Exploring The Advanced Technology Behind Robotic Hand Design and Its Role in Modern Robotics
Discover the Future of Robotic Hands and Their Impact on Real-World Applications.
Throughout history, the capabilities of our hands have played a crucial role in human progress. From early humans using basic tools to modern surgeons demonstrating intricate precision, this dexterity comes from a limb with 27 bones and over 30 muscles, all coordinated by the brain—one of our most advanced organs. This complexity makes controlling a robotic hand particularly challenging. In the field of robotics, achieving the fine motor skills needed to grasp and manipulate objects with precision, speed, and force represents the pinnacle of technology.
Companies like Google DeepMind are pushing the limits of artificial intelligence (AI), exploring what machines can learn to both expand practical possibilities and guide future research. In their pursuit of advancing machine learning for robotic hands, Google DeepMind came across a video of one of their models learning to quickly solve a Rubik’s Cube—a breakthrough that could unlock new potentials in robotic manipulation.

Figure 1. Robotic Hand Design
A Robotic Hand Designed for Real-World Applications
The Shadow Hand, developed by Shadow Robot in collaboration with OpenAI, caught the attention of the Google DeepMind team [1]. However, this new project called for even more advanced capabilities. Figure 1 shows Robotic Hand Design.
Rich Walker, Director of Shadow Robot, explains, “Google DeepMind wanted a robotic hand that could learn and perform real-world tasks. It needed to be the most dexterous and sensitive hand ever created, but unlike other robots they had tested, it had to withstand the impacts of challenging, practical applications.”
To meet these requirements, Google DeepMind requested a high number of sensors for enhanced data collection. As Rich Walker describes it, Shadow Robot designed the hand with “far more sensors than would be considered sensible in any other context.”
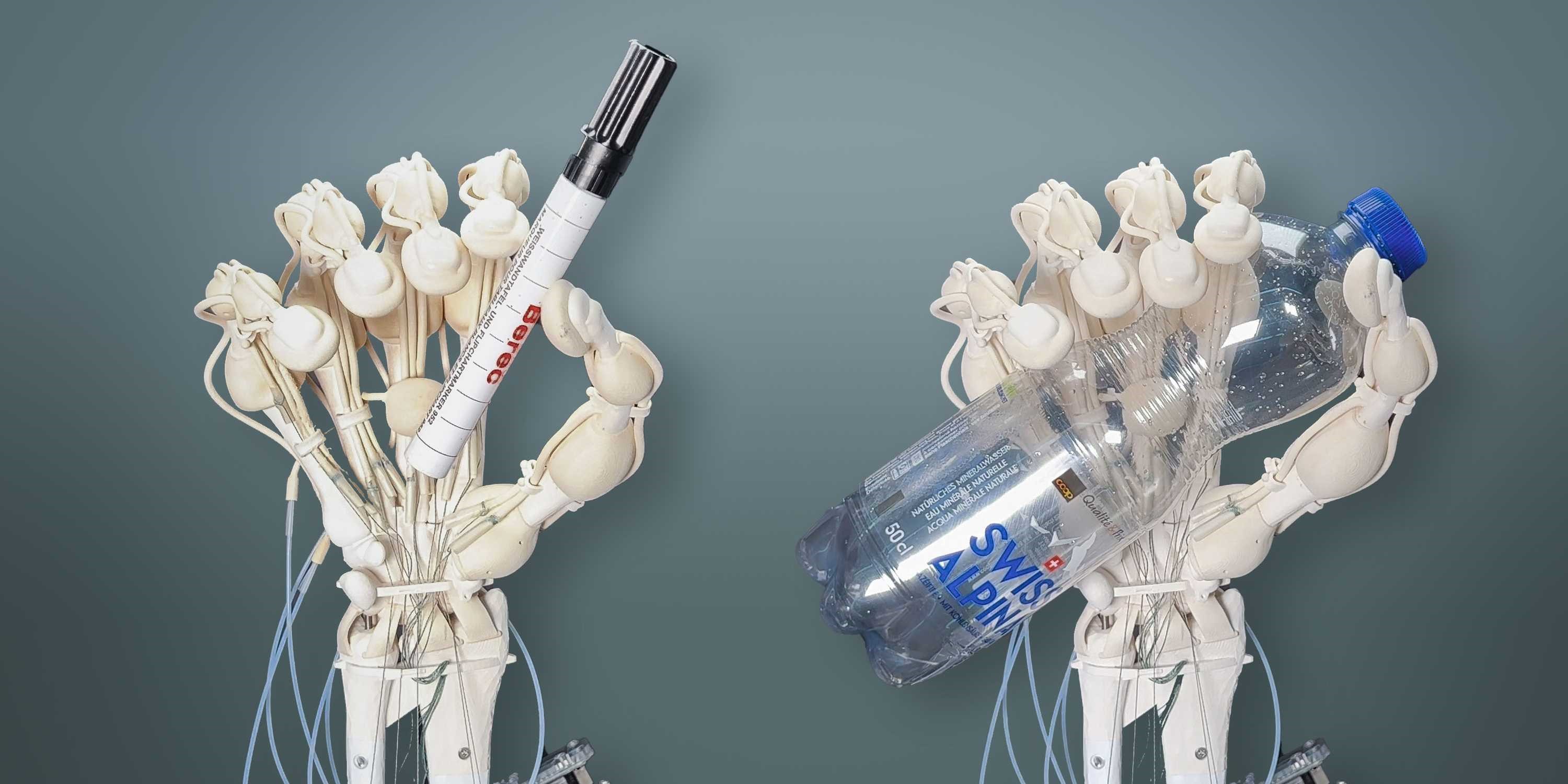
The Objective of DEX-EE: Achieving Dexterity, Sensitivity, and Durability
The goal was to develop a robotic hand that excelled in dexterity, sensitivity, and robustness for real-world tasks, without the need to mimic the exact form of a human hand. To achieve this, the design features three durable fingers and a hand approximately 50% larger than a human hand.
The result is DEX-EE, a robotic hand equipped with high-speed sensor networks that provide comprehensive data, including position, force, and inertial measurements. In addition, each finger is outfitted with hundreds of tactile sensing channels, enhancing pressure sensitivity to an extraordinary degree, nearly matching that of a human hand.
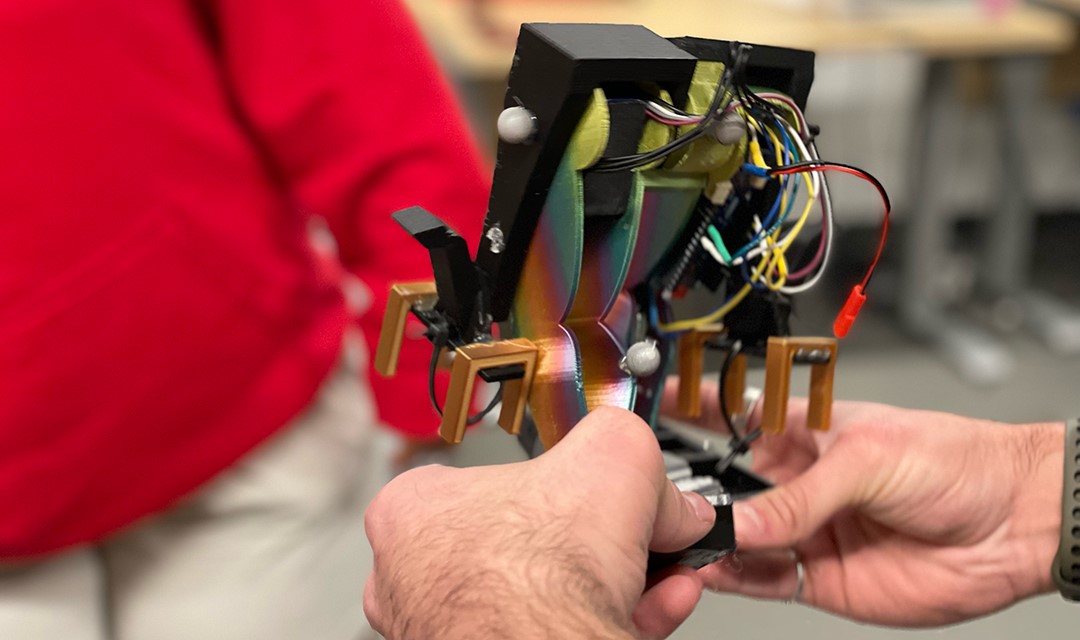
Driving System Innovation for Robotic Hand Technology
To achieve precise control over force application and actuate the joints of the hand, Shadow Robot relied on a highly advanced drive system. One of the standout innovations of DEX-EE is its unique tendon-driven design, which uses multiple motors per joint rather than the conventional one-motor-per-joint approach.
With five motors controlling four joints on each of the three fingers, this design eliminates backlash—the "play" that can occur when movement direction is reversed—ensuring optimized, controlled motion. By meticulously managing each motor, every joint can mimic zero joint torque, giving DEX-EE exceptional sensitivity and the ability to manipulate delicate objects with precision and care.
Collaborative Innovation Through Partnership
To achieve the reliability and performance DEX-EE needed, Shadow Robot turned to its original drive system partner.
“maxon motors have a long manufacturing evolution behind them, and the pedigree they bring was crucial for the demands that would be placed on DEX-EE,” says Rich. “This was especially the case for the rigours of real-world use that Google DeepMind was looking for.”
DEX-EE integrates a total of 15 maxon DCX16 DC motors that achieve the high torque density necessary for the robotic hand to apply sufficient force across the tendons. This enables the hand to move with the required dynamism and strength for actions such as grasping and holding. At the same time, the motors had to be sufficiently compact to fit within the confines of each finger base.
The motor’s ironless winding also eliminates cogging, the relative jerkiness generated by traditional iron core designs. This helps achieve smooth, controlled motion, essential for DEX-EE to reach exacting levels of precision for the most delicate tasks. High tolerances in design and manufacture, along with premium materials, ensure quiet operation and achieve high durability.
Evaluating and Validating DEX-EE
DEX-EE’s performance and reliability were thoroughly tested over 1,000 hours, including policy learning simulations where AI learns task execution through repeated random movements that also put mechanical stress on the hand. The Shadow Robot team subjected DEX-EE to rigorous impact and shock testing using pistons and various tools to ensure its durability.
Google DeepMind has already published research showcasing DEX-EE’s capabilities, including a video demonstrating the robotic hand’s ability to manipulate and plug in a connector within a confined workspace, designed to create impacts when the hand moves. This task underscores DEX-EE’s robustness, showing how it can endure repeated collisions while still completing its function.
“Google DeepMind is using DEX-EE as a research platform to study learning in real-world environments, and the hand's combination of robustness and sensitivity allows it to interact with objects in ways that would damage traditional robots,” says Rich.
The Future of Robotic Hand Innovation
DEX-EE is now available as a research platform for a broader range of organizations. While Shadow Robot’s creation was designed to advance our understanding of machine learning in real-world scenarios, Rich envisions that sophisticated robotic hand technology will soon be integrated into everyday life [2]. As this technology becomes more widespread, he predicts that the term "robot" will gradually lose its relevance, with devices like these becoming an ordinary part of our daily routines.
"In the future, the focus of robotics development will shift to creating tools we use regularly. At that point, we might stop calling them ‘robots,’ and our expectations of what a robot should be will evolve. But in truth, these devices could offer far more value to humanity than we initially anticipated."
References:
- https://www.eurekamagazine.co.uk/content/technology/exploring-the-cutting-edge-technology-behind-robotic-hand-design-and-its-role-in-modern-robotics
- https://technology.nasa.gov/patent/MSC-TOPS-102
Cite this article:
Janani R (2025), Exploring The Advanced Technology Behind Robotic Hand Design and Its Role in Modern Robotics, AnaTechMaz, pp. 121