Ancient Bone Tools May Reshape Our Understanding of Human Evolution
Insights into Early Human Cognitive Abilities
The ability to transfer techniques between different materials suggests that the hominins who created these bone tools had a sophisticated understanding of toolmaking. Their adaptability in applying skills from stone to bone represents a significant intellectual advancement, indicating that early human ancestors may have had more developed cognitive abilities and brain function than previously believed.
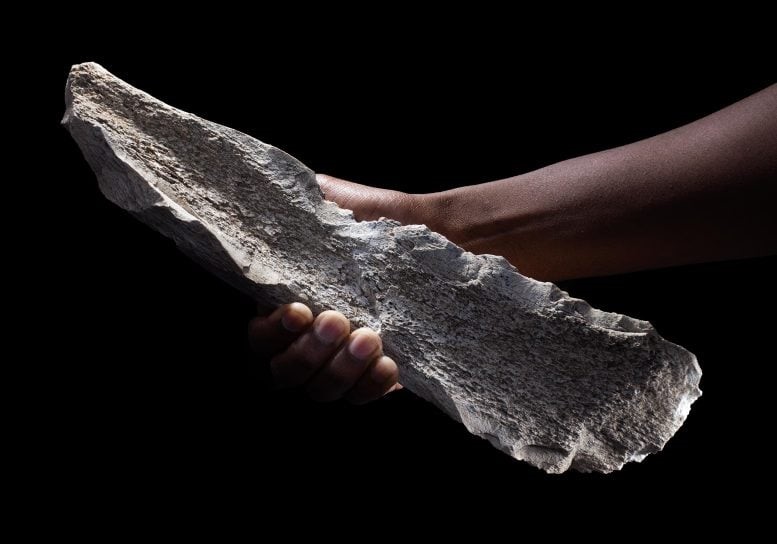

Figure 1. Ancient Bone Tools Rewrite the Story of Human Evolution.
This discovery suggests that early humans greatly expanded their technological capabilities. Previously limited to crafting stone tools, they began incorporating new raw materials into their toolkit. Figure 1 shows Ancient Bone Tools Rewrite the Story of Human Evolution.
At the same time, this technological expansion reflects advancements in the cognitive abilities and mental frameworks of these hominins, who successfully adapted their knowledge of stone toolmaking to shaping bone artifacts.
The Olduvai Gorge Discovery
The bone tools were found in Olduvai Gorge, Tanzania, a site famous for its rich archaeological history and key discoveries that have shed light on human origins.
The researchers uncovered 27 bone tools at the site, primarily crafted from the limb bones of large mammals such as elephants and hippos, chosen for their density and strength.
These tools date back to a pivotal period in prehistory when early hominin cultures were experiencing one of the first major technological transitions.
The Oldowan to Acheulean Transition
The earliest known stone tools belong to the tradition, which lasted from approximately 2.7 million to 1.5 million years ago. This method involved simply chipping one or a few flakes off a stone core using a hammerstone.
The bone tools in this study date to a period when early human ancestors were transitioning into the Acheulean age, which began around 1.7 million years ago. Acheulean technology is distinguished by more sophisticated toolmaking, particularly the production of carefully shaped handaxes through knapping, allowing for more standardized tools.
These newly discovered bone tools reveal that advanced Acheulean techniques were not limited to stone but were also applied to bone—a technological adaptation previously unseen in the fossil record until much later in the Acheulean period.
Significance of the Discovery
Before this find, bone tools had only been identified in rare, isolated instances, with no evidence suggesting that early humans systematically produced them.
Although the exact function of these tools remains unclear, their shape, size, and sharp edges suggest they were likely used for processing animal carcasses for food.
It is also uncertain which species of human ancestor crafted these tools. No hominin remains were found alongside the artifacts, but both Homo erectus and Paranthropus boisei were known to have lived in the region at the time.
Given the unexpected nature of this discovery, researchers hope it will inspire archaeologists to re-examine bone findings worldwide, as similar evidence may have been previously overlooked.
Source: SciTECHDaily
Cite this article:
Priyadharshini S 2025, “Ancient Bone Tools May Reshape Our Understanding of Human Evolution”,AnaTechmaz, pp. 301