The Quantum Blueprint: Unraveling How Photosynthesis Defies Classical Physics
The Quantum Blueprint: Unraveling How Photosynthesis Defies Classical Physics
Engineers have long sought efficient methods to convert solar energy into storable chemical energy. Remarkably, nature mastered this process billions of years ago. A recent study reveals that quantum mechanics, typically linked to physics, also plays a pivotal role in biological systems.
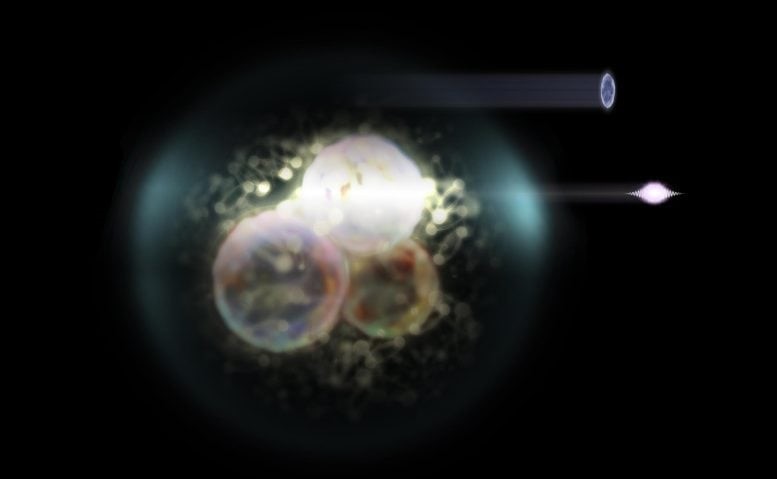
Figure 1. The Quantum Key: Revealing How Photosynthesis Breaks Classical Boundaries.
Photosynthetic organisms, such as green plants, rely on quantum mechanical processes to capture and utilize solar energy. As Professor Jürgen Hauer explains, “When light is absorbed by a leaf, the electronic excitation energy is distributed across multiple states within each excited chlorophyll molecule. This phenomenon, known as superposition of excited states, represents the first stage of an almost loss-free energy transfer within and between molecules, enabling efficient solar energy transport. Quantum mechanics is, therefore, essential for understanding the initial steps of energy transfer and charge separation.” Figure 1 shows The Quantum Key: Revealing How Photosynthesis Breaks Classical Boundaries.
This process, which cannot be fully explained by classical physics alone, occurs continuously in green plants and other photosynthetic organisms, including certain bacteria. However, the precise mechanisms remain partially unexplored.
Implications for Artificial Photosynthesis
Hauer and lead author Erika Keil consider their study a critical step toward unraveling how chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for the green color in leaves, functions. Leveraging these insights could significantly enhance the design of artificial photosynthesis systems, enabling unprecedented efficiency in solar energy conversion for electricity generation or photochemical applications.
In their research, the team focused on two specific spectral regions where chlorophyll absorbs light: the low-energy Q region (yellow to red spectrum) and the high-energy B region (blue to green spectrum). The Q region comprises two distinct electronic states that are quantum mechanically coupled, allowing for near-lossless energy transfer within the molecule. The system then dissipates excess energy through a process akin to “cooling,” releasing it as heat. The study demonstrates that quantum mechanical effects play a crucial role in key biological processes, shedding new light on the sophisticated mechanisms behind photosynthesis.
The Solar Puzzle – Why Classical Physics Falls Short
Overview:Introduce the concept of photosynthesis as one of nature’s most efficient energy conversion processes. Discuss how classical physics explains the basics of light absorption but struggles to account for the near-perfect efficiency of energy transfer in photosynthetic organisms. This sets the stage for introducing quantum mechanics as the missing piece.Key Points:
- Basics of photosynthesis and energy conversion.
- Limitations of classical physics in explaining energy transfer efficiency.
- Introduction to quantum mechanics in biological systems.
Quantum Mechanics in Nature – The Hidden Role in Photosynthesis
Overview:Dive into how quantum mechanics operates in photosynthesis. Explain concepts like quantum superposition and coherence, and how they allow energy to be distributed efficiently across chlorophyll molecules after light absorption.Key Points:
- What happens when light hits a leaf?
- Superposition of excited states in chlorophyll molecules.
- How quantum coherence enables loss-free energy transport.
- Insights from Professor Jürgen Hauer’s research.
The Chlorophyll Code – Unlocking the Secrets of Energy Transfer
Overview:Focus on the structure and function of chlorophyll, the pigment central to photosynthesis. Discuss how its molecular design supports quantum processes, especially in the Q region (yellow-red spectrum) and B region (blue-green spectrum) where light absorption is optimized.Key Points:
- The molecular structure of chlorophyll and its light-absorbing regions.
- Quantum coupling in the Q region for efficient energy transport.
- The process of “cooling” through energy release as heat.
Beyond Nature – The Quest for Artificial Photosynthesis
Overview:Bridge the gap between natural and artificial systems. Explore how understanding quantum effects in photosynthesis could revolutionize artificial photosynthesis technologies, leading to highly efficient solar energy conversion for electricity and fuel production.Key Points:
- The potential of artificial photosynthesis for renewable energy.
- Applying quantum principles to design advanced energy systems.
- Challenges and breakthroughs in mimicking nature’s efficiency.
The Future of Quantum Biology – Redefining Life’s Processes
Overview:Conclude the series by expanding on the broader implications of quantum mechanics in biology. Highlight other biological processes where quantum effects may play a role and discuss the future of quantum biology as an emerging field.Key Points:
- Quantum mechanics beyond photosynthesis: examples in navigation, smell, and enzymes.
- How this research could transform energy, medicine, and technology.
- The evolving field of quantum biology and what lies ahead.
Source: SciTECHDaily
Cite this article:
Priyadharshini S (2025), The Quantum Blueprint: Unraveling How Photosynthesis Defies Classical Physics, AnaTechMaz, pp. 199