Types of Mobility
Mobility refers to the ability of people and goods to move from one place to another. With the advancement of technology, transportation systems have evolved to include various types of mobility methods. There are different types of mobility based on the mode of transportation, purpose, and technology used.

Figure 1. Types of Mobility [1]
Personal mobility:
Personal mobility refers to individual transportation methods such as walking, cycling, or driving a personal vehicle.
Public mobility:
Public mobility refers to transportation systems that are available for public use such as buses, trains, or subways.
Active mobility:
Active mobility refers to transportation methods that require physical activity such as walking or cycling.
Sustainable mobility:
Sustainable mobility refers to transportation methods that are environmentally friendly and reduce the impact on the environment.
Smart mobility:
Smart mobility refers to the use of technology to optimize transportation systems and improve the efficiency of transportation networks.
Shared mobility:
Shared mobility refers to transportation methods that are shared among multiple users such as carpooling or ride-sharing services.
On-demand mobility:
On-demand mobility refers to transportation services that can be requested and used immediately such as ride-sharing or on-demand bike rentals.
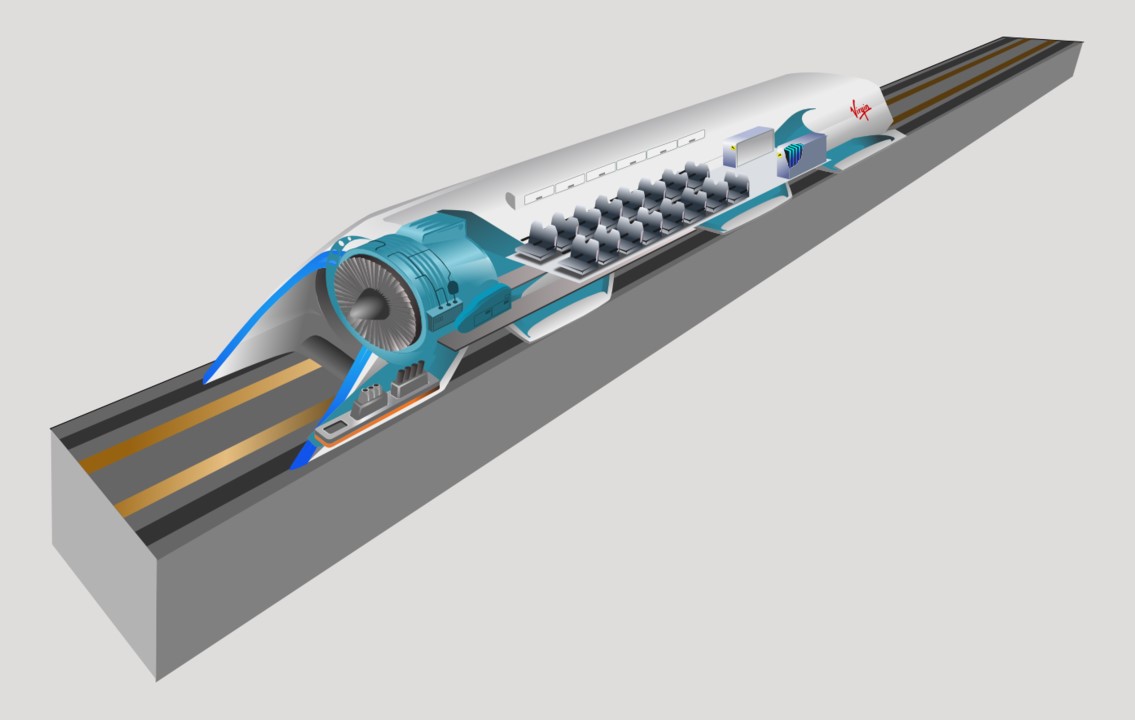
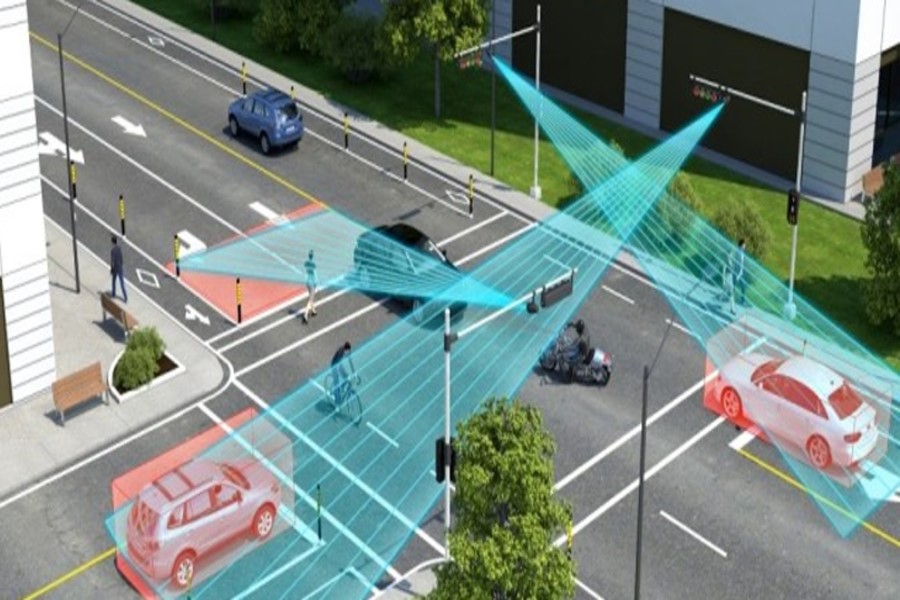
Autonomous mobility:
Autonomous mobility refers to transportation systems that are self-driving and do not require human intervention.
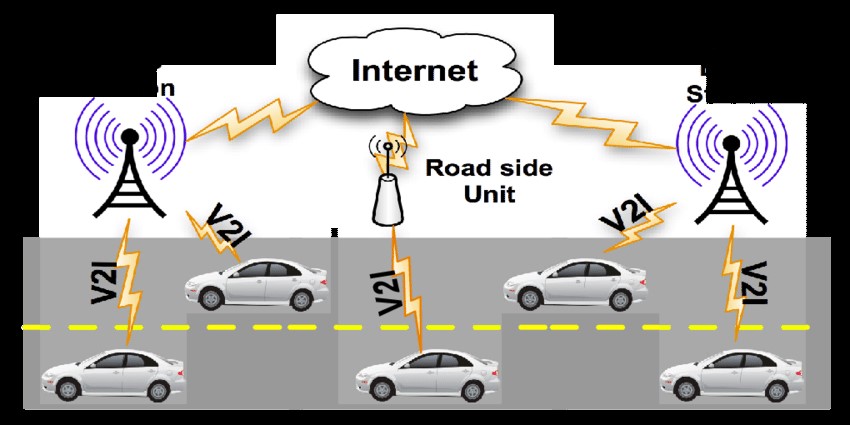
Connected mobility:
Connected mobility refers to transportation systems that are connected to the internet and other communication networks to improve efficiency and safety..
Electric mobility:
Electric mobility refers to transportation methods that are powered by electricity, such as electric cars, buses, or bicycles.
Hybrid mobility:
Hybrid mobility refers to transportation methods that use a combination of electric and fossil fuel power.
Fuel cell mobility:
Fuel cell mobility refers to transportation methods that use hydrogen fuel cells to generate electricity and power the vehicle.
Hydrogen mobility:
Hydrogen mobility refers to transportation methods that use hydrogen as fuel to power the vehicle.
Biofuel mobility:
Biofuel mobility refers to transportation methods that use biofuels, such as ethanol or biodiesel, to power the vehicle.
Mobility as a service:
Mobility as a service (MaaS) refers to a transportation model that combines various modes of transportation, such as public transportation, ride-sharing, and bike-sharing, into a single service.
References:
- https://www.acbconsultingservices.com/construction-management-for-transportation/what-is-urban-mobility-and-why-is-it-important-to-build-better-cities/
Cite this article:
Hana M (2023), Types of Mobility, AnaTechMaz, pp.124