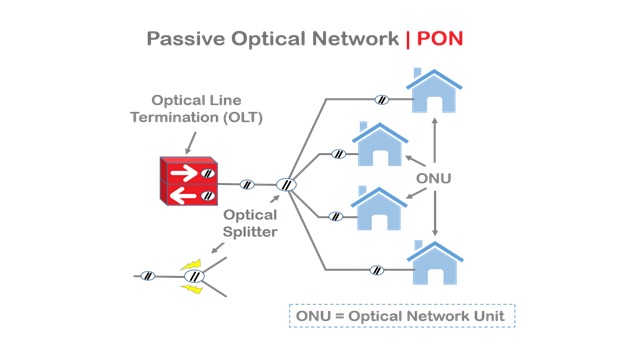
The MANET Technology
MANET stands for Mobile Adhoc Network also called a wireless Adhoc network or Adhoc wireless network that usually has a routable networking environment on top of a Link Layer ad hoc network.. They consist of a set of mobile nodes connected wirelessly in a self-configured, self-healing network without having a fixed infrastructure. MANET nodes are free to move randomly as the network topology changes frequently. Each node behaves as a router as they forward traffic to other specified nodes in the network. [1]
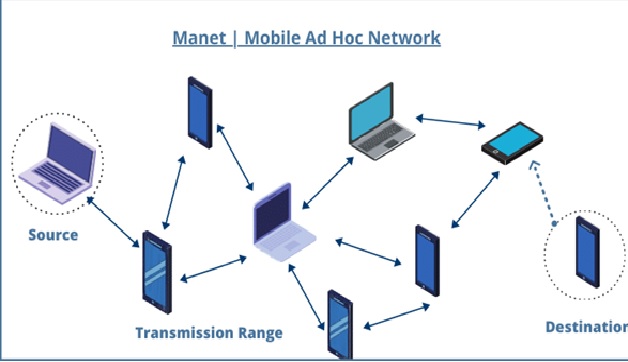
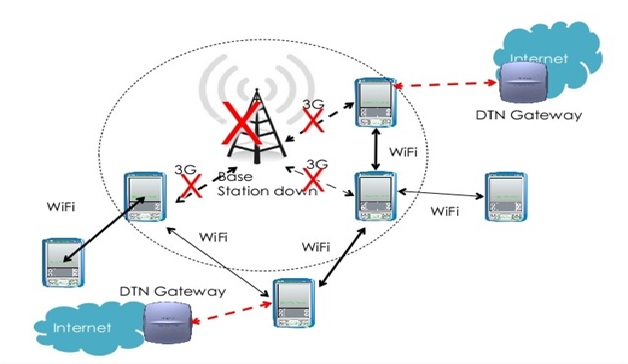
Figure 1. The MANET Technology
Figure 1 shows • A MANET consists of a number of mobile devices that come together to form a network as needed, without any support from any existing internet infrastructure or any other kind of fixed stations. A MANET can be defined as an autonomous system of nodes or MSs(also serving as routers) connected by wireless links, the union of which forms a communication network modeled in the form of an arbitrary communication graph. [3]
Major Applications of MANET
- Military - In the Army, Navy, Marines, Air Force, and Coast Guard, MANET makes possible independent information networks between soldiers, vehicles, ships, planes, and headquarters. MANET’s basic techniques have their roots in the military.
- Commercial - Commercial use of MANET includes emergency rescue and disaster relief. It allows rescuers to communicate in remote areas, maintain safety, and complete faster, more efficient rescues.
- Low Level Use - MANET is seen in law enforcement as well as civilian use like taxicabs, sports stadiums, boating and small aircraft.
- Data Networks - Commercially, MANET can extend the reach of installed infrastructure with regard to computer networks, increasing ease of use and availability.
- Sensor Networks - MANET makes possible a network consisting of a large number of sensors in an area that can detect vibration, temperature, pressure, toxins, pollution, and more. Since the capability of each sensor is limited and failure a common occurrence, such a redundant network can increase overall accuracy and reliability of data. Such networks could be the future of homeland security. [2]
Some characteristics of adhoc network are as follows:
- Dynamic topologies: nodes are free to move arbitrarily; thus the network topology may be changed randomly and unpredictably and primarily consists of bidirectional links. In some cases where the transmission power of two nodes is different, a unidirectional link may exist.
- Bandwidth-constrained and variable capacity links: wireless links continue to have significantly lower capacity than infrastructure networks.
- Energy-constrained operation: some or all of the MSs in a MANET may rely on batteries or other exhaustible means for their energy. For these nodes or devices, the most important system design optimization criteria may be energy conservation.
- Limited physical security: MANETs are generally more prone to physical security threats than wire line networks. The increased possibility of eavesdropping, spoofing, and denial of services (DoS) attacks should be considered carefully. To reduce security threats, many existing link security techniques are often applied within wireless networks.[3]
References:
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/introduction-of-mobile-ad-hoc-network-manet/
- https://www.everythingrf.com/community/what-is-manet-technology
- https://www.javatpoint.com/mobile-adhoc-network
Cite this article:
Thanusri swetha J (2021), The MANET Technology, AnaTechMaz, pp. 54