Technologies of Fog Computing
Fog Computing is the term coined by Cisco that refers to extending cloud computing to an edge of the enterprise’s network. Thus, it is also known as Edge Computing or Fogging. It facilitates the operation of computing, storage, and networking services between end devices and computing data centers. [2]
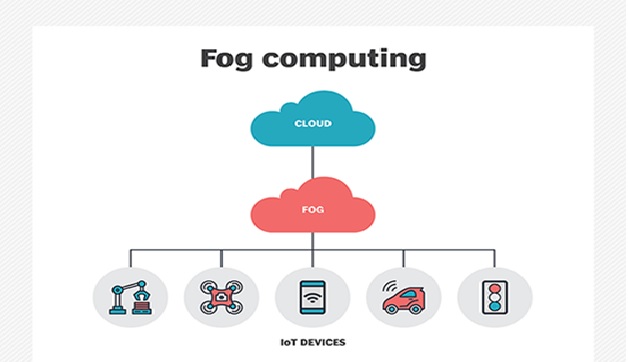
Figure 1. The Technologies of Fog Computing
Figure 1 shows To achieve real-time automation, data capture and analysis has to be done in real-time without having to deal with the high latency and low bandwidth issues that occur during the processing of network data. Although the cloud provided a scalable and flexible ecosystem for data analytics, communication and security challenges between local assets and the cloud lead to downtime and other risk factors.
To mitigate these risks, fog computing and edge computing were developed. These concepts brought computing resources closer to data sources and allowed these assets to access actionable intelligence using the data they produced without having to communicate with distant computing infrastructure. [3]
The benefits of fog computing
Like any other technology, fog computing has its pros and cons. Some of the advantages to fog computing include the following:
- Bandwidth conservation. Fog computing reduces the volume of data that is sent to the cloud, thereby reducing bandwidth consumption and related costs.
- Improved response time. Because the initial data processing occurs near the data, latency is reduced, and overall responsiveness is improved. The goal is to provide millisecond-level responsiveness, enabling data to be processed in near-real time.
- Network-agnostic. Although fog computing generally places compute resources at the LAN level -- as opposed to the device level, which is the case with edge computing -- the network could be considered part of the fog computing architecture. At the same time, though, fog computing is network-agnostic in the sense that the network can be wired, Wi-Fi or even 5G.
The Disadvantages of fog computing
- Physical location. Because fog computing is tied to a physical location, it undermines some of the "anytime/anywhere" benefits associated with cloud computing.
- Potential security issues. Under the right circumstances, fog computing can be subject to security issues, such as Internet Protocol (IP) address spoofing or man in the middle (MitM) attacks.
- Startup costs. Fog computing is a solution that utilizes both edge and cloud resources, which means that there are associated hardware costs.
- Ambiguous concept. Even though fog computing has been around for several years, there is still some ambiguity around the definition of fog computing with various vendors defining fog computing differently. [1]
References:
- https://internetofthingsagenda.techtarget.com/definition/fog-computing-fogging
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/fog-computing/
- https://www.stackpath.com/edge-academy/what-is-fog-computing
Cite this article:
Thanusri Swetha J (2021), Technologies of Fog Computing, AnaTechMaz, pp. 44