SONET (Synchronous Optical Networking)
SONET (Synchronous Optical Networking) is a protocol designed for digital communication that helps in transmitting large volumes of data through long distances over an optical fibre medium. Using SONET, multiple streams of data are transmitted simultaneously over fibre optics using laser beams or LEDs (light emitting diodes). Optical fibre or fibre optics is a technology and a medium that transmits data as light signals from LED or laser. SONET was designed by ANSI (American National Standards Institute). SONET is also known as SDH (Synchronous Digital Hierarchy) in certain countries. [1]
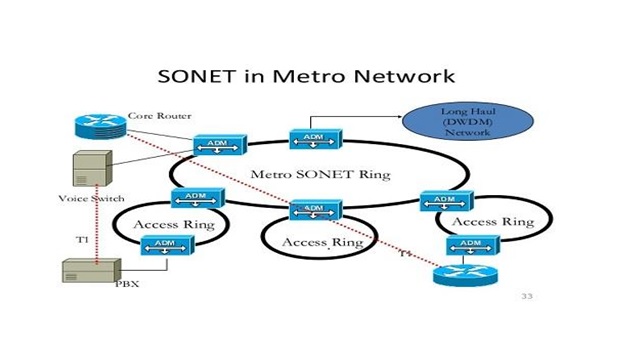
Figure 1. SONET (Synchronous Optical Networking)
Figure 1 shows SONET is built from multiplexed DS0, DS1, or DS3 digital signal channels using optical time-division multiplexing (TDM) to form a single Synchronous Transport Signal (STS) link for communication. The basic SONET transmission rate is 810 bytes transmitted every 125 microseconds, and frames are transmitted whether or not a payload (data) is present. A standard STS-1 SONET data path thus consists of 810 DS0 channels, of which 783 are used for data transmission and 27 are used for framing, error correction, format identification, and other forms of overhead. [2]
SONET standards:
SONET provides standards for a number of line rates up to the maximum line rate of 10 gigabits per second (Gbps). Actual line rates approaching in the 30 gigabits per second range are possible.
Base units of SONET are defined as Optical Carrier level-1, or OC-1. OC-1 supports up to 51.84 megabytes per second (Mbps). The next level up, OC-3, supports up to triple the bandwidth. Each level increases by multiples of four. OC-3, OC-12, OC-24, OC-48 can be used as examples. The set of multiples of the base rate known as "Optical Carrier levels (OCx)." SONET standards are specified in ANSI T1.105 and T1.117.
Benefits:
SONET is seen to have multiple characteristics that are considered advantageous, such as:
- High data rates.
- Large transmit distances.
- Support of multiple data types (data, voice and video).
- Can carry high-level protocols such as IP.
- Defines interoperability standards for organizations.
The one main disadvantage of utilizing SONET, however, is that it is high in cost. [3]
References:
- https://study.com/academy/lesson/synchronous-optical-networking-definition-application.html
- https://networkencyclopedia.com/synchronous-optical-network-sonet/
- https://www.techtarget.com/searchnetworking/definition/Synchronous-Optical-Network
Cite this article:
Thanusri swetha J (2021), SONET (Synchronous Optical Networking), AnaTechMaz, pp. 51