The Technology of Surgical Device: Orthopaedic Implants
An orthopaedic implant is a device surgically placed into the body designed to restore function by replacing or reinforcing a damaged structure as shown in figure 1. [1] For the treatment of back pain, orthopaedic implants such as bone plates and bone screws are used in spinal fusion surgery and fixation of fractured bone segments, as well as implant components used for hip and joint replacement.
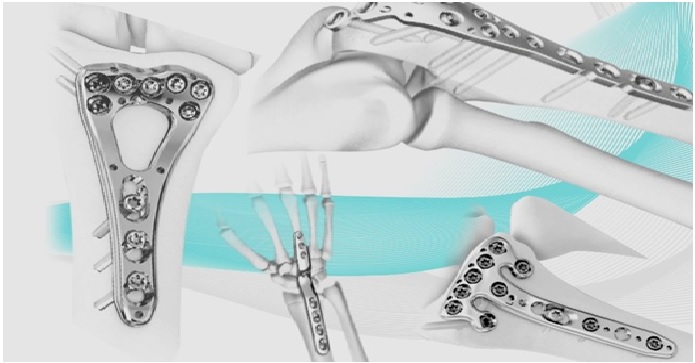
Figure 1. The orthopaedic implants [2]
The material used in orthopaedic implants must be biocompatible to avoid rejection by the body. Other risks associated with orthopaedic implants include implants coming loose or breaking in the bone causing painful inflammation and infection to surrounding tissue.
The orthopaedic surgeon inserts the implants into the body through various surgical methods, depending on the patient’s condition. Suppose a joint is worsened beyond a specific point. [3] In that case, the surgeon removes the injured joint and then replaces it with an orthopaedic implant while utilising various orthopaedic instruments specially designed for the surgery.
Most orthopaedic implants are made of titanium alloys and stainless steel, and a few of them may even be lined with plastic. The metallic structure provides the implant with the necessary strength, while the plastic lining serves as artificial cartilage. Typically, the implant is fitted into place, enabling the bone to grow into it for improved strength. In some cases, the surgeon may also cement the orthopaedic implant to enhance adhesion.
Properties of titanium alloys used in medicine.
In its pure form, [4] titanium features:
- low density,
- high strength
- high level of corrosion resistance
- It is also non-magnetic and non-toxic, two properties that are particularly advantageous for application in biomedical materials.
- Its coefficient of thermal expansion and modulus of elasticity both resemble that of human bone.
- Pure titanium is the most corrosive-resistant form of titanium on the medical market and is frequently used when ductility and malleability is key.
Alloys come into play when strength to weight ratio is vital to the success of the implant. Most interestingly, titanium connects very well to human tissue and bone.
The most common alloys used in medical and dental implants are Titanium 6AL4V / Titanium 6Al4V ELI – alpha-beta alloys containing approximately 90% titanium, 6% aluminum and 6% vanadium. They facilitate a high level of fracture resistance and work in harmony with the body to promote osseointegration.
References:
- https://www.spine-health.com/glossary/orthopedic-implants
- https://orthospinenews.com/2021/04/27/global-orthopedic-implants-market-size-to-grow-above-usd-73-5-billion-by-2026-according-to-facts-factors/
- https://www.merillife.com/blog/medtech/3-types-of-orthopedic-implants-you-need-to-know-before-undergoing-surgery
- https://matmatch.com/resources/blog/titanium-application-orthopedic-implants/
Cite this article:
Vinotha D (2022), The Technology of Surgical Device: Orthopaedic Implants, AnaTechMaz, pp.213