Scientists Discover a New Method to Boost Wireless Speeds Using Graphene
A research team from the University of Ottawa has made significant strides in enhancing the frequency conversion of terahertz (THz) waves using graphene-based structures. Their findings could pave the way for faster and more efficient wireless communication and signal processing technologies.
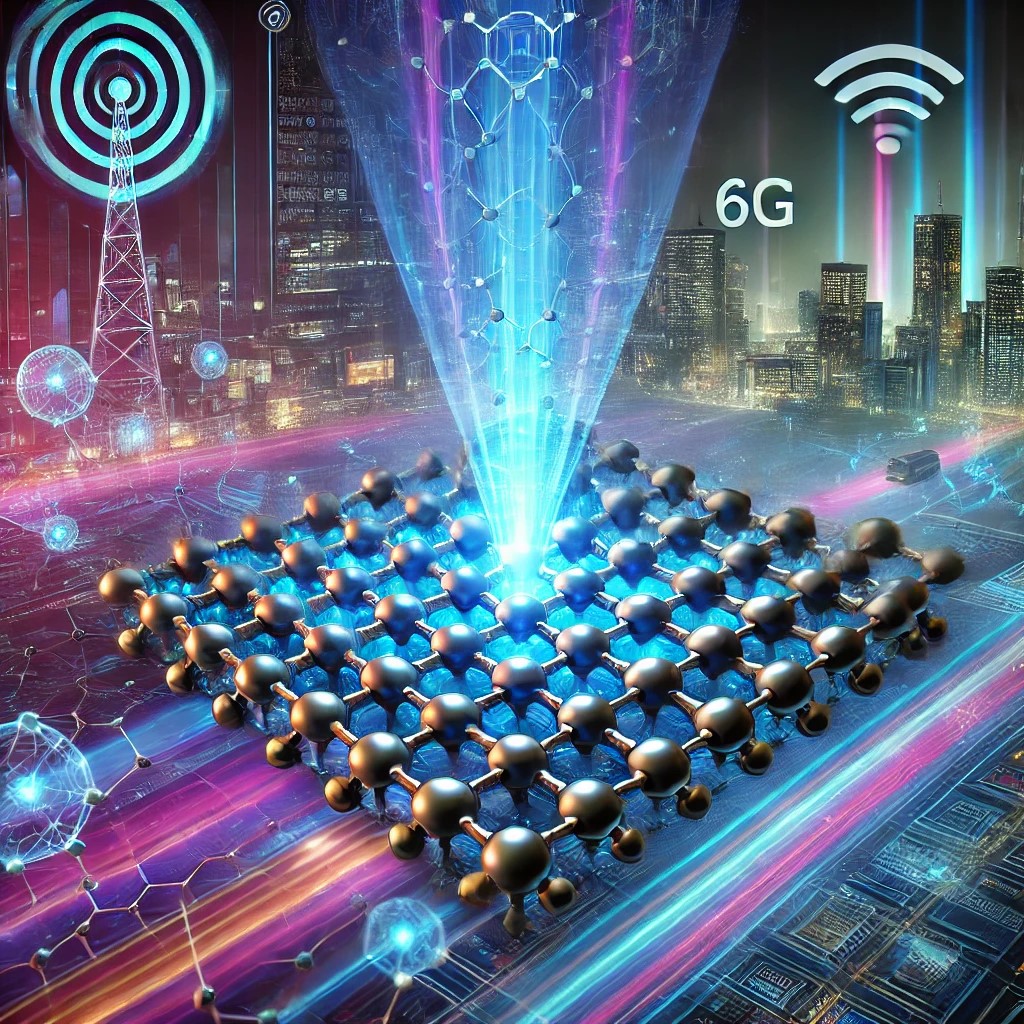

Figure 1. Revolutionizing Wireless Speeds with Graphene Technology.
THz waves, located in the far-infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum, have diverse applications. They can penetrate opaque materials, making them valuable for non-invasive imaging in security and quality control. Moreover, they hold immense potential for next-generation wireless communication. Advances in THz nonlinear optics—techniques that modify electromagnetic wave frequencies—are essential for the development of high-speed wireless networks, including future 6G systems. Figure 1 shows Revolutionizing Wireless Speeds with Graphene Technology.
With THz technology evolving rapidly, it is set to revolutionize fields such as healthcare, communication, security, and quality control. Jean-Michel Ménard, Associate Professor of Physics at the University of Ottawa, and his team have engineered devices capable of converting electromagnetic signals into higher oscillation frequencies. This innovation bridges the gap between conventional GHz electronics and emerging THz photonics, accelerating progress toward next-generation communication systems.
Unlocking Graphene’s Potential for THz Technology
This groundbreaking research highlights innovative methods to harness graphene’s exceptional optical properties. As a single-layer carbon-based quantum material, graphene offers seamless integration into devices, opening new frontiers in signal processing and communication.
Past studies on THz light and graphene primarily focused on fundamental light-matter interactions, often limited to single-parameter experiments that produced weak nonlinear effects. To address this challenge, Professor Jean-Michel Ménard and his team combined multiple advanced techniques to amplify nonlinear effects, fully utilizing graphene’s unique characteristics.
Expanding the Future of THz Technology
“Our experimental platform and novel device architectures provide opportunities to explore a wide range of materials beyond graphene, potentially uncovering new nonlinear optical mechanisms,” says Ali Maleki, a PhD student in the Ultrafast THz group at the University of Ottawa, who collected and analyzed the study’s results.
“Such advancements are essential for refining THz frequency conversion techniques and integrating them into practical applications, particularly in the development of efficient, chip-integrated nonlinear THz signal converters that will power next-generation communication systems.”
The Promise of THz Technology in Wireless Communication
Terahertz (THz) waves, positioned between microwave and infrared frequencies, offer unprecedented potential for ultra-fast wireless communication. As global demand for high-speed networks increases, THz waves are emerging as a crucial component of future 6G and beyond. However, efficient frequency conversion remains a major challenge in harnessing THz technology.
How Graphene Revolutionizes THz Signal Processing
Graphene, a single layer of carbon atoms with exceptional conductivity and optical properties, has shown immense promise in overcoming limitations in THz signal processing. Researchers from the University of Ottawa have developed a new approach that enhances frequency conversion, unlocking graphene’s potential for high-speed data transmission and advanced signal processing applications.
Breaking Barriers with Nonlinear THz Optics
Traditional approaches to THz and graphene interactions often resulted in weak nonlinear effects, limiting practical applications. By combining multiple innovative techniques, Professor Jean-Michel Ménard and his team have significantly amplified these effects, creating more efficient THz frequency conversion mechanisms. This breakthrough bridges the gap between conventional GHz electronics and emerging THz photonics.
From Lab to Real-World Applications
The advancements in THz frequency conversion have far-reaching implications across multiple industries. From faster wireless communication and high-resolution security imaging to non-invasive medical diagnostics and precision quality control, graphene-enabled THz technology is poised to transform the way we interact with digital and physical environments.
The Future of 6G and Beyond
With ongoing research into graphene and other 2D materials, scientists are unlocking new nonlinear optical mechanisms that could further optimize THz-based systems. Efficient, chip-integrated THz signal converters could soon become a reality, paving the way for next-generation wireless networks with ultra-fast speeds, lower latency, and greater energy efficiency.
This revolutionary approach to THz technology signals a major leap toward the future of high-speed communication and beyond.
Source: SciTECHDaily
Cite this article:
Priyadharshini S (2025),Scientists Discover a New Method to Boost Wireless Speeds Using Graphene, AnaTechMaz, pp. 204