The Future Technology of 3D Printed Food
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is the process of creating three-dimensional objects from digital files. [1] Objects are created one layer at a time, and 3D printers can create complex shapes relatively quickly (faster than many traditional manufacturing methods, in fact).
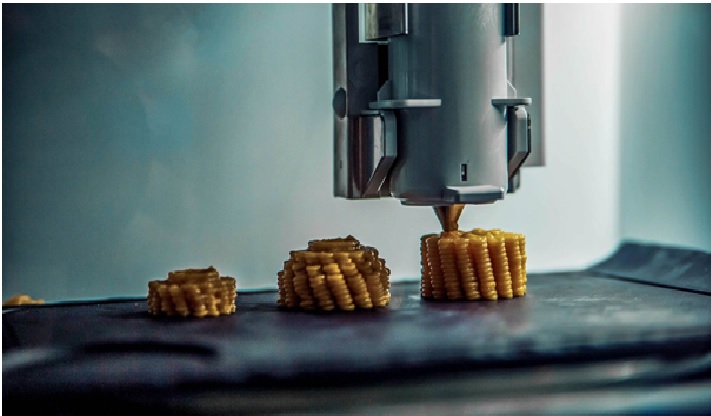

Figure 1: The 3D Food [2]
Most printers for 3D food use a similar technique to regular 3D printers as shown in figure 1. They deposit a food-safe 3D printer filament (like chocolate, tomato, or other flavors) onto a build plate based on a model you design yourself, or one that you download.
Food printers work in a similar way. They deposit the edible filaments into your desired shapes, one layer at a time, creating a three-dimensional food model as it prints.
For 3D printers to become common kitchen appliances, though, the technology needs to mature. [3] The hardware is pretty simple: it’s “literally a machine that can pick up a syringe of food and then shoot it out based on some kind of directed path,” Blutinger explains.
But there’s no standard software or hardware optimized for the specific challenges of printing food. “We’re using industry software designed for printing plastic and metal parts, and we have little hacks to make it work,” Blutinger says. The field also needs to amass standardized digital recipes that home cooks could download and use in their 3D printers, the way that makers can download designs for making plastic toys or tools. At the moment, a chef who wants to print an hors d’oeuvre out of hummus and couscous with a garlic-sage glaze, or a beet-and-walnut cream cheese drop, would have to painstakingly develop a recipe from scratch.
Today, food 3D printers are mostly used for gourmet dining, be it in molecular kitchens or fancy bakeries. This technology is still not scalable, [4] as it requires more time and development to mature. That doesn’t stop pioneers and innovators from using it, though.
But not only in fine dining can you find 3D printed food. Bakers have made headlines for printing edible wedding cake decorations, and for all you pizza lovers, 3D printed pizzas have been in the works for some time and will surely be a reality sooner rather than later. More recently, plant-based meat is being 3D printed as a way to mimic the texture from the real thing, while a German company used 3D printers to create accessible meals for seniors who struggle to process solid foods.
However, it is produced, food for human consumption must meet stringent federal requirements designed to ensure safety. When the Food Safety and Modernization Act became law in 2011, those regulations became more stringent than ever. [5] The FSMA, the most sweeping food safety legislation in seven decades, meshes well with the potential for safe 3D-printed food. Eventually, FSMA regulations regarding food safety may amplify the demand for 3D-printed food. What's more, a custom nutrition process may help those with serious food allergies since it is possible to replicate 3D-printed food with such precision.
References:
- https://bernardmarr.com/what-is-3d-printed-food/
- https://www.ktchnrebel.com/3d-food-printer-restaurant/
- https://cen.acs.org/food/food-science/3D-printed-foods-enter-kitchen/100/i5
- https://all3dp.com/2/3d-printed-food-3d-printing-food/
- https://www.ge.com/additive/additive-manufacturing/industries/food-beverage
Cite this article:
Vinotha D (2022), The Future Technology of 3D Printed Food, AnaTechMaz, pp.181