. Thus, edge computing is reshaping IT and business computing. Take a comprehensive look at what edge computing is, how it works, the influence of the cloud, edge use cases, tradeoffs and implementation considerations.[1]
Benefits of Edge Deployment
Edge Computing for Speech-to-Text services has many advantages:
- Low Network Latencies & High Network Reliability-With Edge Computing processing of speech audio is brought close to where the audio originates. For example, all processing can be done in the same location where the Telco phone lines terminate for an IVR application. If the speech processing were to happen in the Cloud the audio data would need to be sent over Internet which would introduce additional latency, jitter, and would make the service susceptible to occasional incidents on wide internet like trunks overloaded by DDoS attacks, fiber cuts, etc. One can avoid some of those issues by deploying more reliable network connectivity to the Cloud, e.g., Google Cloud Interconnect, but that comes at the cost and still does not solve the basic reality of extra latency.
- Lower Bandwidth Cost-Some Speech-to-Text applications generate a lot of data, e.g., Call Analytics application that processes 100% of the calls. Edge Deployment allows for putting processing resources right next to where the data is generates, e.g. right at the Call Center.
- Data Privacy and Control-with all the incoming and generated data confided to the Edge Computing environment and none of it going to the Voice gain Cloud, the customers can apply their own security protocols to protect the data.[2]
Edge, Cloud, and Edge Cloud
In order to see the challenges involved in deploying edge cloud solutions whilst retaining strong security, it’s worth reminding yourself why edge cloud solutions such as Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) were initially developed. Such solutions are becoming virtually commonplace, to the point that SaaS in particular is projected to account for almost all of the software needs for 86% of companies within the next two years (it already is being used to a lesser extent by 90% of companies right now).[3]
References:
- https://www.techtarget.com/searchdatacenter/definition/edge-computing
- https://www.voicegain.ai/post/benefits-of-edge-deployment
- https://www.infoq.com/articles/secure-edge-systems/
Cite this article:
Gokula Nandhini K (2023), Deploying to the Edge, AnaTechMaz, pp.62