Quantum Encryption Breakthrough Harnesses Light and Color for An Unhackable Internet
The Growing Risk to Data Security
The future of internet security is at risk as quantum computers may one day crack even the most advanced encryption, exposing sensitive data. To combat this, researchers worldwide are developing quantum networks—leveraging quantum mechanics to enable ultra-secure communication.
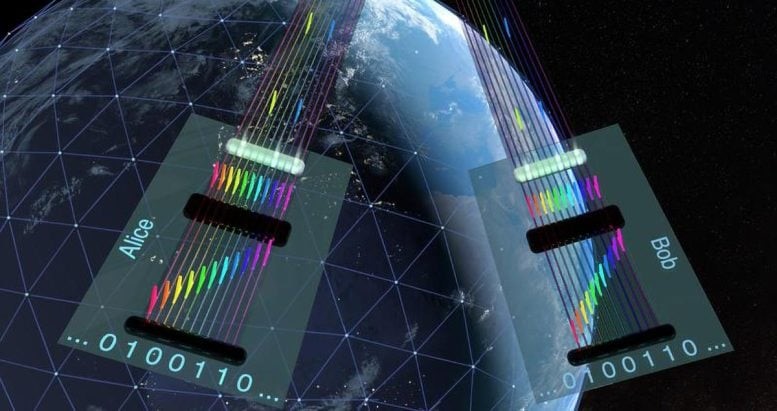

Figure 1. Quantum Encryption Breakthrough Uses Light and Color for Ultra-Secure Internet.
Once fully developed and globally connected, these networks will create a quantum internet, ensuring encryption that is immune to interception or decryption. However, widespread adoption faces challenges, including high costs, substantial energy demands, and complex technological requirements. Figure 1 shows Quantum Encryption Breakthrough Uses Light and Color for Ultra-Secure Internet.
An Innovative Approach to Quantum Encryption
Researchers at Leibniz University Hannover’s Institute of Photonics are pioneering a novel solution to this challenge. They have developed an advanced entanglement-based quantum key distribution method using frequency-bin coding—a technique that encodes quantum information into distinct light frequencies (colors). This approach not only enhances security but also optimizes resource efficiency.
“Our method could enable the future scaling of quantum networks, allowing more users to connect over greater distances while requiring fewer resources,” explains Prof. Dr. Michael Kues, head of the Institute of Photonics and a board member of the PhoenixD Cluster of Excellence at Leibniz Universität Hannover. Optical technologies and photonic quantum bits remain a key focus of the university’s research efforts.
Advantages of Frequency-Based Quantum Key Distribution
Using frequency as a degree of freedom in entanglement-based quantum key distribution offers two key advantages. “Firstly, compared to polarization, frequency is highly resistant to noise caused by environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations and mechanical vibrations in optical fibers, which can disrupt key transmission,” explains Anahita Khodadad Kashi, a doctoral student at the Institute of Photonics. “Secondly, by leveraging frequency, we were able to simplify the process, reducing both complexity and costs,” she adds.
Cutting Costs and Enhancing Security
The researchers achieved a major breakthrough by measuring quantum states using just one detector instead of four highly sensitive photon detectors. They accomplished this using frequency-to-time transfer—a method that maps frequency components into a photon’s arrival time at the detector—eliminating the need for multiple expensive detectors. According to Prof. Dr. Michael Kues, this innovation reduced the cost of standard telecommunications components from around €100,000 to just a quarter of that amount. “Additionally, this approach decreases vulnerability to detector attacks, making the system more secure,” Khodadad Kashi notes.
Scaling Up Quantum Networks
The method also enables multiple channels to operate simultaneously through adaptive frequency division multiplexing, which increases the key distribution rate without requiring additional technical hardware. “With this approach, the quantum network dynamically adjusts its performance based on current demand,” says Khodadad Kashi. “In the future, our method will facilitate dynamic, resource-efficient quantum key distribution between multiple users, paving the way for scalable quantum networks,” Kues adds. These advancements could significantly enhance the security of critical IT infrastructure, particularly in sectors such as banking and healthcare.
The Future of Quantum Communication
Looking ahead, Kues emphasizes the importance of further research into the interaction of nanophotonics and quantum optics to develop new methods and components for multidimensional quantum information coding. “As quantum networks evolve, we will witness a new era of connectivity, capacity, range, and security in quantum communication,” he predicts.
Source: SciTECHDaily
Cite this article:
Priyadharshini S (2025),Quantum Encryption Breakthrough Harnesses Light and Color for An Unhackable Internet, AnaTechMaz, pp. 205