The Application of Nanotechnology in Nanomedicines
Nanomedicine is defined as the medical application of nanotechnology. Nanomedicine can include a wide range of applications, including biosensors, tissue engineering, diagnostic devices, and many others. In the Center for Nanomedicine at Johns Hopkins, we focus on harnessing nanotechnology to Figure 1 shown below more effectively diagnose, treat, and prevent various diseases.
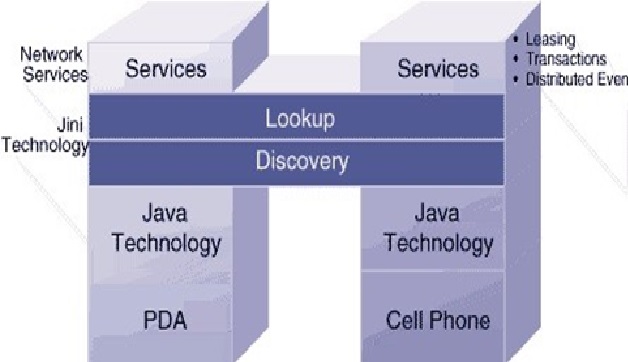
Figure 1. Nanotechnology in Nanomedicine
Our entire bodies are exposed [1] to the medicines that we take, which can lead to unpleasant side effects and minimize the amount of medicine that reaches the places where it is needed. Medications can be more efficiently delivered to the site of action using nanotechnology, resulting in improved outcomes with less medication.
Although nanomedicine research and development is actively pursued in numerous countries, the United States, the EU (particularly Germany), and Japan have made significant contributions from the field’s [2] outset. This is reflected both in the number of articles published and in that of patents filed, both of which have grown exponentially since 2004. By 2012, however, nanomedicine research in China grew with respect to publications in the field, and the country ranked second only to the United States in the number of research articles published.
Nanotechnology has many definitions but in general it is the use and application of materials with sizes in the nanometre range. Just as a millimetre is one-thousandth of a metre, a nanometre is one-millionth of a [3] millimetre. In more understandable terms, a human hair is approximately 80,000 nanometres in diameter and the growing science and industry of nanotechnology utilises materials below 1000 nanometres. Benefits of working at this very small scale have been seen for many years over such diverse areas as electronics and energy storage to sunscreens and food packaging.
Nanomedicine is simply the application of nanotechnologies in a healthcare setting and the majority of benefits that have already been seen involve the use of nanoparticles to improve the behaviour of drug substances.
Today, nanomedicines are used globally to improve the treatments and lives of patients suffering from a range of disorders including ovarian and breast cancer, kidney disease, fungal infections, elevated cholesterol, menopausal symptoms, multiple sclerosis, chronic pain, asthma and emphysema. The nanomedicines that are currently available are overcoming some of the difficulties experienced by normal medical approaches in delivering the benefit from the drug molecules used.
References:
- https://cnm-hopkins.org/what-is-nanomedicine/
- https://www.britannica.com/science/nanomedicine
- https://www.britishsocietynanomedicine.org/what-is-nanomedicine/
Cite this article:
Nandhinidwaraka. S (2021) The Application of Nanotechnology in Nanomedicines, AnaTechMaz, pp. 48