Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0, also known as the fourth industrial revolution, refers to the current trend of automation and data exchange in manufacturing technologies. It involves the integration of physical and digital systems to create a more efficient and flexible production process. Here are some of the key components of Industry 4.0:
Figure 1. Industry 4.0
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS): The integration of physical systems, such as machines and sensors, with digital systems, such as software and data analytics.
Internet of Things (IoT): The connection of devices and machines to the internet, allowing for data exchange and remote control.
Big Data Analytics: The use of advanced data analytics tools to analyze large amounts of data and generate insights that can be used to optimize production processes.
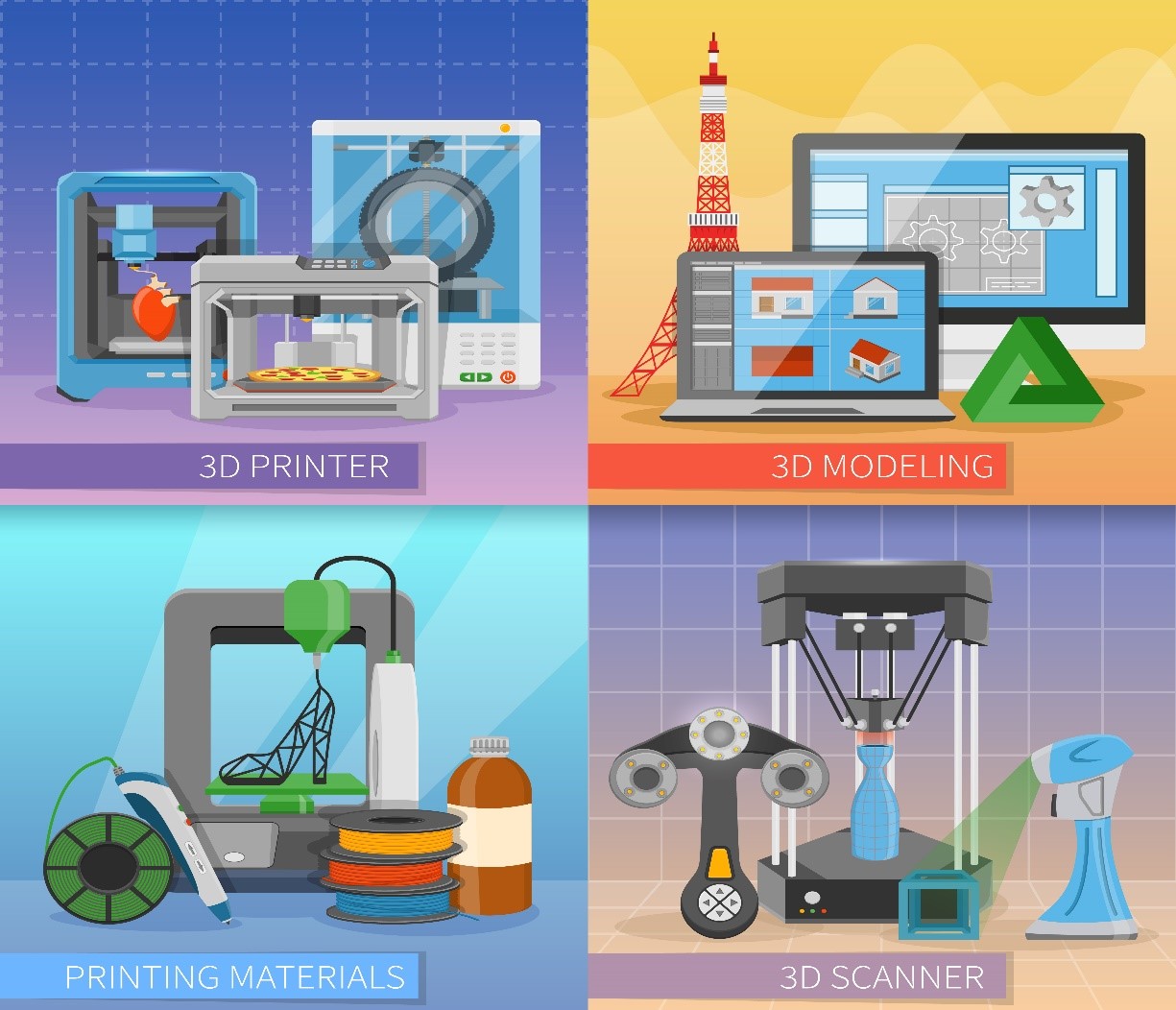
Additive Manufacturing: The use of 3D printing and other additive manufacturing techniques to create products and components more quickly and with greater precision.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): The use of machine learning and other AI technologies to automate tasks and make more informed decisions based on data.
Augmented Reality (AR): The use of AR technologies to provide workers with real-time information and guidance during the production process.
Cloud Computing: The use of remote servers to store and process data, allowing for more flexible and scalable production processes.
Autonomous Systems: The use of robots and other autonomous systems to perform tasks with minimal human intervention.
Digital Twin: The creation of a digital replica of a physical product or system, allowing for simulation and optimization before physical production.
Edge Computing: The use of local devices to process data in real-time, reducing latency and improving efficiency.
Four themes are presented that summarise an Industry 4.0:
Interconnection: The ability of machines, devices, sensors, and people to connect and communicate with each other via the Internet of things, or the internet of people (IoP). [1]
Information transparency: The transparency afforded by Industry 4.0 technology provides operators with comprehensive information to make decisions. Inter-connectivity allows operators to collect immense amounts of data and information from all points in the manufacturing process, identify key areas that can benefit from improvement to increase functionality. [1]
Technical assistance: The technological facility of systems to assist humans in decision-making and problem-solving, and the ability to help humans with difficult or unsafe tasks. [1]
Decentralized decisions: The ability of cyber physical systems to make decisions on their own and to perform their tasks as autonomously as possible. Only in the case of exceptions, interference, or conflicting goals, are tasks delegated to a higher level. [1]
Industry 4.0 represents a significant shift in the way manufacturing is done, with a focus on automation, data exchange, and advanced technologies. It has the potential to greatly increase efficiency and reduce costs in manufacturing, as well as create new opportunities for innovation and growth.
References:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fourth_Industrial_Revolution
Cite this article:
Hana M (2023), Industry 4.0, AnaTechMaz, pp.239