Curiosity Rover to Measure Organic Carbon in Martian Rocks
Scientists are using data from NASA’s Curiosity rover to measure the total organic carbon in Martian rocks for the first time. Organic carbon is a key component in life molecules. There is evidence that the red planet’s climate was similar to Earth billions of years ago, with a thicker atmosphere and liquid water that flowed into rivers and seas.
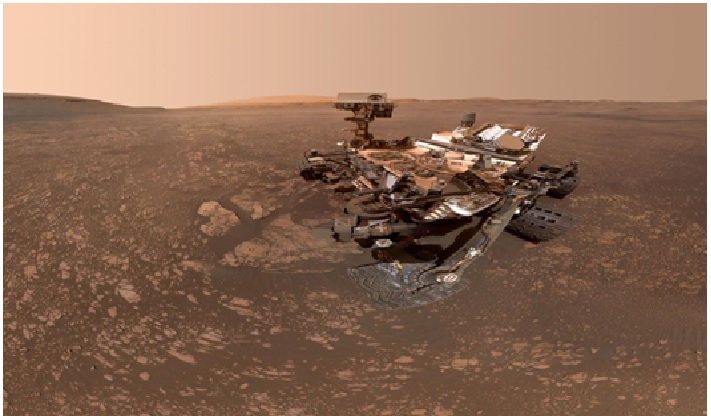

Figure 1: NASA’s rover to measure the total organic carbon in Martian rocks.
Figure 1 shows that Since liquid water is necessary for life as we know it now, scientists believe that Martian life, if it ever existed, could have been sustained by key ingredients such as organic carbon if present in sufficient amounts such as organic carbon, if present in sufficient amounts.
Organic carbon is carbon bound to a hydrogen atom. It is the basis of organic molecules, which are created and used by all known forms of life. [1]
NASA's Curiosity Mars rover is the largest and most capable rover ever sent to the Martian surface. The rover is investigating Mars' habitability, studying its climate and geology to help advance the field of astrobiology.
The rover drilled samples from 3.5-billion-year-old mudstone rocks in the "Yellowknife Bay" formation of Gale Crater, the site of an ancient lake on Mars. Mudstone at Gale Crater was formed as very fine sediment in water settled on the bottom of a lake and was buried. Organic carbon was part of this material and got incorporated into the mudstone, according to NASA. [2]
Stern said, “We found at least 200 to 273 parts per million of organic carbon. This is comparable to or even more than the amount found in rocks in very low-life places on Earth, such as parts of the Atacama Desert in South America, and more than has been detected in Mars meteorites."
Scientists are of the opinion that the sediment was formed via the physical and chemical weathering of volcanic rocks before it settled to the bottom of the lake.
In addition to organic carbon, researchers identified other signs suggesting Gale crater may have once supported life, including the presence of chemical energy sources and chemical compounds like nitrogen, Sulphur, oxygen etc. and the location would have offered a habitable environment for life if it ever existed there. [3]
References:
- https://indianexpress.com/article/technology/science/scientists-using-curiosity-rover-data-to-measure-key-life-ingredient-on-mars-7995920/lite/
- https://www.devdiscourse.com/article/science-environment/2090335-16-killed-in-lightning-strikes-thunderstorm-in-bihar
- https://www.indiatimes.com/technology/science-and-future/life-on-mars-rock-samples-collected-by-curiosity-rover-contain-ingredients-of-life-573590.html
Cite this article:
Sri Vasagi K (2022), Curiosity Rover to Measure Organic Carbon in Martian Rocks, AnaTechMaz, pp.186