4D Printing
4D printing is an emerging technology that builds on the principles of 3D printing but adds a new dimension of "time" to the process. 4D printing refers to the ability of a printed object to change its shape or function over time in response to external stimuli, such as heat, moisture, or light.
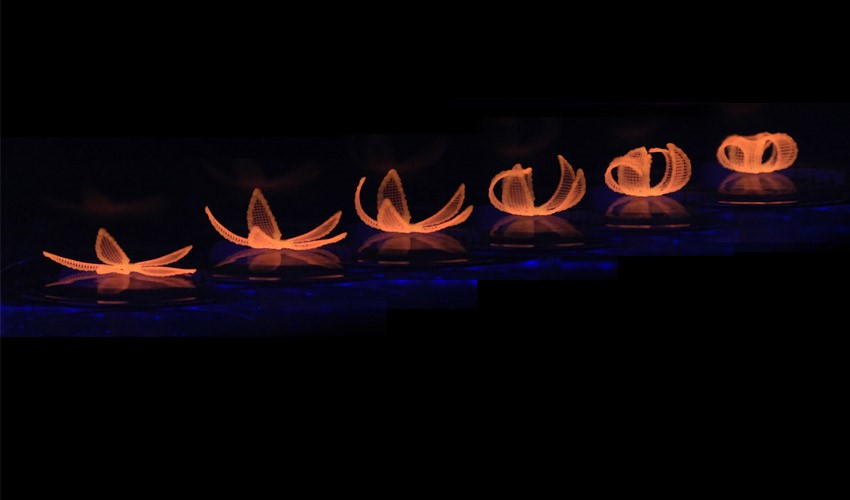

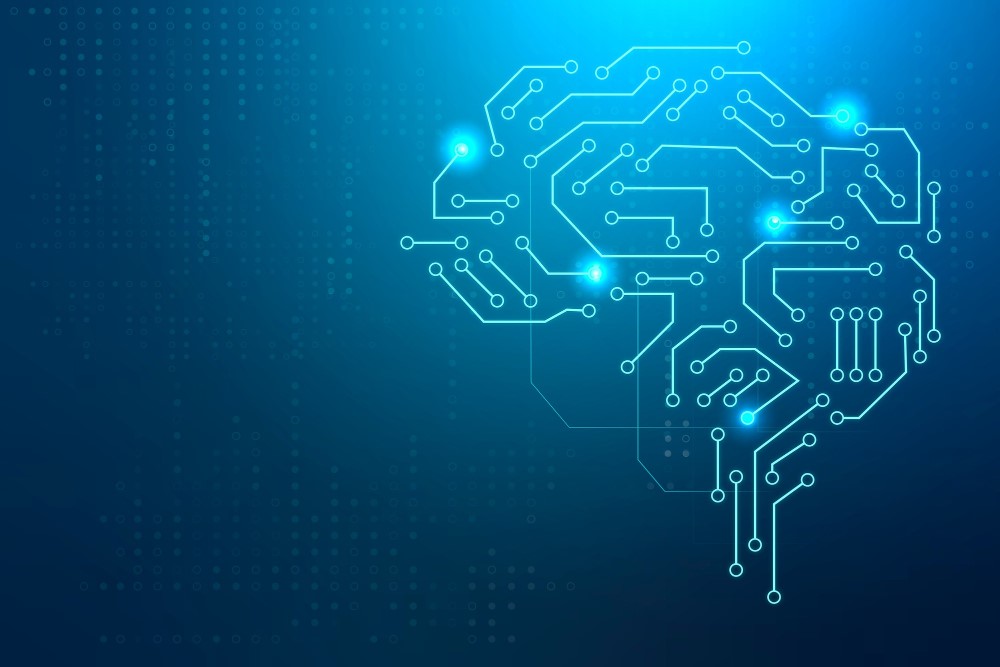
Figure 1. 4D Printing [1]
Figure 1 shows 4D Printing. The fourth dimension in 4D printing refers to time, which is used to describe the process of the printed object's transformation. 4D printed objects are typically printed using materials that have properties that can be manipulated through an external stimulus, such as shape-memory alloys, hydrogels, and smart polymers.
The transformation of a 4D printed object can be triggered by various external factors such as temperature changes, exposure to water or light, or even magnetic fields. This allows 4D printed objects to have unique applications in various fields such as medicine, aerospace, and architecture.
Material Selection
Materials for 4D printing are classified based on their environment or the external stimuli they react with. Current classes of smart materials are currently classified into the below categories:
Thermo Responsive Materials
These materials work on the mechanism of the Shape Memory Effect (SME). They are classified into Shape Memory Alloys (SMA), Shape Memory Polymers (SMP), Shape Memory Hybrids (SMH), Shape Memory Ceramics (SMC), and Shape Memory Gels (SMG). Most of the researchers prefer SMPs as it becomes easy to print on these materials. They form and deform when heat or thermal energy is applied as a stimulus. [2]
Moisture Responsive Materials
Materials that react when in contact with water or moisture are classified under this category. Such materials are widely preferred by researchers, as water is available in abundance, and it can be used in a wide range of applications. The hydrogel is one of the smart materials that fall under this category as it reacts vigorously with water. For instance, hydrogels can increase its size by up to 200% of its original volume, when it comes in contact with water. [2]
Photo/Electro/Magneto Responsive Materials
These materials react with light, current, and magnetic fields. For instance, when photo responsive chromophores are infused with polymer gels at specific locations, they swell up absorbing light when exposed to natural light. Similarly, when current is applied to an object containing ethanol, it evaporates, thereby increasing its volume and expanding the overall matrix. Magnetic nanoparticles are embedded into the printed object to gain magnetic control of the object. [2]
Some of the potential applications of 4D printing include self-assembling structures, medical implants that can adapt to the body's changing needs, and self-repairing materials.
However, the technology is still in its early stages, and much research is being done to explore its full potential.
References:
- https://www.3dnatives.com/en/4d-printing-disrupting-current-manufacturing-techniques-230920194/
- https://www.futurebridge.com/industry/perspectives-mobility/4d-printing-the-technology-of-the-future/
Cite this article:
Hana M (2023), 4D Printing, AnaTechMaz, pp.240