Smart Farming
Smart farming is an approach to agriculture that leverages technology and data analytics to optimize agricultural production and reduce waste. Smart farming systems typically involve the use of sensors, drones, GPS, and other technologies to collect data on various aspects of the farming process, such as soil moisture levels, crop health, and weather conditions. This data is then analyzed using machine learning algorithms to provide farmers with insights and recommendations on how to optimize their farming practices.

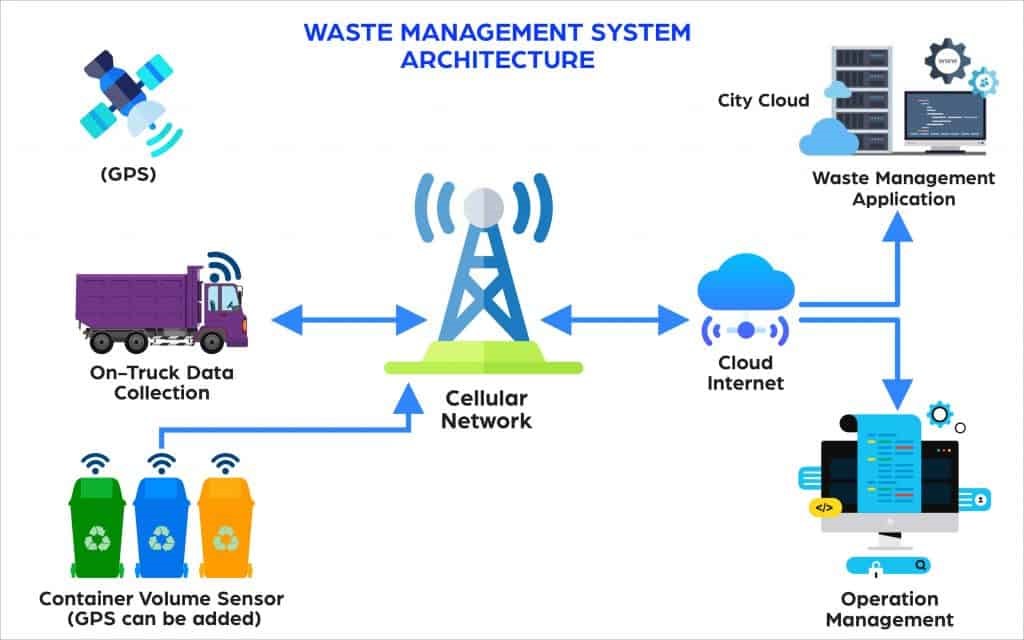
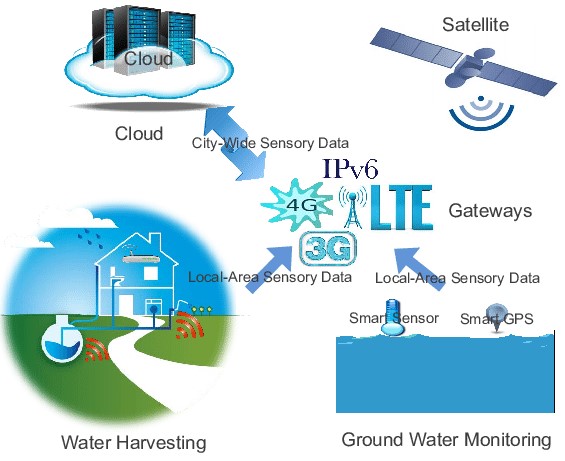
Figure 1. Smart Farming
The IoT-Based Smart Farming Cycle
Figure 1 shows smart farming. The core of IoT is the data you can draw from things and transmit over the internet. To optimize the farming process, IoT devices installed on a farm should collect and process data in a repetitive cycle that enables farmers to react quickly to emerging issues and changes in ambient conditions. Smart farming follows a cycle similar to this one:
- Observation: Sensors record observational data from the crops, livestock, soil, or atmosphere. [1]
- Diagnostics: The sensor values are fed to a cloud-hosted IoT platform with predefined decision rules and models—also called “business logic”—that ascertain the condition of the examined object and identify any deficiencies or needs. [1]
- Decisions: After issues are revealed, the user, and/or machine learning-driven components of the IoT platform determine whether location-specific treatment is necessary and, if so, which. [1]
- Action: After end-user evaluation and action, the cycle repeats from the beginning. [1]
Advantages of smart farming
The benefits of smart farming include increased efficiency, reduced waste, and improved sustainability. By leveraging data and technology, farmers can optimize their use of resources such as water, fertilizer, and pesticides, reducing waste and lowering costs. Smart farming also enables farmers to monitor crop health more effectively, allowing them to detect and address issues such as disease or pest infestations before they become widespread.
Examples of smart farming
Some examples of smart farming technologies include precision agriculture, which involves the use of sensors and GPS to optimize the use of resources and increase yields, and vertical farming, which involves growing crops in vertical stacks using artificial lighting and controlled environments to optimize growing conditions.
Smart farming has the potential to revolutionize agriculture and help address some of the pressing challenges facing the global food system, such as climate change and the need to feed a growing population. As the field continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more advanced smart farming technologies that leverage AI and other cutting-edge technologies to improve agricultural production and sustainability.
References:
- https://www.iotforall.com/smart-farming-future-of-agriculture
Cite this article:
Hana M (2023), Smart Farming, AnaTechMaz, pp.231