Difference Between Multi Cloud Vs Hybrid Cloud
Multicloud is the use of cloud services from more than one cloud vendor. It can be as simple as using software-as-a-service (SaaS) from different cloud vendors – e.g., Salesforce and [1] Workday. But in the enterprise, multicloud figure 1 shown below typically refers to running enterprise applications on platform-as-a-service (PaaS) or infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) from multiple cloud service providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform, IBM Cloud and Microsoft Azure.
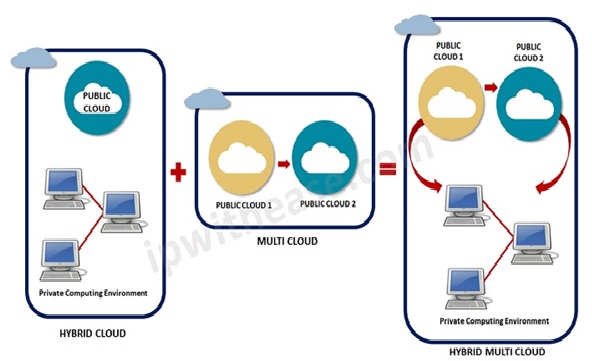
Figure 1: Multi Cloud Vs Hybrid Cloud
A multi-cloud can also be a hybrid cloud, and a hybrid cloud can also be a multi-cloud, but these [2] terms represent two distinct concepts.
"Hybrid cloud" describes the mixing of two or more distinct types of infrastructure: it combines a private cloud, an on-premises data center, or both with at least one public cloud. Multi-cloud refers to several different public clouds being deployed, and it doesn't necessarily include a private cloud, although it can.
A hybrid cloud is an IT infrastructure that consists of a private cloud and one of the available public clouds. Both are connected with a persistent virtual private network (VPN). Both use a single identity management (IdM) system and unified logging, monitoring, and alerting (LMA) stack. Even their internal networks are [3] integrated, so in fact, the public cloud becomes an extension of the private cloud. As a result, both behave as a single environment which is fully transparent from the workloads’ point of view.
The goal behind such an architecture is to use the public cloud only if the private cloud can no longer handle workloads. As the private cloud is always a cheaper option, an orchestration platform always launches workloads in the private cloud first. However, once the resources of the private cloud become exhausted, an orchestration platform moves some of the workloads to the public cloud and starts using it by default when launching new workloads. Once the peak period is over, the workloads are moved back to the private cloud, which becomes the default platform once again.
- Hybrid always includes private and public, while multi-cloud always includes multiple public clouds but can also incorporate physical and virtual infrastructure (including private clouds.) [4]
- Unlike a multi-cloud model, in which different clouds are used for different tasks, the components of a hybrid cloud typically work together. As a result, data and processes tend to intermingle and intersect in a hybrid environment, while in a multi-cloud situation, usage typically remains in its “own” cloud’s silo.
- Frontend applications are directly exposed to end users or devices. As a result, these applications are often performance sensitive and might be subject to frequent releases as new features and improvements are developed. Because they usually rely on backend applications to store and manage data, frontend applications are often stateless or manage only small volumes of data.
- Backend applications usually focus on managing data. Key challenges for such applications include handling data in volume and securing it appropriately. New releases of backend applications tend to be less frequent than for frontend applications.
References:
- https://www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/multicloud
- https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/cloud/what-is-multicloud/
- https://ubuntu.com/blog/hybrid-cloud-and-multi-cloud
- https://www.bmc.com/blogs/hybrid-cloud-vs-multi-cloud-whats-the-difference/
Cite this article:
Nandhinidwaraka. S (2021), Difference Between Multi Cloud Vs Hybrid Cloud, AnaTechMaz, pp. 30